![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
165 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
RFC stands for |
Request for Comment |
|
|
Bits in an IPv4 Address |
32-bits |
|
|
Bits in an IPv4 Octet |
8-bits |
|
|
How many Octets are there in an IPv4 address |
4 |
|
|
Class A bit pattern |
0nnnnnnn |
|
|
Class B bit pattern |
10nnnnnn |
|
|
Class C bit pattern |
110nnnnn |
|
|
Class A Network Address Range |
1-126 |
|
|
Class B Network Address Range |
128-191 |
|
|
Class C Network Address Range |
192-223 |
|
|
Binary 00000000 |
0 |
|
|
Binary 10000000 |
128 |
|
|
Binary 11000000 |
192 |
|
|
Binary 11100000 |
224 |
|
|
Binary 11110000 |
240 |
|
|
Binary 11111000 |
248 |
|
|
Binary 11111100 |
252 |
|
|
Binary 11111110 |
254 |
|
|
Binary 11111111 |
255 |
|
|
1 Subnet Bit has dotted decimal of |
128 |
|
|
2 Subnet Bits have a dotted decimal of |
192 |
|
|
3 Subnet Bits have a dotted decimal of |
224 |
|
|
4 Subnet Bits have a dotted decimal of |
240 |
|
|
5 Subnet Bits have a dotted decimal of |
248 |
|
|
6 Subnet Bits have a dotted decimal of |
252 |
|
|
7 Subnet Bits have a dotted decimal of |
254 |
|
|
8 Subnet Bits have a dotted decimal of |
255 |
|
|
Class A: Network Bits |
8 |
|
|
Class A: Host Bits |
24 |
|
|
Class A: Total networks |
127 |
|
|
Class A: Addresses per Network |
16,777,216 |
|
|
Class B: Network bits |
16 |
|
|
Class B: Host bits |
16 |
|
|
Class B: Total Networks |
16,384 |
|
|
Class B: Addresses per Network |
65,536 |
|
|
Class C: Network bits |
24 |
|
|
Class C: Hosts Bits |
8 |
|
|
Class C: Total Networks |
2,097,152 |
|
|
Class C: Addresses per Network |
256 |
|
|
What is IP Subnet Zero |
The subnet with all zeros that correspond to the mask (i.e 255.255.255.0 192.168.0.0) |
|
|
Formula to calculate Subnets (no ip subnet zero) |
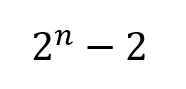
|
|
|
Formula to calculate Subnets (with ip subnet zero) |

|
|
|
Formula to calculate the number of hosts per subnet |

|
|
|
What is a host? |
Any device that is able to be assigned an IP Address |
|
|
Which routing protocols require fixed length subnet masks |
RIP (Version 1) & IGRP (Interior Gateway Routing Protocol) |
|
|
Which routing protocols do not required a fixed length subnet mask |
RIP (Version 2), OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) and EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol) |
|
|
Application Layer # |
Layer 7 |
|
|
Presentation Layer # |
Layer 6 |
|
|
How many layers OSI model |
7 |
|
|
How many layers in the TCP/IP (DOD Model) |
4 |
|
|
Session Layer # |
5 |
|
|
Transport Layer # |
4 |
|
|
Network Layer # |
3 |
|
|
Data-Link Layer # |
2 |
|
|
Physical Layer # |
1 |
|
|
What are the 4 fields of a frame? |
Destinate MAC Source MAC Type FCS |
|
|
Size of the data field for a frame? (min & max) |
Minimum: 46 bytes Maximum: 1500 bytes |
|
|
How many bytes does a Layer 2 frame add to the L3PDU? |
18 bytes |
|
|
10 Mbps common name? |
Ethernet |
|
|
100 Mbps common name? |
Fast Ethernet |
|
|
1000 Mbps common name? |
Gigabit Ethernet |
|
|
Maximum distance for UTP Ethernet, Fast Ethernet & Gigabit Ethernet? |
100 m |
|
|
Field that CISCO added to HDLC? |
Type |
|
|
IEEE standard HDLC headers? |
Flag, Address, Control & FCS |
|
|
Field of the TCP header that controls flow? |
Window |
|
|
Fields of the TCP header that deal with guarteed delivery? |
Sequence & Acknolwedge |
|
|
Process used to establish a TCP connection called? |
TCP Three way Handshake |
|
|
What sequence of flags are sent during the TCP way handshake? |
SYN, SYN, ACK ACK |
|
|
Port 20 |
FTP Data |
|
|
FTP Data port |
20 |
|
|
Port 21 |
FTP Control |
|
|
FTP Control port? |
21 |
|
|
SSH Port? |
22 |
|
|
Port 22? |
SSH |
|
|
Telnet Port? |
23 |
|
|
Port 23? |
Telnet |
|
|
SMTP Port? |
25 |
|
|
Port 25? |
SMTP |
|
|
DNS Port? |
53 |
|
|
Port 53? |
DNS |
|
|
Port 67? |
DHCP Server |
|
|
DHCP Server port? |
67 |
|
|
DHCP Client port? |
68 |
|
|
Port 68? |
DHCP Client |
|
|
Port 69? |
TFTP Server |
|
|
TFTP Port? |
69 |
|
|
Port 80 |
HTTP |
|
|
HTTP Port? |
80 |
|
|
Port 110 |
POP3 |
|
|
POP3 Port? |
110 |
|
|
Port 161 |
SNMP |
|
|
SNMP Port? |
161 |
|
|
Port 443 |
HTTP Secure (TLS/SSL) |
|
|
HTTP Secure Port (TLS/SSL)? |
443 |
|
|
Port 514? |
Syslog |
|
|
Syslog port? |
514 |
|
|
FTP Transport Protocol? |
TCP |
|
|
SSH Transport Protocol? |
TCP |
|
|
TelnetTransport Protocol? |
TCP |
|
|
SMTP Transport Protocol? |
TCP |
|
|
DNS Transport Protocol? |
UDP + TCP |
|
|
DHCP Transport Protocol? |
UDP |
|
|
TFTP Transport Protocol? |
UDP |
|
|
HTTP Transport Protocol? |
TCP |
|
|
POP3 Transport Protocol? |
TCP |
|
|
SNMP Transport Protocol? |
UDP |
|
|
HTTP Secure (TLS/SSL)Transport Protocol? |
TCP |
|
|
Syslog Transport Protocol? |
UDP |
|
|
What does the Administrative mode of a switchport represent? |
The configured switchport mode for an interface
|
|
|
What does the operational mode of a switchport represent? |
The current opertating mode of the switchport |
|
|
Administrive mode: access |
The port will be used for access devices (User PC) and will not try and become a trunk and will never negotiate to become a trunk regardless of the far end |
|
|
Administrive mode: trunk |
Form a trunk and try negotiate the neighbour into becoming a trunk. Will become a trunk regardless of the far ends mode |
|
|
Administrive mode: dynamic auto |
Don't attempt to initiate trunk formation but negotiate a trunk if prompted with a DTP frame |
|
|
Administrive mode: dynamic deseriable |
Actively try and negotiate to become a trunk with the far end by sending out DTP frames. If the far end does not respond, become access. |
|
|
Switchport nonnegotate |
Disable DTP on the port |
|
|
administrively down, down |
disabled |
|
|
disabled (two word status) |
administrively down, down |
|
|
err-disabled (two word status) |
down, err-disable |
|
|
down, err-disable |
err-disable |
|
|
down, down |
notconnect |
|
|
notconnect (two word status) |
down, down |
|
|
up, up |
connected |
|
|
connected (two word status) |
up, up |
|
|
Layers of the 4 layer TCP/IP model |
Application Transport Internetwork Link |
|
|
What does the switch do with the source MAC Address? |
The switch will learn the MAC address from the source field and put that into the MAC Address table with the port it arrived on |
|
|
What does the switch do with the destination Mac address? |
The switch uses the destination MAC address for forwarding operations |
|
|
Layer 4 PDU common name? |
Segment |
|
|
Layer 3 PDU common name |
Packet |
|
|
Layer 2 PDU common name |
frame |
|
|
Layer 1 PDU common name |
Bit |
|
|
Layer 5-7 PDU common name |
Data |
|
|
Devices that transmit on pins 1, 2 |
PC NIC Router AP |
|
|
Devices that transmit on pins 3, 6 |
Switches Hubs |
|
|
How many bits are in a MAC Address? |
48-bits |
|
|
How many hexadecimal digits are in a MAC address? |
12 hex digits |
|
|
How many bits is a Hexadecimal digit? |
4 |
|
|
How many bytes are in a MAC address? |
6 bytes |
|
|
What is the purpose of ARP |
Discover the MAC address of PC based on the IP Address. A layer 2 broadcast is sent in order to discover the machine. |
|
|
Layer 2 broadcast address? |
FFFF.FFFF.FFFF |
|
|
Settings for a console port? |
9600 bps 8-bit ASCII No parity 1 stop bit No flow control |
|
|
IEEE Autonegotiation failure defaults? |
Speed: Slowest supported speed Duplex: If 10/100 Mbps (half) otherwise (full) |
|
|
CISCO Autonegotiation failure defaults? |
Speed: Sense speed Duplex: If 10/100 Mbps (half) otherwise (full) |
|
|
Port security default violation mode? |
Shutdown |
|
|
Router IOS default transport inputs? |
Disabled SSH & Telnet |
|
|
Default port status for router interfaces? |
Shutdown |
|
|
Default port status for switch interfaces |
up |
|
|
Default Layer 2 protocol for Serial interfaces? |
HDLC |
|
|
Default hold-down timer for CDP |
180 seconds |
|
|
Default timer for sending CDP updates? |
60 seconds |
|
|
Numbers allowed for Numbered Standard ACL |
1-99 & 1300-1999 |
|
|
Numbers allowed for Numbered Extended ACL |
100-199 & 2000-2699 |
|
|
Comparison operators used for Extended IP ACL |
gt, lt, eq, ne, range |
|
|
ACL keywords for allowing is disallowing traffic |
permit & deny |
|
|
Standard ACLs check which Address of an IP packet? |
Source Address |
|
|
Where does Cisco recommend a Standard ACL be placed? |
Close to the Destination of the Packet. |
|
|
Where does Cisco recommend an Extended ACL be placed? |
Close to the source of the Packet |
|
|
Password type 5 |
MD5 Hash |
|
|
Password type 7 |
Encrypted password (service password-encryption) |
|
|
Password type 8 |
PBKDF2 |
|
|
Password type 9 |
Scrypt |
|
|
Boot flag 0 |
Load ROMMON |
|
|
Boot flag 1 |
First IOS image found in flash |
|
|
Boot flag 2-F |
Checking startup-config for boot system command, otherwise load first flash IOS image |
|
|
0x2102 |
Startup normal (0 = load startup-config) |
|
|
0x2142 |
Ignore startup config (4 = ignore startup-config) |

