![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
209 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How to determine if an airway is present? |
The patient is conscious and speaking in a normal tone of voice |
|
|
What can cause a lost airway? Do what? |
Expanding hematoma or neck emphysema; secure the airway! |
|
|
How do you know an airway is needed? |
(1) Patient is unconscious (2) Voice is breathy or gurgly (3) There is severe inhalation injury (breathing smoke) (4) If pt must be connected to a respirator Always secure the airway first, even before a cervical spine injury |
|
|
How is an airway inserted? Describe what's needed. |
Orotracheal intubation; use a laryngoscope to see and a pulse ox to monitor pt. Use topical anesthetics if necessary. |
|
|
How is an airway secured in the event of a cervical spine injury? |
(1) Orotracheal intubation, but secure the head. (2) Nasotracheal intubation (> fiber optic bronchoscope) |
|
|
Need to secure an airway, but there's neck emphysema- what to do? |
Fiber optic bronchoscope |
|
|
What is SQ neck emphysema an indication of? |
Major disruption of the tracheobronchial tree |
|
|
Name the regular intubation methods. If can't do them, resort to what? |
1) Orotracheal 2) Nasotracheal 3) Fiber optic bronchoscopy 4) Cricothyroidectomy (12+ yo) |
|
|
What indicates normal breathing? |
B/L breath sounds, good pulse Ox |
|
|
Sx shock? |
Systolic bp < 90 Tachy pulse Oliguria (<0.5 mL/kg/h) Pale, cold, shivering, sweating, thirsty, apprehensive patient |
|
|
Causes of shock (trauma) |
Bleeding (hypovolemic-hemorrhagic) Pericardial tamponade Tension pneumothorax |
|
|
Causes of pericardial tamponade or tension pneumothorax |
Blunt/penetrating traumam to the chest |
|
|
CVP in shock caused by bleeding vs tension pneumothorax vs cardiac tamponade
|
High CVP: tension pneumo + pericardial tamponade
Low CVP: bleeding (empty veins) |
|
|
Tx non-traumatic hemorrhagic shock? |
Surgical intervention to stop bleeding then fluid replacement |
|
|
Tx traumatic hemorrhagic shock? |
Fluid replacement then surgical intervention (to stop bleeding) |
|
|
Preferred route of fluid resuscitation in trauma setting? |
1) 2 peripheral IV lines, 16-gauge 2) alternatives: percutaneous femoral vein catheters or saphenous vein cut-downs |
|
|
Alternate route of resuscitation in < 6yo for resuscitation in the trauma setting? |
Intraosseous cannulation of the proximal tibia |
|
|
Mgmt pericardial tamponade? |
Dx clinical Tx evacuate pericardial sac (pericardiocentesis, tube, pericardial window, open thoracotomy) |
|
|
Mgmt tension pneumothorax |
Dx clinical Tx big needle or IV catheter in affected pleural space, follow with chest tube connected to underwater seal (both inserted high in anterior chest wall) |
|
|
Causes of hypovolemic shock? |
Bleeding or other sources of massive fluid loss (burns, peritonitis, pancreatitis, massive diarrhea) |
|
|
Key finding of hypovolemic shock? |
Low CVP |
|
|
Cause of intrinsic cardiogenic shock? |
Massive myocardial damage (eg massive MI or fulminating myocarditis) |
|
|
Key finding in cardiogenic shock? |
High CVP (big, distended veins) |
|
|
Tx cardiogenic shock |
Circulatory support |
|
|
Where is vasomotor shock seen? |
Anaphylactic reactions and high spinal cord transection or high spinal anesthetic |
|
|
Presentation vasomotor shock? |
Flushed, "pink and warm" patient due to circulatory collapse |
|
|
Key finding in vasomotor shock? |
Low CVP |
|
|
Tx vasomotor shock? |
Vasopressors + IVF; vasopressors restore peripheral resistance |
|
|
Tx penetrating head trauma |
Surgery |
|
|
Tx linear skull fractures |
1) closed - leave alone 2) open - must close 3) comminuted or depressed - OR |
|
|
Mgmt head trauma x unconscious? |
CT - look for intracranial hematomas. Go home if family will wake up frequently in next 24 hrs to make sure they are not going into coma |
|
|
What are signs that a fracture is affecting the base of the skull? |
Raccoon eyes, rhinorrhea, and otorrhea or ecchymosis behind the ear |
|
|
Tx fracture at the base of the skull? |
Expectant management bc any trauma to the base of the skull is very severe; the integrity of the cervical spine must be assessed (CT) |
|
|
Avoid what for pts w fracture at base of skull? |
Endotracheal intubation |
|
|
What causes neurologic damage from trauma? |
1) Initial blow 2) Subsequent developing hematoma that displaces midline structures 3) Later increased ICP |
|
|
Tx neurologic damage from trauma |
Treat the root cause. 1) Initial blow.. can't do anything 2) Progressive hematoma - surgery 3) Increased ICP - medical mgmt |
|
|
Where does an acute epidural hematoma occur? |
Side of the head (modest trauma) |
|
|
Sx acute epidural hematoma? |
Sequence: 1) trauma 2) unconsciousness 3) lucid interval (ASx pt returns to previous activity) 4) fixed dilated pupil (side of hematoma 90%x) 5) contralateral hemiparesis w decerebrate posture |
|
|
Dx acute epidural hematoma? |
Biconvex, lens-shaped hematoma |
|
|
Tx acute epidural hematoma? |
Emergency craniotomy (cure!) |
|
|
Similarities and differences bt acute epidural hematoma and acute subdural hematoma? |
Similarities: same sequence (trauma, unconsciousness, dilated pupil, contralateral hemiparesis Differences: bigger trauma, sicker pt (NO lucid interval; doesn't fully awaken at any point), severe neurologic damage (due to initial blow) |
|
|
Dx subdural hematoma? |
Semilunar, crescent-shaped hematoma |
|
|
Tx subdural hematoma? |
1) Deviated midline structures - craniotomy (bad prognosis) 2) No deviation - prevent increase in ICP: monitor ICP, raise head of bed, hyperventilate, avoid fluid overload, and give mannitol or furosemide. |
|
|
When to stop diuresing pt w subdural hematoma? |
Just don't let systemic arterial pressure fall |
|
|
When is hyperventilation recommended? |
Signs of herniation |
|
|
What is the goal of hyperventilation? |
PCO2 of 35 |
|
|
What happens in more severe trauma? |
Diffuse axonal injury |
|
|
CT shows diffuse blurring of the gray-white matter interface and multiple small punctuate hemorrhages- what is it? |
Diffuse axonal injury |
|
|
Tx diffuse axonal injury? |
Prevent further damage from increased ICP |
|
|
Who tends to get chronic subdural hematoma? |
The very old or in severe alcoholics |
|
|
What happens (pathophys) in chronic subdural hematoma and what are the consequences? |
A shrunken brain is rattled around the head by minor trauma, tearing venous sinuses. Over several days or weeks, mental function deteriorates as the hematoma forms. |
|
|
Dx chronic subdural hematoma? |
CT |
|
|
Tx chronic subdural hematoma? |
Surgical evacuation |
|
|
What can't be a result of intracranial bleeding? |
Hypovolemic shock |
|
|
Why can't hypovolemic shock result from intracranial bleeding? |
There isn't enough space inside the head for the amount of the blood needed to produce shock, so look for another source! |
|
|
Mgmt penetrating trauma to the neck? |
Surgical exploration everywhere (except GSW to the neck) |
|
|
When is surgical exploration done for penetrating trauma to the neck? |
1) Expanding hematoma 2) Deteriorating vital signs 3) Clear signs of esophageal or tracheal injury (coughing or spitting up blood) |
|
|
Mgmt GSW upper zone of neck? |
Dx arteriography |
|
|
Mgmt GSW to the base of the neck |
Dx 1) arteriography, 2) esophagogram (water-soluble, followed by barium if negative), 3) esophagoscopy, and 4) bronchoscopy first before Tx Tx surgery |
|
|
Mgmt stab wounds to the upper and middle neck in ASx pts? |
Observe |
|
|
What to do if a pt has severe blunt trauma to the neck? |
Ascertain integrity of the cervical spine |
|
|
Mgmt severe blunt trauma to neck x neurologic deficits |
CT cervical spine |
|
|
Mgmt severe blunt trauma to neck x local pain to palpation over cervical spine |
CT cervical spine |
|
|
Mgmt blunt trauma to neck ED |
CT (we're assessing the status of the cervical spine) |
|
|
Sx complete transection |
Nothing works (sensory or motor) below the lesion |
|
|
Sx hemisection (Brown-Séquard) |
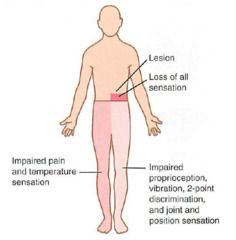
Loss of movement and positioning distal to injury on injured side, loss of pain sensation distal to injury on opposite side |
|
|
MCC Brown-Séquard? |
Clean-cut injury (knife blade) |
|
|
A person falls off from a high building, what does he probably have? |
Anterior cord syndrome, burst fractures of the vertebral bodies
|
|
|
Sx anterior cord syndrome? |
Loss of movement and loss of pain+temp sensation both sides distal to injury(Okay- positioning and vibrational sense) |
|
|
Elderly person involved in a rear-end collision. Most likely will have what? |
Central cord syndrome, burning and paralysis in upper extremities (LE okay) |
|
|
Mgmt spinal cord injuries? |
Dx MRI
Tx high-dose corticosteroids immediately after injury might help |
|
|
Progression of rib fracture? |
Pain → hypoventilation → atelectasis → PNA |
|
|
Rib fracture may be deadly in what population? |
Elderly |
|
|
Tx rib fracture? |
Local nerve block, epidural catheter |
|
|
Penetrating trauma may lead to? |
Plain pneumothorax or hemothorax |
|
|
Sx plain pneumothorax? |
Moderate SOB, no breath sounds on one side of chest, hyperresonance to percussion |
|
|
Tx plain pneumothorax? |
1) CXR 2) Chest tube (upper, anterior) 3) Connect to underwater seal. |
|
|
Sx plain- vs hemo- thorax |
Plain: Moderate SOB, no breath sounds on one side of chest, hyperresonance to percussion Hemo: Moderate SOB, no breath sounds on one side of chest, dull to percussion |
|
|
Dx hemothorax? |
CXR |
|
|
What should be done for hemothorax? Why? |
Evacuate blood to prevent development of empyema
|
|
|
Mgmt hemothorax? |
Place low chest tube. (No surgery) Bleeding will stop by itself. |
|
|
MCC bleeding source (hemothorax)? |
Lung (bleeding stops by itself bc lung is a low pressure system)
|
|
|
When is surgery needed for hemothorax? What kind of surgery? |
If-- 1) A systemic vessel (usu intercostal artery) is the source of bleeding 2) Recover 1500+ mL blood when chest tube inserted or 3) Collect 600+ mL blood in 6h Do thoracotomy. |
|
|
Mgmt severe blunt trauma to the chest? Why? |
Monitor 1) ABGs + CXR (to detect developing pulmonary contusion) 2) Troponins (MI) 3) EKG (MI) |
|
|
What is a sucking chest wound? |
Check out PE: there is a flap that sucks air w inspiration and closes during expiration |
|
|
What can a sucking chest wound lead to? |
Deadly tension pneumothorax |
|
|
Mgmt sucking chest wound? |
First aid w occlusive dressing on 3 sides only (to allow air out, but not in) |
|
|
What is flail chest? |
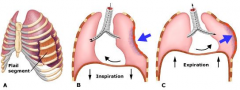
When multiple rib fractures allow a segment of the chest wall to cave in during inspiration and bulge out during expiration (paradoxic breathing) |
|
|
What is problematic about flail chest? |
Pulmonary contusion bc a contused (bruised lung*, see below) is very sensitive to fluid overload, so Tx includes fluid restriction and use of diuretics. *As a result of damage to capillaries, blood and other fluids accumulate in the lung tissue. The excess fluid interferes with gas exchange, potentially leading to inadequate oxygen levels (hypoxia). |
|
|
Mgmt flail chest? Why? |
Monitor ABGs bc pulmonary dysfunction may develop |
|
|
Mgmt flail chest x respirator use? Why? |
B/L chest tubes to prevent tension pneumothorax from developing (multiple broken ribs may have punctured the lung) |
|
|
Look for what in flail chest? |
Traumatic transection of the aorta bc only severe trauma can lead to flail chest, severe enough to include the aorta |
|
|
When does pulmonary contusion occur/appear? |
Immediately or up to 48h after chest trauma |
|
|
See what if pulmonary contusion occurs right after trauma? |
Deteriorating blood gases and "white out" of lungs on CXR |
|
|
Sternal fracture. What should be suspected? |
Myocardial contusion |
|
|
Mgmt myocardial contusion? |
1) EKG 2) Troponins Tx → complications (eg arrhythmias) |
|
|
Mgmt traumatic rupture of diaphragm |
Dx CXR bowel in chest → laparoscopy Tx surgery (from abdomen) |
|
|
Quickly hit brakes (big deceleration) may lead to what injury? |
Traumatic rupture of the aorta |
|
|
Worst hidden injury? |
Traumatic rupture of aorta |
|
|
Where does traumatic rupture of the aorta occur? |
Junction of the aortic arch and the descending aorta |
|
|
When does traumatic rupture of the aorta become symptomatic? |
When the hematoma contained by the adventitia blows up and kills the pt -_- |
|
|
Other suspicious event that may cause traumatic rupture of the aorta? |
Presence of fractures in chest bones that are "very hard to break": first rib, scapula, sternum; or by presence of wide mediastinum |
|
|
Noninvasive Dx tests for traumatic rupture of the aorta? |
Transesophageal echo, CT, MRI angiography |
|
|
Most practical Dx test for traumatic rupture of aorta in ED |
Spiral CT w IV contrast = CT angio |
|
|
Large "air leak" from a chest tube may lead to? |
Traumatic rupture of the trachea or major bronchus |
|
|
Subcutaneous emphysema in the lower neck and upper chest may lead to? |
Traumatic rupture of the trachea or major bronchus |
|
|
Dx traumatic rupture of the trachea or major bronchus? |
1) CXR - confirms presence of air in tissues 2) Fiberoptic bronchoscopy - identifies lesion, allows intubation to secure an airway beyond the lesion |
|
|
DDx subcutaneous emphysema |
1) Rupture of esophagus (after endoscopy) 2) tension pneumothorax (find shock and resp distress) |
|
|
Sudden death in a chest trauma pt who is intubated and on a respirator? |
Air embolism |
|
|
May occur after supraclavicular node Bx or central venous line placement? |
Air embolism; subclavian vein is opened to the air; may also lead to sudden collapse and cardiac arrest |
|
|
Mgmt air embolism |
Cardiac massage (left side down) |
|
|
How to prevent air embolism? |
Trendelenburg position when the great veins at the base of the neck are to be entered |
|
|
Pt has multiple trauma, such as several long bone fractures. May develop petechial rashes in the axillae and neck- what is likely to occur? |
Fat embolism
|
|
|
Additional Sx fat embolism? |
Fever, tachy, low platelets; may develop respiratory distress (hypoxemia and B/L patchy infiltrates on CXR) |
|
|
Tx fat embolism |
Main: Respiratory support, so don't really need precise Dx (fat droplets in the urine) Other: Heparin, steroids, EtOH, LMW dextran |
|
|
Tx gunshot wound to the abdomen |
Ex lap for repair of intraabdominal injuries (not necessarily to "remove the bullet") |
|
|
Abdomen is defined as..? |
Any entrance or exit wound below the level of the nipple line |
|
|
Tx gunshot wound to RUQ |
Conservative therapy if pt is properly monitored w close follow-up of clinical signs and serial CT abd |
|
|
Tx stab wound + penetration w protruding viscera |
Ex lap |
|
|
Tx stab wound + hemodynamic instability |
Ex lap |
|
|
Tx stab wound + peritoneal irritation |
Ex lap |
|
|
Tx stab wound only (extra! what are you excluding?) |
Digital exploration of the wound in ER and observation (CT later) Excluding: 1) penetrating w protruding viscera 2) hemodynamic instability 3) signs of peritoneal irritation |
|
|
Mgmt blunt trauma to the abdomen + peritoneal irritation (acute abdomen) |
Ex lap |
|
|
Mgmt goal of blunt trauma to the abdomen |
Figure out 1) Are there internal injuries? 2) Is there bleeding into the peritoneal cavity? 3) Is the bleeding likely to stop independently or will it require surgical intervention? |
|
|
When should blunt trauma to the abdomen be investigated? |
Signs of internal bleeding: 1) bp drop 2) tachy 3) Low CVP 4) oliguria (low urine output) 5) Cold, pale, anxious, thirsty, sweaty, shivering pt Also, no obvious external source of blood loss |
|
|
When do signs of shock present? |
25-30% of blood volume is acutely lost (about 1,500 mL in avg sized adult) |
|
|
Where does internal bleeding typically occur? What is the rationale? |
The abdomen, thighs, and pelvis because those areas could actually secretly "hide" 1.5 L blood |
|
|
Bleeding in the head would result in.. |
Lethal neurologic damage by brain compression and displacement |
|
|
Bleeding in the neck.. |
would be too obvious. Huge hematoma. |
|
|
Bleeding in the pericardial sac.. |
Would lead to pericardial tamponade |
|
|
Bleeding in the pleural cavities.. |
can accomodate 1.5L blood, but too easily visible on CXR. Can run, but can't hide. |
|
|
Pt w hypovolemic shock, multiple trauma, first places to check? |
Femurs and pelvis |
|
|
Dx intraabdominal bleeding, dependent on what? see what? |
CT if pt is hemodynamically stable; shows: 1) presence of blood 2) injury from where blood is coming (usu liver or spleen) 3) roughly how bad injury is |
|
|
Intraabdominal bleed pt, when to do surgery? |
Major injuries and vital signs that don't improve w resuscitation (unstable vitals) |
|
|
How to quickly Dx intraabdominal bleeding in hemodynamically unstable pt? |
Diagnostic peritoneal lavage (DPL) or sonogram for yes/no answer (whether or not there's blood in the peritoneal cavity) |
|
|
Do what if DPL or sonography turn out positive? |
Prompt ex lap |
|
|
The sonogram is also known as..? |
FAST (focused abdominal sonogram for trauma); greatly displaced DPL bc it's noninvasive, but accuracy's not great |
|
|
MC source if intraabdominal bleeding? |
Significant + insignificant - liver Significant - spleen |
|
|
Mgmt ruptured spleen? |
Repair, but if must remove, remember to vaccinate post-op (pneumo, Hib, meningo) |
|
|
A pt comes in w multiple trauma and undergoes prolonged abdominal surgery. He develops intraoperative coagulopathy. What do you do? |
Dx empiric Tx give platelet packs and FFP (10 units each) |
|
|
Mgmt coagulopathy + hypothermia + acidosis? |
Stop ex lap, pack bleeding surfaces, temporarily close incisions. Resume procedure when pt warmed and coagulopathy treated.
|
|
|
What causes abdominal compartment syndrome? |
Lots of blood and fluids are given during the course of prolonged laparotomies, so by the time of closure, all the tissues are swollen and the abdominal wound can't be closed without undue tension. |
|
|
Mgmt abdominal compartment syndrome |
Place a temporary cover, such as an absorbable mesh (that can later be grafted over) or nonabsorbable plastic to be removed later over the abdominal contents |
|
|
It's post-op day 2. What may your pt be experiencing? |
Abdominal compartment syndrome in a pt on whom closure was done |
|
|
Sx abdominal compartment syndrome? |
Distention with retention sutures cutting through the tissues, hypoxia secondary to inability to breathe, and renal failure from the pressure on the vena cava |
|
|
How to avoid coagulopathy, hypothermia, or abdominal compartment syndrome? |
Limit the operation in very badly injured pts to "damage control lap" |
|
|
Mgmt pelvic hematoma? |
Leave it alone if it's not expanding!!! |
|
|
Mgmt expanding pelvic hematoma? |
Dx hypovolemic shock in someone w pelvic fracture (neg DPL or CT shows no intraabdominal injuries and a huge pelvic hematoma) Tx External fixation to diminish the bleeding |
|
|
Mgmt arterial bleeding in bleeding pelvic hematoma? |
Arteriographic embolization; no surgery bc opening a pelvic hematoma loses the tamponade effect. Tx pelvic fixators followed by a visit to interventional radiology for angiographic embolization of both internal iliac arteries |
|
|
Pt who's sustained penetrating or blunt abdominal trauma goes to the bathroom peeing blood. What's going on? |
Urologic injury |
|
|
Mgmt penetrating urologic injury? |
Surgical exploration and repair |
|
|
Pt with lower rib fracture may have..? |
Kidney injury |
|
|
Pt with pelvic fracture may have..? |
Bladder or urethra |
|
|
Who usu experiences urethral injury? |
Men |
|
|
Presentation urethral injury? |
Blood at the meatus, scrotal hematoma, and a "high-riding" prostate on rectal exam |
|
|
A man with pelvic fracture comes in and constantly feels the need to void, but can't do it. What is he likely to have? |
Posterior urethral injury |
|
|
Mgmt urethral injury? |
Retrograde urethrogram |
|
|
Mgmt bladder injury? |
Dx retrograde cystogram with postvoid films to see extraperitoneal leaks at the base of the bladder that might be obscured by a bladder full of dye |
|
|
Mgmt bladder leaks into extraperitoneum? |
Flace a Foley |
|
|
Mgmt bladder leaks into intraperitoneum? |
Surgical repair and protection with a suprapubic cystostomy |
|
|
Mgmt renal injury? |
CT Tx nothing (no surgery) |
|
|
Complication of injury to kidney hilum? |
Development of AV fistula, leading to CHF |
|
|
Pt develops renal artery stenosis after trauma, what might happen? |
Renovascular hypertension |
|
|
Mgmt scrotal hematoma? |
Nothing unless the testicle ruptures (Dx sonogram) |
|
|
A pt presents with sudden pain and development of a large penile shaft hematoma with a normal-appearing glans, what happened? |
Penile fracture; vigorous intercourse with woman on top |
|
|
Mgmt penile fracture |
Emergent surgery or impotence will ensue! (due ti AV shunts) |
|
|
A pt comes in with a stab wound to the arms/legs; what's important to know? |
Whether a vascular injury has occurred; identify the anatomic location and figure out if there are major vessels in the area |
|
|
A pt comes in with a stab wound to the arms/legs; mgmt? |
No major vessels - tetanus prophylaxis and wound cleaning Near major vessels, ASx pt - doppler studies or CT angio Obvious vascular injury - surgical exploration and repair |
|
|
A pt comes in with a stab wound to the arms/legs, how would he present if a blood vessel were damaged? |
Absent distal pulses, expanding ematoma |
|
|
A pt comes in with a combination of artery, nerve, and bone injury. What do you do? |
1) Stabilize the bone 2) Do delicate vascular repair (this would otherwise be disrupted by the rough handling need to put together a bone) 3) Nerve 4) Fasciotomy (prolonged ischemia can lead to a compartment syndrome |
|
|
A military pt or hunter comes in presenting with a high-velocity gunshot wound; what do you find? Mgmt? |
Find large cone of tissue destruction that requires extensive debridements and potential amputations |
|
|
What might crush injuries of the extremities result in? |
Hyperkalemia, myoglobinemia, myoglobinuria, renal failure, and potential development of compartment syndrome. |
|
|
Mgmt crush injury of the extremities? |
For lab abnormalities - 1) IVF 2) Osmotic diuretics 3) Alkalinization of urine For compartment syndrome - 4) Fasciotomy |
|
|
Mgmt chemical burn? |
Massive irrigation (tap water, shower) where injury occurred. Better than trying to neutralize. |
|
|
Rank the severity of burns |
Alkaline (Liquid Plumr, Drano) >>> Acid (battery) |
|
|
How do high-voltage electrical burns present? |
Deeper and worse than they appear |
|
|
Mgmt high-voltage electrical burns? |
Massive debridements or amputations |
|
|
Complications of high-voltage electrical burns? |
1) Myoglobinemia-myoglobinuria-renal failure (give fluids, osmotic diuretics like mannitol, and alkalinize the urine) 2) Orthopedic injuries secondary to massive muscle contractions (posterior dislocation of the shoulder, compression fractures of vertebral bodies) 3) Late development of cataracts and demyelinization syndromes |
|
|
A pt comes in with burns around the mouth or soot inside the throat. What might have caused this? |
Flame burn in an enclosed space leading to respiratory burn/inhalation injury |
|
|
Mgmt respiratory burn/inhalation injury? |
Dx fiberoptic bronchoscopy + ABG (determines whether respirator needed) Tx intubate if airway inadequate, monitor levels of carboxyhemoglobin (100% oxygen if high) |
|
|
What can happen if a pt has a circumferential burn of the extremity? |
Edema can accumulate under the unyielding eschar, resulting in cutoff of the blood supply? |
|
|
What can happen if a pt has a circumferential burn of the chest? |
Edema accumulation may result in difficult breathing due to compression |
|
|
Mgmt circumferential burn of chest or extremities? |
Bedside escharotomy for immediate relief |
|
|
How much fluid is needed 48 hrs after a burn? |
Initial infusion rate of 1 L/h of Ringer lactate (without sugar) in an adult with burns > 20% body surface then adjust fluid administration based on urinary output (1-2 mL/kg/h, but avoid CVP > 15 mm Hg) |
|
|
How is the extent of a burn in an adult estimated? |
The rule of nines! Each of these = 9% body surface: 1) 9% Head + both arms 2) 18% both legs 3) 36% Trunk Calculations include second and third degree burns |
|
|
Why is sugar not included in the Ringer lactate? |
To avoid osmotic diuresis from glycosuria |
|
|
How is the amount of fluid in burned babies that is needed estimated? |
Babies have bigger heads and smaller legs, so a variation of the rule of 9s: 1) 2 head = 18% 2) 3 legs = 27% |
|
|
How will third degree burns look in babies vs adults? |
Babies - deep bright red Adults - leathery, dry, gray |
|
|
How much fluid should be administered to babies? |
If >20% body surface area is burned, administer 20 mL/kg/h for babies (as opposed to 1,000 mL for adults); subsequently fine-tune in response to urinary output. |
|
|
What else must be done to care for burn wounds? |
Tetanus prophylaxis, cleaning of burn areas, and use of topical agents (silver sulfadiazine, but mafenide acetate if thick eschar & cartilage) |
|
|
How are burns near the eyes treated? |
Triple Abx ointment (silver sulfadiazine is irritating to the eyes) |
|
|
Mgmt of burns (timeline) |
IV pain meds early on 1-2d NG suction Intensive nutritional support with high-calorie/high nitrogen diets Graft burned areas that have not regenerated after 2-3 w of wound care |
|
|
What is early excision and grafting? Why is it used? |
Day 1 removal of burned areas with immediate skin grafting in the OR to save costs and minimize pain, suffering, and complications
|
|
|
When is early excision and grafting done? |
<20% surface area (limited) third-degree burns |
|
|
All bites require what? |
Tetanus prophylaxis and wound care |
|
|
What is considered a provoked dog bite? |
If a dog is pet while he is eating or otherwise teased |
|
|
Mgmt provoked dog bite |
Observe, immunize. Discontinue observation if dog is reassuring. |
|
|
Mgmt unprovoked dog bites or bites from wild animals |
Animal available: kill animal to examine brain for signs of rabies Animal unavailable: rabies prophylaxis |
|
|
What are the signs of snake envenomation? |
Severe local pain, swelling, and discoloration developing within 30m of bite |
|
|
Mgmt snake envenomation? |
Draw blood for typing and crossmatch, coagulation studies, and liver and renal function. Tx based on antivenin; CROFAB for crotalids. Splint extremity during transportation. DO NOT make cruciate cuts, suck out venom, wrap with ice, or apply a tourniquet!!!! This is medicine. |
|
|
Administration dosage for antivenin? |
Depends on size of envenomation |
|
|
Presentation bee sting? |
Vasomotor shock Sx - wheezing, rash, hypotension |
|
|
Tx bee sting? |
Epinephrine and stinger removal (without squeezing) |
|
|
Pt presents with nausea, vomiting, and severe generalized muscle cramps. What happened? |
Likely black widow bite.
|
|
|
Tx black widow bite?
|
IV calcium gluconate (antidote). Muscle relaxants also help. |
|
|
Pt presents with skin ulcer with a necrotic center and a surrounding halo of erythema. What happened? |
Brown recluse spider bite. |
|
|
Tx brown recluse spider bite? |
Dapsone. Surgical excision may be needed, but should be delayed until full extent of the damage is evident. Skin grafting may be needed. |
|
|
Dirtiest bite possible? |
Human bite. |
|
|
Mgmt human bite? |
Extensive irrigation and debridement (OR). |

