![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
279 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What structures make up the External genitalia in females?
|
Mons Pubis
Labia majora, minora Clitoris Vestibular glands Vaginal vestibule Vaginal orifice Urethral opening |
|
|
The pad of adipose tissue that covers the pubic symphysis in females =
|
Mons pubis/mons veneris
|
|
|
What is special about the mons pubis in postpubertal females
|
its covered with coarse terminal hair
|
|
|
What is the fourchette?
|
Where the two labia minora meet posteriorly
|
|
|
THe Vestibule contains 6 openings:
|
1 Urethra
1 Vagina 2 Ducts of Bartholin Glands 2 Ducts of Skene glands |
|
|
A CT membrane that may be circular, crescentic or fimbriated that surrounds the vaginal opening =
|
Hymen
|
|
|
During sexual excitement what secretes mucus into the introitus for lubrication?
|
Bartholin Glands
|
|
|
The vagina sits posteriorly at an incline of what angle?
|
45 degrees
from the vertical plane of the body |
|
|
What separates the anterior vagina from the bladder and urethra?
|
Vesicovaginal Septum
|
|
|
What separates the posterior wall of the vagina and the rectum?
|
Rectovaginal Septum
|
|
|
What is the Pouch of Douglas?
|
a Deep recess formed by the peritoneum as it covers the lower posterior wall of the uterus and upper portion of the vagina, separating it from the rectum
|
|
|
The uterus inclines forward at what angle?
|
45 degrees
|
|
|
What are the dimensions of a nulliparous woman's uterus?
|
5.5 - 8 cm long
3.5 - 4 cm wide 2 - 2.5 cm Thick |
|
|
Dimensions of a parous woman's uterus
|
2 - 3 cm in all dimensions
|
|
|
How much does the non-pregnant uterus weigh?
|
60 - 90 g
|
|
|
The uterus consists of what two main areas
|
Corpus and Cervix
|
|
|
What makes up the corpus?
|
- Fundus
- Body - Isthmus |
|
|
The uterus opens into the vagina via what structure?
|
External Cervical Os
|
|
|
How long are the fallopian tubes usually?
|
8 - 14 cm
|
|
|
What structure supports the fallopian tubes?
|
Mesosalpinx
|
|
|
At what level do the ovaries lie?
|
ASIS
|
|
|
How big are the ovaries during the reproductive years?
|
3cm long
2 cm wide 1 cm thick |
|
|
What 4 pairs of ligaments support the internal genitalia?
|
- Cardinal
- Uterosacral - Round - Broad ligament |
|
|
What 4 bones form the Pelvis
|
2 innominates
sacrum coccyx |
|
|
What are the 4 pelvic joints
|
Pubic symphysis
Sacrococcygeal 2 sacro iliac joints |
|
|
What hormones are released during pregnancy that relax the pelvic joints?
|
Estrogen and Relaxin
|
|
|
How long is the uterus of a female infant?
|
35 mm long
the cervix is 2/3 of the entire length of the uterus |
|
|
What shape is the hymen in an infant?
|
Crescent shape
|
|
|
When does menarche occure on average?
|
age 11 - 14
|
|
|
What's responsible for making the uterus enlarge in the first 3 months of pregnancy?
|
High levels of Estrogen and Progesterone
|
|
|
What about after the first trimester?
|
the mechanical pressure of the growing fetus
|
|
|
When does the uterus reach the abdominal in pregnancy?
|
By 12 weeks
|
|
|
How thick is the uterine wall at Term/at the end of the pregnancy?
|
< 1.5 cm
|
|
|
How much does uterine weight increase in pregnancy?
|
more than 10-fold to ~100g
|
|
|
How much does the capacity of the uterus increase in pregnancy?
|
500 - 1000 times
|
|
|
What color does the cervix take on during pregnancy?
|
Takes on a Bluish appearance
|
|
|
What happens to the cervix immed. after conception?
|
A thick mucus plug keeps it closed
Glands near the external os proliferate w/eversion of the columnar endocervical glands which tend to be friable |
|
|
What color does the vagina take on during pregnancy?
|
Violet
|
|
|
How does the length of the vagina change with pregnancy?
|
Lengthens
|
|
|
What does it mean if the papillae of the vaginal mucosa have a "hobnailed" appearance?
|
Its normal with pregnancy
|
|
|
How does the vaginal pH change during pregnancy and why?
|
becomes more ACIDIC b/c of increased Lactic Acid secretion by vaginal epithelium
|
|
|
When does menopause usu occur?
|
Between 40 and 55
Period ends but fertility doesn't |
|
|
What is the definition of Menopause?
|
1 year with no menses
|
|
|
What happens to adrenal androgens and testosterone after menopause
|
they decrease along with estrogen
|
|
|
How does the vagina change with menopause?
|
- introitus gradually constricts
- vagina narrows - shortens - loses its rugation - mucosa becomes thin, pale, dry |
|
|
When does ovulation usu. cease?
|
1-2 years BEFORE menopause
|
|
|
What are the systemic effects of menopause?
|
- Increase body fat
- intraabdominal fat distribution and male fat distrib. pattern - increase in Total and LDL cholesterol - Thermoregulation altered --> hot flushes - Increased risk of cardiovascular disease |
|
|
What is considered a SHORTENED interval between periods?
|
less than 19 - 21 days
|
|
|
What is considered a LENGTHENED time between periods?
|
more than 37 days
|
|
|
How long is a prolonged menses?
|
longer than 7 days
|
|
|
Risk Factors for Cervical Cancer
|
- Not getting Pap's freguently
- HPV infxns - Sex before 16 y.o. - Multiple sexual partners - Smoking DOUBLES risk - HIV -> higher risk of HPV infxn - Diet LOW in fruits and veggies - Overweight - Blacks, Hispanics, Native Am. - Diethylstilbestrol (DES) 1940-1971 - Low social status |
|
|
Risk Factors for Ovarian Cancer
|
- Older age. half are older than 63
- Early Menarche before age 12 - Infertility, nulliparity, or preg. after 30y.o. - Menopause after age 50 - Family hx: first deg. relatives - FH of Breast, ovarian, colon CA - Personal hx of Breast, endometrial, colon CA - BRCA1 or 2 mutation - White 50% more freq. > blacks - High fat diet - HRT slightly increases risk |
|
|
Risk Factors for Endometrial Cancer
|
- Increases with the amt. of time endometrium is exposed to Estrogen
- Early menarche before 12 - Late Menopause after 50 - Combo of the 2 is worse = longer exposure to estrogen - Infertility or Nulliparity - Obesity - TAMOXIFEN - ERT (estrogen alone w/o progestin) - PCOS, & Granulose-theca cell tumors - Diet high in Animal fat - Diabetes Type I & II - age, 95% are in 40yo+ - FH: endometrial, breast, ovarian, colorectal - Personal hx: Breast, ovarian - BRCA1 or 2 mutation - Pelvic Radiation |
|
|
If masturbation activity in a kid is occasional, discreet, private, and only external stimulation is involved, is that healthy? or abnormal?
|
Healthy
|
|
|
What is considered abnormal masturbation practices in children, and should be further assessed?
|
- Frequent, compulsive
- No regard for privacy - Often preferred over other activity/play - Produces genital discomfort, irritation or pysical signs - Involves penetration of the genital orifices; includes bizarre practices or rituals |
|
|
Is anxiety before a female pelvic exam normal?
|
No, it usu means that something's wrong
|
|
|
What should you maintain before and during the examination?
|
Eye contact
|
|
|
During the exam, when should the door to the room be opened?
|
Only with BOTH the patient's and doctor's permission
|
|
|
How should the examination table be positioned?
|
So that the patient faces AWAY from it during the examination
|
|
|
Which gender examiner should be chaperoned by a female assistant?
|
Both sexes, male and female examiners
|
|
|
What should you always have the patient do BEFORE the exam
|
Empty the Bladder
|
|
|
How should you drape the patient?
|
Cover her knees and symphysis, depressing the drape between her knees
|
|
|
When you actually start the exam, where you should you touch first?
|
A neutral position like her thigh, working your way to her external genitalia
|
|
|
** Labial swelling, redness or tenderness, esp. unilateral, can indicate what?
|
Bartholin Gland Abcess
|
|
|
Excoriation, rashes, or lesions of the Labia Majora may indicate what?
|
Infectious or inflammatory processes
|
|
|
What should the inner surface of the labia minora look like?
|
moist and dark pink
|
|
|
Inflammation, irritation, excoriation or cakng of discharge of the labia minora may indicate what?
|
Vaginal infection or poor hygiene
|
|
|
Discoloration or tenderness of the labia minora may indicate what?
|
Traumatic bruising
|
|
|
Ulcers or vesicles of the labia minora may indicate what?
|
STI's
|
|
|
How long is the clitoris normally?
|
less than 2 cm
|
|
|
Whats the diameter of the clitoris?
|
0.5 cm
|
|
|
What does enlargement clitoris indicate?
|
Masculinization
|
|
|
What can irritation, inflammation, or dilation of the urethral orifice indicate?
|
Repeated UTI's, or insertion of foreign objects
|
|
|
When you see something in the pelvic exam that catches your eye, when should you ask questions?
|
the pt feels more vulnerable during the exam, so ask AFTER the exam is over.
|
|
|
What are myrtiform caruncles?
|
Hymenal remnants on the vaginal introitus
|
|
|
When palpating the Skene gland how far should you put your finger in the vagina and in what position
|
Palm up
put index finger, up to 2nd joint |
|
|
What does discharge from the Skene gland or urethra indicate?
|
Infection
|
|
|
Whats the most common infection causing discharge from the Skene gland or urethra?
|
Gonococcal
|
|
|
Where are the Bartholin Glands located?
|
in the Posterolateral part of the Labia MAJora
|
|
|
painful Swelling, HOT to the touch, and fluctuant and pus-filled in the labia majora =
|
Bartholin gland ABCESS
|
|
|
What bugs usu cause Bartholin gland abcess?
|
Gonococcal or Staphylococcal
|
|
|
nontender mass in labia majora =
|
Batholin cyst
|
|
|
What causes Batholin cysts?
|
Chronic inflammation of the gland
|
|
|
When should you test muscle tone of a woman's vaginal area?
|
If she's given birth, or complained of urinary incontinence or complaining of weak muscle tone
|
|
|
When the pt bears down, what does bulging of the ANTERIOR wall and urinary incontinence indicate?
|
Cystocele
|
|
|
When the pt bears down, what does bulging of the POSTERIOR wall and urinary incontinence indicate?
|
Rectocele
|
|
|
What does protrusion of the cervix or uterus on straining indicate?
|
Uterine Prolapse
|
|
|
What does the perineum feel like in a Nulliparous woman?
|
Thick and smooth
|
|
|
What does the perineum feel like in a Multiparous woman?
|
Thinner and rigid
|
|
|
What should you do between the vaginal and rectal exams?
|
Change your gloves :)
|
|
|
When preparing the speculum for examination, what should you use to lubricate it?
|
use Water or water-soluble lubricant on speculum and glove
|
|
|
What color should the cervix be?
|
Pink
|
|
|
What does a Bluish cervix color indicate?
|
Increased vascularity which may be a sign of pregnancy
|
|
|
Symmetric, circumscribed erythema around the os indicates what?
|
an expected finding, it indicates that the columnar epithelium from the cervical canal is exposed outwardly
|
|
|
Any reddened areas should be considered what, to a beginning practitioner?
|
an unexpected finding
|
|
|
A PALE cervix =
|
Anemia
|
|
|
a Cervix that points ANTERIORLY =
|
RETROVERTED Uterus
|
|
|
a Cervix that points POSTERIORLY =
|
ANTEVERTED Uterus
|
|
|
Deviation of the Cervix to the Right or Left indicates what?
|
Pelvic Mass
Uterine Adhesions Pregnancy |
|
|
How much does the Cervix normally protrude into the Vagina?
|
1 - 3 cm
|
|
|
If the Cervix protrudes into the Vagina > 3cm then that =
|
Pelvic / Uterine Mass
|
|
|
How big is the Cervix of a woman of child-bearing age?
|
2 - 3 cm diameter
|
|
|
What does an enlarged cervix =
|
Cervical infection
|
|
|
A symmetric, reddened circle around the os of the cervix =
|
Squamo-columnar epithelium junction
|
|
|
What are small, white, yellow, raised, round areas on the cervix?
|
Nabothian cysts
|
|
|
What are Nabothian cysts? Are they pathological or normal?
|
Retention cysts of the endocervical glands
NORMAL FINDING |
|
|
What do infected Nabothian cysts look like?
|
the cysts become swollen, with fluid and they distort the shape of the cervix
|
|
|
What does Friable tissue, red patchy areas, granlar areas and white patches indicate?
|
Cervicities
Infection Carcinoma |
|
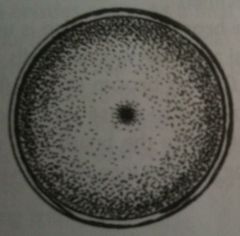
|
Normal Nulliparous cervix
|
|
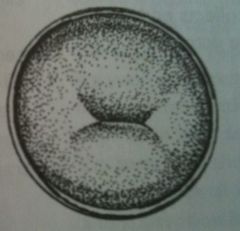
|
Parous cervix, note slit appearance of os
|
|
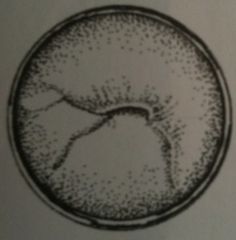
|
Multigravidous, laterated
|
|
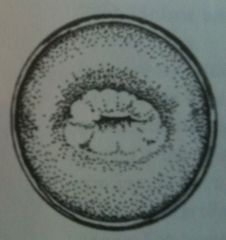
|
Everted
Columnar mucosal cells usu found in the endocervical canal have extended out into the surface of the cervix --> raised circular erythematous look. Note that its non purulent and NORMAL |
|
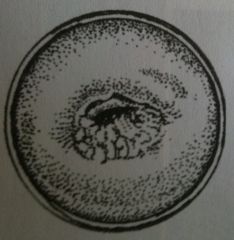
|
Eroded
|
|
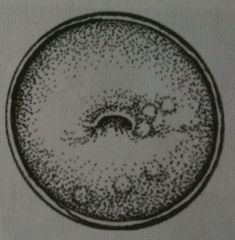
|
Nabothian cysts
|
|
|
Odorless, creamy/clear, thick, thin/stringy discharge =
|
Normal
|
|
|
When is discharge normal?
|
Midcycle or immed. BEFORE menstruation
|
|
|
Discharge with odor, white-yellow/ green/gray =
|
Bacterial or fungal
|
|
|
When can a nulliparous woman have a slit-like os?
|
- Induced abortion
- Difficult removal of an IUD |
|
|
What is the cylindric-type brush used for?
|
To collect ENDOcervical cells only
|
|
|
What do you collect with the Spatula?
|
ECTO-cervical cells
|
|
|
How much do you rotate the spatula?
|
360 degrees
|
|
|
How much do you turn the brush?
|
180 degrees
|
|
|
Which device do you use first for taking cervical specimens?
|
Ecto- first with Spatula - 360 deg.
Endo second with Brush - 180 deg. |
|
|
What is the Broom used for?
|
Both endo- and ecto-cervical specimens
|
|
|
What's the benefit of using the broom?
|
causes less blood spotting after the exam
|
|
|
How many times do you turn the broom?
|
3-4 times left and right
|
|
|
Which test involves sticking a cotton swab into the cervical os for 10-30 sec and spreading it on a culture medium in a Z pattern?
|
Gonococcal Culture specimen
|
|
|
Which test involves using a Dacron swab into the cervival os, and turning it for 30 sec, avoiding the vaginal mucous membranes?
|
DNA Probe for Chlamydia and Gonorrhea
|
|
|
Trichomonads on Wet Mount =
|
Trichomonas Vaginalis
|
|
|
Bacterial "Clue" cells on Wet Mount =
|
Bacterial vaginosis
|
|
|
Fishy odor on KOH prep =
|
Bacterial Vaginosis
|
|
|
Mycelial fragments, hyphae, budding yeast cells on KOH prep =
|
Candidiasis
|
|
|
What should the vaginal wall look like?
|
- same color pink as cervix or a little lighter
- Moist, Smooth, rugated and homogenous |
|
|
Should you do Pap smears on women who have had hysterectomy?
|
no you don't need to necessarily
|
|
|
Where do you do pap smear on pts with Vaginal hysterectomy?
|
From the Suture line in the posterior fornix.
It looks like a white or pink suture |
|
|
What kind of pressure should you keep during the Speculum exam and why?
|
Downward pressure to avoid trauma to the urethra
|
|
|
How does the cervix feel in a NON-pregnant woman?
|
Firm, like the tip of the nose
|
|
|
What does the cervix feel like in a pregnant woman?
|
Softer like lips
|
|
|
On Cervical motion tenderness, how much should the cervix move?
|
1 - 2 cm in each direction with minimal or no discomfort
|
|
|
What does painful cervical movement suggest?
|
Acute Pelvic Inflammatory disease
-or- Ruptured Tubal Pregnancy |
|
|
What position is the uterus in most women?
|
Anteverted, Anteflexed
|
|
|
Which uterine position will allow you to feel the uterine fundus on bimanual palpation of the uterus?
|
Anteverted, anteflexed
|
|
|
Where are your fingers in in the fornix when palpating an anteverted or anteflexed uterus?
|
in the ANTERIOR fornix
|
|
|
Where are your fingers in in the fornix when palpating an retroverted or retroflexed uterus?
|
in the POSTERIOR fornix
|
|
|
When will you NOT be able to palpate the uterine fundus on bimanual exam?
|
When its in the MIDPOSITION
|
|
|
Why do you need to know the position of the Uterus?
|
for intrauterine procedures like inserting an intrauterine device
|
|
|
What is MITTELSCHMERZ?
|
Lower abdominal pain associated wtih ovulation.
It may also have tenderness on the side ovulation took place that month and even U/L adnexal tenderness too (usu mild) Sudden onset, spontaneous remisison |
|
|
What size and shape should normal non-pregnant uterus be?
|
5.5 - 8 cm long
Pear-shaped |
|
|
What does an unexpected enlarged uterus indicate?
|
Pregnancy or Tumor
|
|
|
The uterus should be mobile in which plane?
|
Anteroposterior plane
|
|
|
What does an immobile uterus indicate?
|
Adhesions
|
|
|
What does tenderness on movement of the uterus indicate?
|
Pelvic inflammatory process
or Ruptured tubal pregnancy |
|
|
Where are your fingers in the fornix when palpating the Adnexal areas and ovaries?
|
in the Right or Left Lateral Fornix depending on the side you're palpating
|
|
|
How should the Ovaries feel?
|
Firm, smooth, ovoid
A healthy ovary is moderate to slightly tender on palp |
|
|
What are the dimensions of the ovaries?
|
3 x 2 x 1 cm
|
|
|
What other structure around the ovaries can also be palpated soemtimes?
|
Round ligament
|
|
|
Are the fallopian tubes usu palpable?
|
no
|
|
|
Doing the Rectovaginal exam allows you to reach how much farther into the Pelvis?
|
2.5 cm
(1 inch) |
|
|
If a pt. refuses the rectovaginal exam, what should you tell her?
|
Explain that it is important and why it is necessary
|
|
|
An extra TIGHT anal sphincter =
|
- Anxiety from the procedure
- Scarring - spasticity caused by fissures, lesions, or inflammation |
|
|
A LAX sphincter =
|
Neurological deficit
|
|
|
An ABSENT Sphincter tone =
|
improper repair of 3rd degree perineal laceration after childbirth
|
|
|
When palpating the rectovaginal septum, you can feel the uterine body and fundus when?
|
in a retroflexed uterus
|
|
|
In what position do you examine an infant's external genitalia?
|
Frog position
|
|
|
A premature/newborn baby girl is born, and with an enlarged clitoris. What does this indicate?
|
It may be normal, due to the influence of the mother's hormones
|
|
|
What is the chance a baby will be born with an endocrine problem?
|
1/5000
|
|
|
How big is the central opening in the Hymen of an infant?
|
0.5 cm diameter
|
|
|
An imperforated hymen can lead to what later?
|
hydrocolpos in the child
hematocolpos in the adolescent |
|
|
How does breech delivery affect the baby's external genitalia?
|
It causes the genitalia to be swollen and bruised
|
|
|
What does a Mucoid, Whitish vaginal Discharge in the infant indicate?
|
Passive transfer of hormones from the mother
An expected finding |
|
|
How long does the vaginal discharge last for?
|
4 weeks after birth
|
|
|
Newborn baby has adhesions between the labia minora which are difficult to separate. What does this indicate and how would you treat it?
|
Often happens, not abnormal
Tx with Estrogen cream or gentle teasing apart |
|
|
What kind of discharge do infants or small children usu. have?
|
Mucoid
|
|
|
Which part of the exam do you do on a well child?
|
Inspection & Palpation of External genitalia only
|
|
|
When would you do an internal exam on a child?
|
Sx of bleeding, discharge, trauma, or suspected sexual abuse
|
|
|
What exam do you do on a girl with Bubble bath vaginitis?
|
just external exam, not internal exam
|
|
|
When can a child lay on the examining table for genital exam?
|
Preschool age, with the bed raised to 30 degrees
|
|
|
When does the child begin to feel vulnerable about genital exam?
|
School-age child
|
|
|
How should a school-aged child be positioned for female genital exam?
|
On her back with knees flexed and drawn up
|
|
|
Is it necessary to have a chaperone during the exam of a child?
|
yes.
|
|
|
What do you use Anterior Labial Traction for?
|
To visualize an obscured hymenal opening in pre-pubertal children
|
|
|
If Bartholin or Skene gland infection occurs in a child it is usually what?
|
Gonococcal infection
|
|
|
A foul smell from the genital area in a preschool girl is most likely what?
|
A foreign body
|
|
|
Where would you see signs of sexual abuse more?
|
On the softer tissues and more posteriorly
|
|
|
Where would you see signs of a straddly injury from a bicycle seat?
|
over the Pubic symphysis or on more fixed structures
|
|
|
Vaginal bleeding in a child is the result of what?
|
Injury
Forein bodies Sexual abuse |
|
|
All sexually active teenagers should have what done annually?
|
Pelvic exam
Pap smear STI eval |
|
|
Young women who are not sexually active should have their first exam by what age?
|
age 21
|
|
|
What position do you use in the female GU exam on Adolescents?
|
Same as adults
|
|
|
Which speculum would you use on a teen thats a virgin?
|
A pediatric speculum of 1 - 1.5 cm wide
|
|
|
By menarche, how big should the vaginal opening be?
|
1 cm wide
|
|
|
When does the cervix start softening in pregnancy?
|
2nd MONTH
|
|
|
What does the cervix feel like in the first month of pregnancy?
|
still firm
|
|
|
When does the cervix start turning blue??
|
2nd month
|
|
|
What does the cervix feel like once it softens?
|
Like lips, instead of like the tip of a nose
|
|
|
What are the four types of pelvis shapes?
|
Gynecoid
Android Anthropoid Platypelloid |
|
|
When is the Size of the Bony Pelvis estimated?
|
During THIRD trimester of pregnancy
|
|
|
What % of all women have Gynecoid pelvic type?
|
50%
|
|
|
Which race has more ANDROID type pelvic shapes?
|
White women
|
|
|
Which race has more ANTHROPOID type pelvic shapes?
|
Black women
|
|
|
Round shaped pelvis =
|
Gynecoid
|
|
|
Heart chaped pelvis =
|
Android
|
|
|
Oval shaped pelvis =
|
Anthropoid
|
|
|
Flattened shaped pelvis =
|
Platypelloid
|
|
|
Which Pelvic shape has Moderate Depth?
|
Gynecoid
|
|
|
Which Pelvic shape(s) are DEEP
|
Android and Anthropoid
|
|
|
Which pelvic shape is shallow
|
Platypelloid
|
|
|
Which pelvic chape has CONVERGENT side walls? What do the rest have?
|
ANDROID
The rest have STRAIGHT side walls |
|
|
Which pelvic shapes have BLUNTED and widely separated ISCHIAL Spines??
|
GYNECOID
& PLATYPELLOID |
|
|
Which Pelvic shapes have PROMINENT, NARROW interspinous diameter of ISCHIAL SPINES?
|
ANDROID
& ANTHROPOID |
|
|
Which Pelvic shape has a DEEP and curved Sacrum?
|
GYNECOID
|
|
|
Which pelvic shape has a "Beaked" terminal sacrum?
|
ANDROID
|
|
|
Which Pelvic shapes have a WIDE Subpubic Arch?
|
GYNECOID
& PLATYPELLOID |
|
|
Which Pelvic shapes have NARROW Subpubic Arch?
|
ANDROID
& ANTHROPOID |
|
|
****Which Pelvic Shape makes it really difficult to deliver the baby vaginally so C-section is done
|
ANDROID
|
|
|
What are the 6 "Early Signs of Pregnancy"?
|
1. Goodell
2. Hegar 3. McDonald 4. Braun von Fernwald 5. Piskacek 6. Chadwick |
|
|
Softening of the Cervix
4 - 6 weeks |
Goodell sign
|
|
|
Softening of the uterine isthmus
6 - 8 weeks |
Hegar Sign
|
|
|
Fundus flexes easily on the cervix
7 - 8 weeks |
McDonald Sign
|
|
|
Fullness and softening of the fundus near the site of implantation
7 - 8 weeks |
Braun von Fernwald sign
|
|
|
Palpable lateral bulge or soft prominence
7 - 8 weeks |
Piskacek sign
|
|
|
Bluish color of the cervix, vagina, and vulva
|
Chadwick sign
|
|
|
The most important clinical measurement for estimating the AP diameter of the pelvic inlet?
|
Diagonal Conjugate
|
|
|
Diagonal Conjugate is from where to where?
Normal length = |
Inf. border of pubic symphysis to sacral promontory
12.5 - 13 cm |
|
|
If the Pelvis is ABnormal, the AP diameter is usu.
|
Shortened
|
|
|
The AP Diameter of the Pelvic inlet obtained only by X-Ray or estimated from the Diagonal Conjugate
|
Obstetric Conjugate
|
|
|
Obstetric conjugate is measure from
|
Posterior border of Pubic symphysis to Sacral promontory
|
|
|
Normal length of Obstetric conjugate
|
11 cm radiographically
The Diagonal conjugate minus 1.5-2cm depending on the pubic arch |
|
|
What types of measurements do you use to measure the Pelvic Inlet?
|
Diagonal Conjugate
& Obstetric Conjugate |
|
|
What types of measurements do you use to measure the Midplane?
|
Direct measurement is not possible
use the Transverse Diameter or Interspinous diameter |
|
|
What is the Transverse diamter/Interspinous Diamter
Normal = |
The narrowest transverse diamter in the Midplane between teh interspinous processes
Nml = 10.5 cm |
|
|
What types of measurement do you use to measure the Pelvic OUTLET?
|
Biischial diameter
Intertuberous Diameter or Transverse Diameter of the Outlet |
|
|
What tool do you use to measure the Biischial diameter?
|
Thom Pelvimeter
|
|
|
Where is the Biiischial diamter?
Normal = |
From the interior border of one ischial tuberosity to the other
(sits bones) Nml = >8 cm |
|
|
**Uterus Positions with weeks of gestation**
|
**Uterus Positions with weeks of gestation**
|
|
|
Uterus within Pelvis
|
Weeks 10 - 12
|
|
|
Uterus palpable just above pubic symphysis
|
Week 12
|
|
|
Uterus palpable halfway between symphysis and umbilicus
|
Week 16
|
|
|
Uterine fundus at lower border of umbilicus
|
Week 20
|
|
|
Uterus changes from globular to avoid shape
|
Weeks 24 - 26
|
|
|
Uterus approx. halfway between umbilicus and xiphoid
|
Week 28
|
|
|
Uterine fundus just below xiphoid
|
Week 34
|
|
|
Fundal height drops as fetus begins to engage in pelvis
|
Week 40
|
|
|
** Fetal signs with weeks gestation **
|
** Fetal signs with weeks gestation **
|
|
|
Fetal heart-beat can be detected with Doppler
|
Weeks 10 - 12
|
|
|
Ballottement of fetus is possible by abdominal and vaginal examination
|
Week 16
|
|
|
Fetal Heartbeat can be auscultated with Fetoscope
|
Week 20
|
|
|
Fetus Palpable
|
Weeks 24 - 26
|
|
|
Fetus easily palpable
|
Week 28
|
|
|
** Uterine Lengths & Widths w/ Weeks Gestation **
all in cm's |
** Uterine Lengths & Widths w/ Weeks Gestation **
all in cm's |
|
|
Week 6
|
Length: 7.3 - 9.1 cm
Width: 3.9 |
|
|
Week 8
|
Length: 8.8 - 10.8 cm
Width: 5.0 |
|
|
Week 10
|
Length: 10.2 - 12.5 cm
Width: 6.1 |
|
|
Week 12
|
Length:11.7 - 14.2 cm
Width: 7.1 |
|
|
Week 14
|
Length: 13.2 - 15.9 cm
Width: 8.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Width: 5.0 cm
|
Week 8
|
|
|
Width: 6.1 cm
|
Week 10
|
|
|
Width: 7.1 cm
|
Week 12
|
|
|
Width: 8.2 cm
|
Week 14
|
|
|
Full dilation of the cervix during labor is how big?
|
10 cm
|
|
|
What is effacement during labor?
|
Thinning of cervix from myometrial activity pulling the cervix upward, allowing the cervix to become part of the lower uterine segment during prelabor or early labor
|
|
|
What happens to the cervix length throughout pregnancy? What is the length at the end of the THIRD Trimester
|
It decreases in length
3 - 4 cm by the end off 3rd trimester |
|
|
Shortening of the cervix less than what during midpregnancy indicates the risk for what?
|
< 29 mm
Preterm Delivery |
|
|
In which type of patient does Effacement precede Dilation?
|
the Primipara woman
Happen together in the Multipara woman |
|
|
The relationship of the presenting part to the Ischial Spines of the Mother's pelvis
|
Station
|
|
|
A station recording of +2 and -1 means what??
|
the station is 2 cm BELOW the spines adn 1 cm ABOVE the spines
|
|
|
In what order do you record the routine cervical exam findings during labor?
|
Dilation, Cervical length, Station
|
|
|
When can the position of the fetal head be determined?
|
Once dilation has begun
|
|
|
What may happen to the Uterus in the first 3 months/first trimester, causing what sx
|
May become more anteflexed pressing on the urinary bladder --> frequency
|
|
|
When doe Asymmetrical uterine enlargement occur?
|
around Week 8 - 10
(Piskacek sign) |
|
|
What may palpable ovaries in an elderly woman indicate?
|
Tumor
|
|
|
What should you look for in the rectal exam particularly in an older woman
|
Stress incontinence
Prolapse of vaginal walls or uterus |
|
|
Elderly are particularly susceptible to what
|
Atrophic Vaginits
|
|
|
What position should you use for a disable patient who prefers to lay on their side?
|
Knee-Chest position
|
|
|
Which direction should the speculum handle be pointing in the Diamond-shaped position?
|
Handle UP
|
|
|
Which direction should the speculum handle be pointing in the Obstetric Stirrups position?
|
Handle DOWN
|
|
|
Which direction should the speculum handle be pointing in the M-shaped position?
|
Handle UP
|
|
|
Which positions require the use of stirrups?
|
Lithotomy and Obstetric stirrup positions
V-shape depends |

