![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
643 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is the control center of the brain
|
thalamus
part of the diencephalon |
|
|
what are the 3 main parts of the brain
|
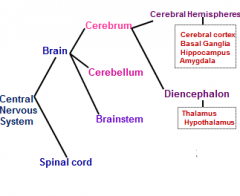
cerebellum
cerebrum brainstem |
|
|
cerebellum
- what do - where |
motor control
|
|
|
what are the 2 parts of the diencephalon?
which is part of which of the 3 main components of the brain |
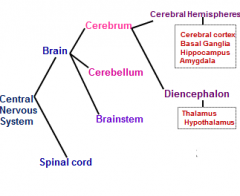
diencephalon = thalamus + hypothalamus
which is part of the cerebrum |
|
|
___________ are large groups of cells that have the same function
|
ganglia = are large groups of cells that have the same function
|
|
|
Basal ganglia - deals with?
|
Basal ganglia - motor
|
|
|
the dips in the convolutions of the cerebral hemispheres are called? peaks?
|
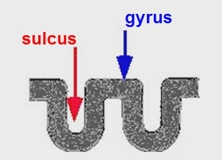
dips = sulcus
peaks = gyrus |
|
|
__________ is a ridge in cerebral cortex surface btw adjacent sulcus
|
gyrus
|
|
|
ventricles are filled with?
|
CSF
|
|
|
what cell does these things:
- anchor neurons - regulate external chemical environment (ions) - recycle neurotransmitters - building blocks of BBB |
astrocytes
|
|
|
what cell type makes and have cilia that circulate CSF as well as make up the blood-CSF barrier
|
ependymal cells
|
|
|
name the cell type:
specialized macrophages capable of phagocytosis that protect neurons of the central nervous system.[11] They are derived from hematopoietic precursors rather than ectodermal tissue; they are commonly categorized as such because of their supportive role to neurons. These cells are found in all regions of the brain and spinal cord. Microglial cells are small relative to macroglial cells, with changing shapes and oblong nuclei. They are mobile within the brain and multiply when the brain is damaged. In the healthy central nervous system, microglia processes constantly sample all aspects of their environment (neurons, macroglia and blood vessels). |
microglial
|
|
|
what are the cells called that make the myelin sheath?
|
oligodendrocytes
|
|
|
upper motor neuron axons project
- from (2x) - to (2x) |
from
- cerebral cortex - brainstem to - spinal cord - cranial nerve morot nucleus (in brainstem) |
|
|
lower motor neuron axons project from? to?
|
from spinal cord or brainstem to TARGET MUSCLES
|
|
|
name the 12 cranial nerves
|
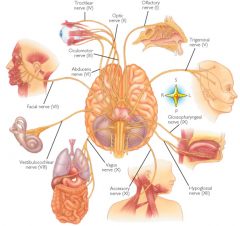
I - olfactory
II - optic III - oculmotor IV - trochlear V - trigeminal VI - abducens VII - facial VIII - vestibulocochlear IX - glosopharyngeal X - vagus XI - accessory XII - hypoglossal |
|
|
a group of mylinated axons the size of a pencil is called
|
fasiculous
|
|
|
a group of mylinated axons the size of a thumb (connect cerebral cortex and cerebellum) is called
|
peduncle
|
|
|
which side of the brain does this:
i. Spatial abilities ii. Face recognition iii. Music |
right
|
|
|
which side of the brain does this:
i. Logic ii. Math iii. Language |
left
|
|
|
which lobe is the
motor cortex |
frontal lobe
|
|
|
which lobe is the
somatosensory cortex |
parietal
|
|
|
which lobe is the center for
visual |
occipital
|
|
|
which lobe is the center for
auditory |
temporal
|
|
|
which lobe is the center for
emotion / memory /drive |
limbic
|
|
|
which lobe is the center for
pain/gustatory/auditory |
insular
|
|
|
speech area of the brain
|
inferior frontal gyrus
|
|
|
the primary sensory cortex?
|
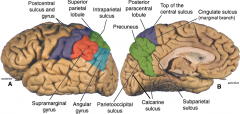
(purple)
postcentral sulcus and gyrus |
|
|
language processing
area of the brain |
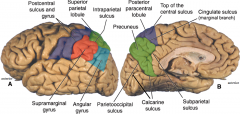
supramarginal gyrus
|
|
|
visual processing
area of the brain |
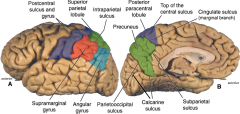
angular gyrus
|
|
|
Where language is first processed
|
Wernicke's area
of the superior temporal gyrus of the temporal lobe |
|
|
function of Transverse temporal gyri (of Heschl)?
in what lobe? |
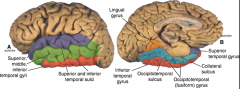
primary auditory
of temporal lobe |
|
|
what does the Lingual gyrus do?
what lobe? |
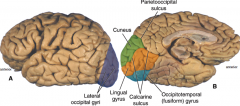
visual processing
occipital lobe |
|
|
what lobe is the calcarine sulcus in?
|
occipital
|
|
|
Parahippocampal gyrus
- lobe? - function? |
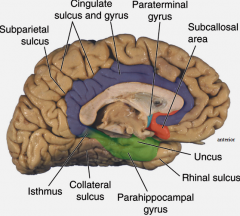
limbic lobe
memory |
|
|
Subcallosal area
- lobe? - function? |
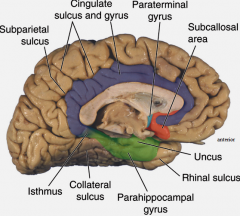
limbic lobe
smelling |
|
|
what does the
insular cortex do |
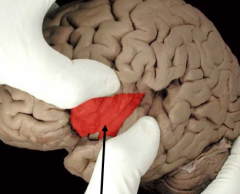
taste (gustatory
|
|
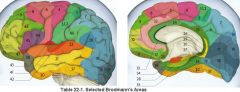
primary clinical significance (function) of Broadmann's area:
4 |
primary motor cortex
|
|
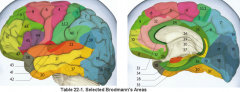
primary clinical significance (function) of Broadmann's area:
17 |
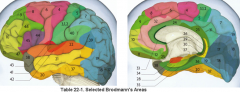
primary visual area
|
|
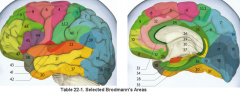
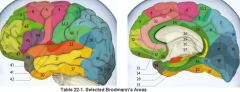
primary clinical significance (function) of Broadmann's area:
44, 45 |
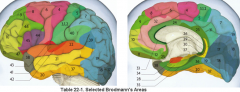
production of speech - motor C
Broacca's area |
|
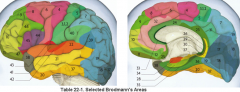
primary clinical significance (function) of Broadmann's area:
3,1,2 |
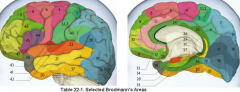
primary sensory
|
|
|
what are the 2 main cell types of the cerebral cortex and their cooresponding function
|
![pyramidal cells - agranular cortex - motor (primary output / excitatory [glutamate] neurons
nonpyramidal cells (stellate)
- principal interneurons (GAG - inhibits / glutamate excites)](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/52/00/17/3520017_m.png)
pyramidal cells - agranular cortex - motor (primary output / excitatory [glutamate] neurons
nonpyramidal cells (stellate) - principal interneurons (GAG - inhibits / glutamate excites) |
|
|
what connects the left/right cerebral cortex?
|
commissural fibers
|
|
|
what are the 3 parts of the corpus callosum and what do they do?
|
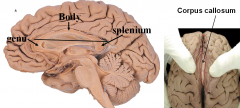
i) Genu - connects prefrontal cortex
ii) Body - connects motor/sensory/parietal corticies iii) Splenium - connects temporal/occipital lobes |
|
|
what does the Anterior commissure do?
|
Connects olfactory and temporal structures
|
|
|
what does the posterior commissure do?
|
visual processing
|
|
|
what do long and short association fibers (U fibers)
|
short association fibers - pass from gyrus to gyrus within a lobe
long association fibers - links lobes |
|
|
what are
Fasciculi |
bundles of fibers
|
|
|
what does this fasiculi (bundle of fibers) connect?
superior longitidinal fasiculus |
ant/post cortex
|
|
|
what does this fasiculi (bundle of fibers) connect?
acruate fasiculus function? |
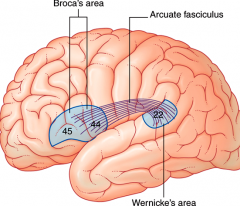
Wernicke's area - Broca's area
language |
|
|
what does this fasiculi (bundle of fibers) connect?
unicinate fasiculus |
orbital cortex - temporal lobes
|
|
|
what does this fasiculi (bundle of fibers) connect?
cinfulum |
limbic cortical areas
|
|
|
what does this fasiculi (bundle of fibers) connect?
inferior longitudinal fasiculus |
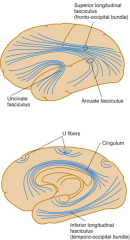
occipital - temporal lobes
|
|
|
Broadmann's area 22 is also called?
and is what function? |
Wenicke;s area
language comprehension |
|
|
Broadmann's areas 44,45 are also called?
and is what function? |
Broca's area
production of language |
|
|
this is the definition of what?
Disturbance in the dominant hemisphere that produces a defect in the expression or comprehension of any of the forms of language |
aphasia
|
|
|
what is aphasia
|
Disturbance in the dominant hemisphere that produces a defect in the expression or comprehension of any of the forms of language
|
|
|
what is this called
i. NON-FLUENT ii. Comprehension of language is normal iii. Cant convert thought into meaningful language iv. Inability to organize words into sentences v. Articulation is impaired Brodmanns area 44, 45 |
Broca's aphasia
|
|
|
what is
Broca's aphasia |
i. NON-FLUENT
ii. Comprehension of language is normal iii. Cant convert thought into meaningful language iv. Inability to organize words into sentences v. Articulation is impaired Brodmanns area 44, 45 |
|
|
what is Wenicke's aphasia
|
i. FLUENT
ii. Cant COMPREHEND language iii. Fluent speech that is UNINTELLIGIBLE iv. Brodmanns area 22 1) Can see on film |
|
|
what is this called:
i. FLUENT ii. Cant COMPREHEND language iii. Fluent speech that is UNINTELLIGIBLE iv. Brodmanns area 22 1) Can see on film |
Wernicke's aphasia
|
|
|
what is contralateral neglect syndrome?
|
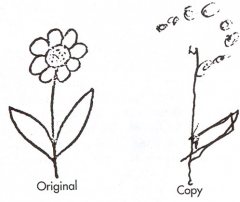
b. RIGHT PARIETAL cortex damage
c. Neglect left of world d. Sx/Dx i. Visuospatial task ii. Personal neglect |
|
|
what are the structures called that are Between endothelial cells of capillaries
|
tight junctions
|
|
|
what are the 3 layers between the skull and the brain in order
|
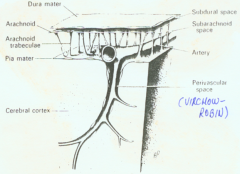
skull
dura mater arachnoid pia mater brain |
|
|
what cell does this:
Regulate endothelial cell proliferation / survival / migration / differentiation / branchin |
pericyte
|
|
|
what do pericytes do?
|
a) Regulate endothelial cell proliferation / survival / migration / differentiation / branching
b) Allow blood vessels to function c) Phagocytize bad molecules incoming |
|
|
what do astrocytes do?
|
i) Determine BBB function / morphology / protein expression
ii) Guide vessel growth - interacts w/capillaries and neurons |
|
|
what cell does this:
i) Determine BBB function / morphology / protein expression ii) Guide vessel growth - interacts w/capillaries and neurons |
astrocytes
|
|
|
what 3 types of molecules does the BBB restrict
|
- large
- low lipid soluble (water soluble) - electrically charged |
|
|
what do Adherens junction do?
|
holds the cells together - 20nm - communicate through junctional cleft
|
|
|
what do occludens junctions do?
2 proteins? |
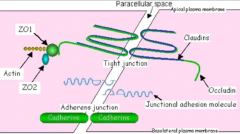
TIGHT JUNCTION
- completly occluded made of - occludin - binds cytoskeletons - claudins - FORMS THE PRIMARY SEAL OF THE TIGHT JUNCTION |
|
|
what do
Zonula occludens do |
figure out where to put the tight junctions
|
|
|
what to
junctional adhesion molecules (JAM) do |
a gene of the immunoglobulin superfamily
- promotes lymphocyte transendothelial migratio |
|
|
what is kernicterus
|
when bilirubin enters the brain in newborns
|
|
|
4 key differences btw peripheral and brain endothelial cells
|
1 - ↑ mitochondria
2 - enzymatic barrier 3 - ↓ capillary wall thickness 4 - polarity - has charge to keep things out |
|
|
what are the 2 main molecular transport mechanisms and for 1 of them what are the 2 subtypes
|
1 - lipid mediation - passive diffusion for small lipid soluble drugs
2 - catylyzed transport 2a - carrier mediated - facilitated active - miliseconds 2b - receptor mediated - specific receptor - minutes - for proteins |
|
|
what is the choroid plexus?
|
blood / CSF barrier
|
|
|
where is CSF made?
|
choroid plexus
|
|
|
where is choroid plexus and what does it do
|
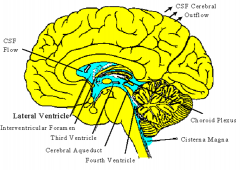
makes CSF
|
|
|
what are the walls of the 3rd ventricle
|
hypothalamus
|
|
|
L-dopa
which crosses the BBB is used to Tx what? |
Parkinsons disease
|
|
|
what is btw the cerebral hemispheres
|
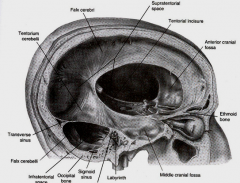
falx cerebri
|
|
|
what is Btw cerebral hemispheres and cerebellum
|
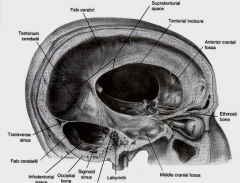
Tentorium cerebelli
|
|
|
partially separates 2 cerebellar hemispheres
|
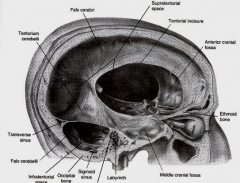
Falx cerebelli
|
|
|
space in tentorium through which brainstem passes
|
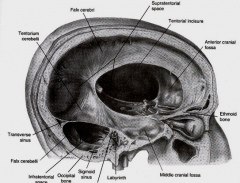
Tentorial notch
|
|
|
POTENTIAL space btw skull and dura
|
Epidural
|
|
|
POTENTIAL space btw dura and arachnoid
|
Subdural
|
|
|
1) CSF filled
2) Btw arachnoid and pia 3) Structural separation by arachnoid trabecula |
Subarachnoid
|
|
|
tearing of meningeal artery or venous sinus results in?
|
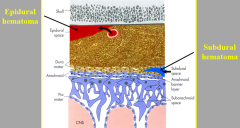
epidural hematoma
|
|
|
tearing of cerebral vein as it penetrates arachnoid and enters sinus results in?
|
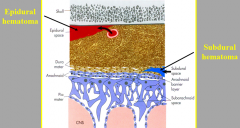
subdural hematoma
|
|
|
volume of CSF
|
130mL
|
|
|
what serves as a pathway for pineal secretions to reach the pituitary gland
|
CSF
|
|
|
what:
midline cavity in the diecephalon a) Connects lateral ventricles - through interventricular foramina b) Connects 4th ventricle through cerebral aqueduct |
3rd ventricle
|
|
|
where is the 4th ventricle
|
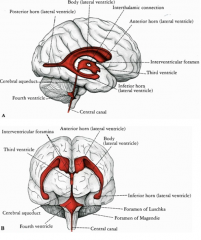
btw cerebellum, pons, and medulla
|
|
|
where is the thalmus
|
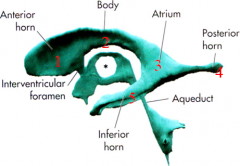
in the middle of the 3rd ventricle (star)
|
|
|
6 steps of CSF flow
|
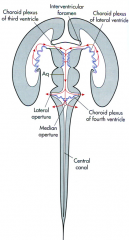
1 - lateral ventricles
2 - interventricular foramen 3 - 3rd ventricle 4 - cerebral aqueduct 5 - 4th ventricle (median and lateral aperture) 6 - cisterns (pontine cistern & cistern magna) |
|
|
6 steps of CSF flow
|
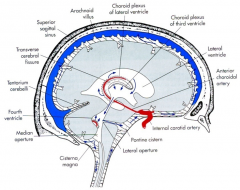
1 - lateral ventricles
2 - interventricular foramen 3 - 3rd ventricle 4 - cerebral aqueduct 5 - 4th ventricle (median and lateral aperture) 6 - cisterns (pontine cistern & cistern magna) |
|
|
a spinal tap is at what level and into what
|
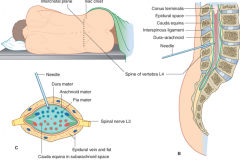
L4
pia mater |
|
|
Major place / structure where CSF goes into VENOUS system
where is this located |
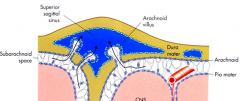
arachnoid villi
superior sagital sinus |
|
|
Brain
__% body mass 15% CO __% of O2 consumption |
Brain
2% body mass 15% CO 20% of O2 consumption |
|
|
MABP (mean arterial BP) cerebral blood flow
|
MABP 60-150mm Hg
|
|
|
normal intracranial pressure (H2O or Hg)
|
65-150 mm H20
5-15mm Hg |
|
|
what is Hydrocephalus
3 causes? |
e. Hydrocephalus
i. ↑ CSF pressure ii. Causes 1) ↑ CSF production (papillomas - tumors) 2) CSF circulation blocked 3) Reabsorption def |
|
|
↑ ICP → herniation
what are the 3 types of hermiations in the brain |
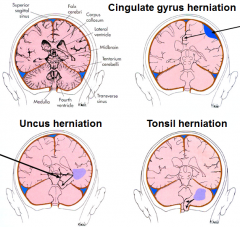
- cingulate gyrus herniation (subdural hematoma)
- uncus herniation ) herniation through tentorial notch - presses midbrain) - tonsil herniation (tonsil of cerebellum herniated through foramen magna - compresses medulla - shuts down cardiovascular respiration = die) |
|
|
what type of brain herniation can kill you and why
|
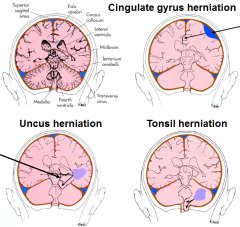
tonsil herniation (tonsil of cerebellum herniated through foramen magna - compresses medulla - shuts down cardiovascular respiration = die)
|
|
|
CPP (cerebral perfusion pressure)
CPP = ? |
CPP (cerebral perfusion pressure)
CPP = MABP - ICP |
|
|
what is Cushing reflex (triad) and what is it a sign of?
|
6) Cushing reflex (triad) - signs of ↑ ICP
a) ↑ systolic BP b) ↑ pulse pressure (S - D) ↓ HR as ICP ↑ to fatal levels |
|
|
3 types of cerebral edema
|
Vasogenic edema
1) ↑ BBB permiability 2) ↑ extracellular fluid 3) Responds to steroids / diuretics Cytotoxic edema 1) Hypoxia 2) Na/K pump failure 3) ↑ intracellular fluid / cell swelling Interstitial edema 1) ↑ fluid in white matter around ventricles 2) Usually associated w/hydrocephalus (↑ CSF) |
|
|
Hyperventilate via respirator (24hrs)
will inc/dec ICP |
Hyperventilate via respirator (24hrs) (→ vasoconstrict and ↓ flow)
|
|
|
Ischemic stroke - Caused by?
|
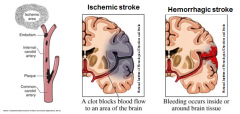
Embolism - foreign matter carried by bloodstream
|
|
|
Hemorrhagic stroke - Caused by?
|
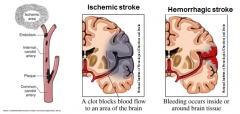
rupture of small perforating arteries
|
|
|
what is a
Penumbra |
interface btw a region of permanent tissue damage and an area that will most likely not be damaged
Area of concern - where your intervention can make a difference |
|
|
name for:
interface btw a region of permanent tissue damage and an area that will most likely not be damaged Area of concern - where your intervention can make a difference |
Penumbra
|
|
|
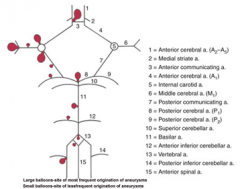
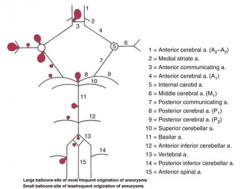
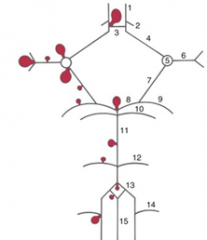
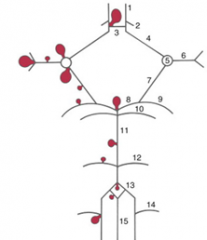
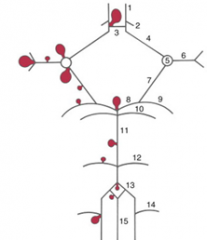
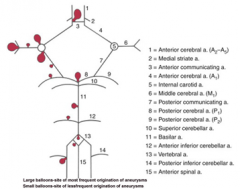
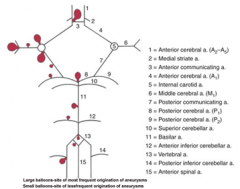
balloon like swelling of arterial walls
Usually at site of bifurcation (branch point) |
Aneurysms
|
|
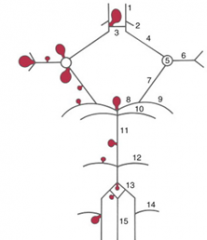
1
|

|
|
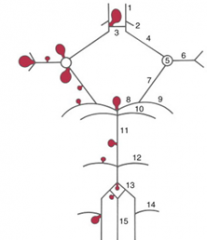
2
|
|
|
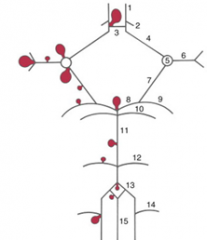
3
|
|
|
4
|

|
|
5
|

|
|
6
|

|
|
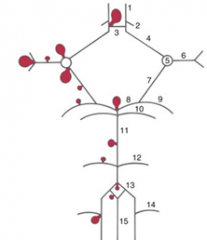
7
|

|
|
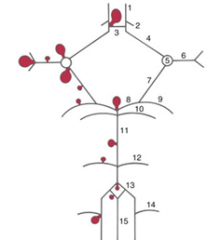
8
|

|
|
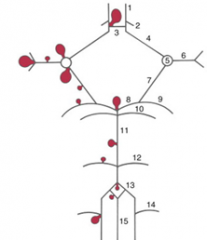
9
|

|
|
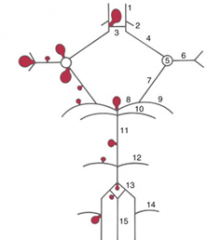
10
|
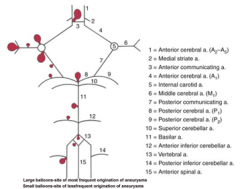
|
|
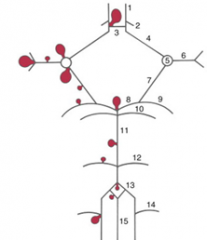
11
|

|
|
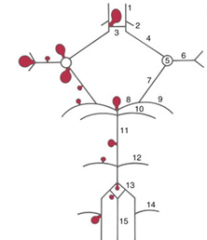
12
|

|
|
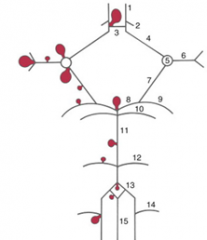
13
|
|
|
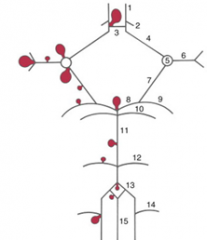
14
|
|
|
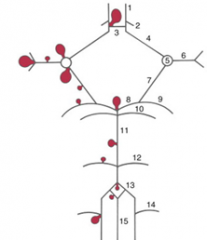
15
|
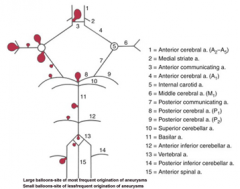
|
|
|
blood to brain is via what 2 main sets of arteries and what do they supply
|
internal carotid (anterior cerebrum / diencephalon)
vertebral-basilar arteries (posterior cerebrum / brainstem / cerebellum / spinal cord) |
|
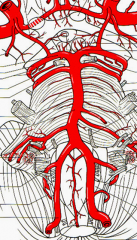
ID
basilar a anterior inferior cerebellar a posterior inferior cerebellar a vertebral a |

|
|
|
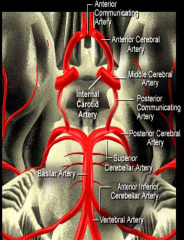
5 components of the Circle of Willis
|
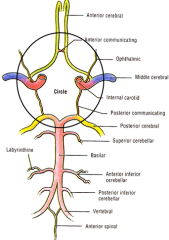
i. Interconnects internal carotid and vertebral-basilar systems
ii. Components 1) Anterior cerebral artery 2) Anterior communicating artery 3) Internal carotid 4) Posterior communicating artery 5) Posterior cerebral artery |
|
|
Anterior spinal artery - from ?
|
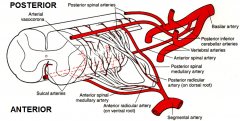
Anterior spinal artery - from vertebral artery
|
|
|
Posterior spinal artery - from ?
|
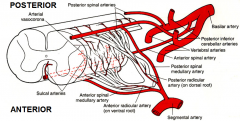
Posterior spinal artery - from posterior inferior cerebellar artery
|
|
|
blood supply to the brain for the precentral gyrus (motor) and postcentral gyrus (sensory) for the arm, hand, face, tongue comes from what artery?
|
middle cerebral a
|
|
|
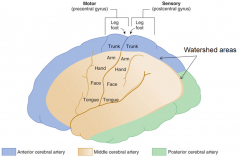
what is a
Watershed area |
2) Watershed area = area where nutrients must diffuse to
Gets bigger as brain shrinks with age - nutrients must diffuse farther |
|

|
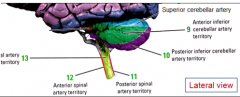
|
|

|

|
|
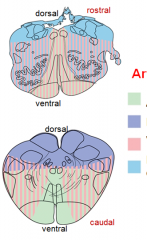
blood supply - medulla
what is each color |
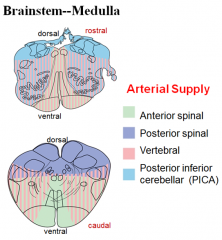
|
|
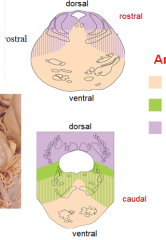
blood supply - pons
what is each color |

|
|
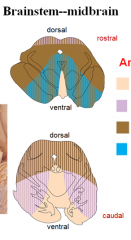
blood supply - midbrain
what is each color |

|
|
|
3x blood supply to thalamus
|
a) Posterior cerebral (p)
b) Posterior communicating (p) c) Anterior choroidal |
|
|
3x supply to hypothalamus
|
a) Posterior communicating (p)
b) Anterior communicating (p) c) Internal carotid (p) |
|
|
2 structures of diencephalon
|
thalamus
hypothalamus |
|
|
lenticulostriate is the perforating (of basal structures) branch of what artery?
|
middle cerebral a
|
|
|
what cerebral artery occludes the most causing stroke?
and it is a branch of what? |
lenticulostriate
from middle cerebral a |
|
fill in each line
|

|
|
|
flow through brain veins
|

|
|
|
what does the
Anterior comissure do |
Communicates information from one side to the other
|
|
|
Pyriform area
what special function |
smell
|
|
|
lateral geniculate nucleus
to and from what function |
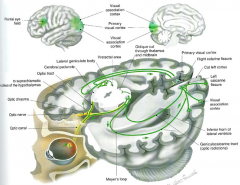
from thalamus
to visual cortex vision |
|
|
what are the 3 cranial nerves that move eye muscles and which muscles do they move
|
III - occulomotor nerve
Medial rectus superior rectus inferior rectus inferior oblique IV - traochlear nerve - Superior oblique VI - abducens nerve - Lateral rectus |
|
|
EYE MOVEMENT IS ESSENTIALLY CONTROLLED WITH CRANIAL NERVE NUCLEI LOCATED IN THE ____________ and one in the _____
|
EYE MOVEMENT IS ESSENTIALLY CONTROLLED WITH CRANIAL NERVE NUCLEI LOCATED IN THE MIDBRAIN and one in the pons
|
|
|
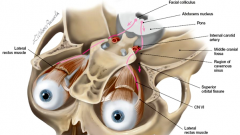
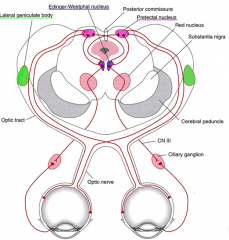
Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- where is it located - main motor function |
midbrain
pupil and lens function |
|
|
which cranial nerve innervates superior rectus
|
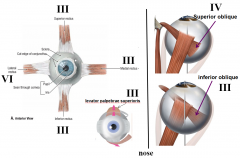
3
|
|
|
which cranial nerve innervates medial rectus
|
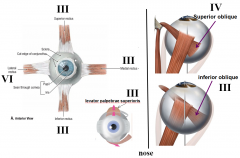
3
|
|
|
which cranial nerve innervates lateral rectus
|
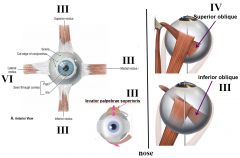
4
|
|
|
which cranial nerve innervates inferior rectus
|
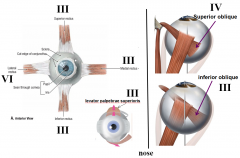
3
|
|
|
which cranial nerve innervates superior oblique
|
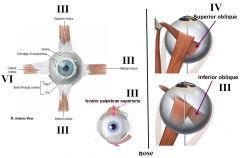
4
|
|
|
which cranial nerve innervates inferior oblique
|
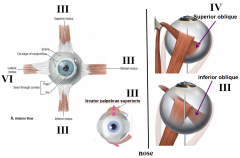
3
|
|
|
what is Ptosis
what nerve malfunctions to cause it |
eyelid drooping
occulomotor (3) |
|
|
if the left eye points down and out what nerve is busted and on what side
|
right trochlear nerve (4)
|
|
|
what innervates the lateral rectus muscle
|
6 - abducens
|
|
|
IF HAVE PROBLEM WITH FACIAL EXPRESSION - PROBLEM IS IN THE _______ AREA OF THE BRAINSTEM
|
IF HAVE PROBLEM WITH FACIAL EXPRESSION - PROBLEM IS IN THE PONS AREA OF THE BRAINSTEM
|
|
|
what is the Accommodation reflex
|
Adaption of the visual apparatus of the eye for near vision
|
|
|
what is the
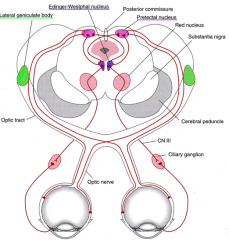
Consensual pupillary light reflex? explain |
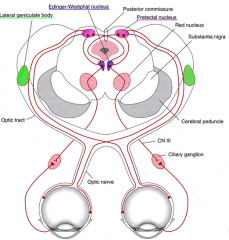
response from the opposite eye being illuminated
|
|
|
afferent and efferent nerves
|
afferent - II - optic nerve
efferent - III - occulomotor |
|
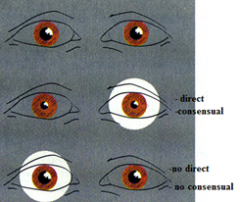
what is damaged here
|
right optic nerve
|
|
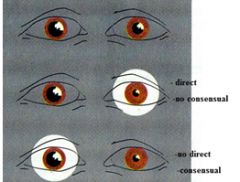
what is damaged here
|
right occulomotor nerve
|
|
|
what does the
Paramedian pontine reticular formation or PPRF coordinate? |
lateral gaze
|
|
|
what is
Internuclear opthalmoplegia? where is the lesion |
paresis of adduction in one eye and horizontal nystagmus in contralateral abducting eye
MLF - medial longitudinal fasiculus |
|
|
what nerve gathers Sensory information from face and head?
|
trigeminal (5)
|
|
|
what are the 3 branches of CN5
|
trigeminal
- opthalmic - maxillary - mandibular |
|
|
what does the motor aspect of the trigeminal nerve do (function) and where is its nucleus?
which branch has the motor |
chewing - small nucleus in the pons
mandibular |
|
|
dilineate on your own face where the 3 branches of the trigeminal innervate for sensory (and the names of the 3 branches
|
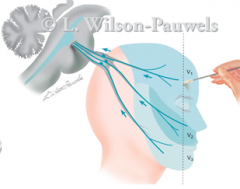
ophthalmic
maxillary mandibular |
|
|
where do the 3 branches of the trigeminal go through the skull
|
V1 (ophthalmic) - superior orbital fissure
V2 (maxillary) - foramen rotundum V3 (mandibular) - foramen ovale |
|
|
where do the 3 branches of the trigeminal go through the skull
|
V1 (ophthalmic) - superior orbital fissure
V2 (maxillary) - foramen rotundum V3 (mandibular) - foramen ovale |
|
|
muscles of mastication are innervated by?
which goes through? |
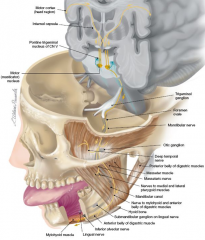
mandibular branch of trigeminal
which goes through foramen ovale |
|
|
FOREHEAD IS _____________, LOWER FACE IS _____________
(SAME SIDE / CONTRALATERAL - for each) |
FOREHEAD IS SAME SIDE, LOWER FACE IS CONTRALATERAL
|
|
|
main 3 funcs of function of CN7
|
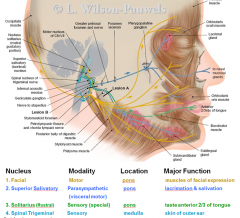
- muscles of facial expression
- lacrimation / salvation - taste (ant 2/3 of tongue) |
|
|
main 2 funcs of CN8
|
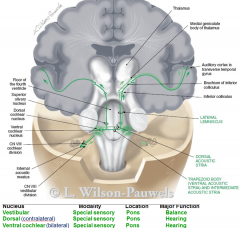
vestibulocochlear
- balance (vestibular) - hearing all from pons (special sensory) |
|
|
test for CN9
|
glossopharyngeal
gag reflex |
|
|
test for CN10
|
vagus
gag reflex or say hi |
|
|
test for CN11
|
spinal accessory
life shoulders |
|
|
test for CN12
|
hypoglossal
tongue movement |
|
|
CRANIAL NERVRES 9-12 NUCLEI LOCATED IN __________ OF BRAINSTEM
|
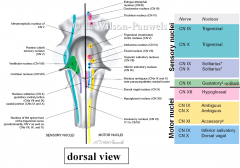
CRANIAL NERVRES 9-12 NUCLEI LOCATED IN MEDULLA OF BRAINSTEM
|
|
|
carotid body
carotid sinus each is what type of receptor where is each exactly |
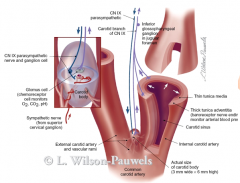
carotid body - chemoreceptor (O2, CO2) - at plit
carotid sinus - baroreceptor (BP) - internal carotid |
|
|
what innervates the carotid sinus and body
to what nucleus |
9 - glossopharyngeal
tractus soltarius |
|
|
main very general thing vagus does
|
parasympathetic - brains stem to colon
|
|
|
CN10 stim does what to these
cardiac lungs GI |
Cardiac
↓ HR Lungs ↑ bronchiolar secretions and bronchoconstriction GI tract ↑ secretions and motility |
|
|
how test vagus in isolation
|
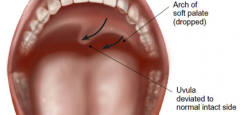
uvula deviation - to unaffected side
|
|
|
CN 9 and 10 both use nucleus ___________ as motor output
|
CN 9 and 10 both use nucleus ambiguus as motor output
|
|
|
CN11 leaves skull through
along with which others |
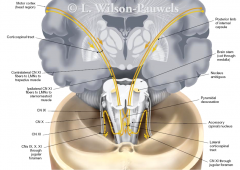
jugular foramen
with 9, 10 |
|
|
2 major functions of CN11
|
spinal accessory
- contralateral trapezious - ipsilateral sternomastoid |
|
|
what nerve innervates the muscles that allow for protrusion of the tongue
|
CN 12 - hypoglossal
|
|
|
UMNL (upper motor lesion) - tongue deviates _______ from lesion side
|
UMNL (upper motor lesion) - tongue deviates AWAY from lesion side
|
|
|
LMNL (lower motor lesion) - tongue deviates ___________ lesion side
|
LMNL (lower motor lesion) - tongue deviates TOWARD lesion side
Ipsilateral side of tongue appears atrophied and fasciculations |
|
|
*** where is each of the 12 cranial nerve nuclei located
|
I - olfactory []
II - optic [] III - occulmotor [midbrain] IV - trochlear [midbrain] V - trigeminal [midbrain, pons, medulla] VI - abducens [pons] VII - facial [pons] VIII - vestibulocochlear [pons] IX - glosopharyngeal [medulla] X - vagus [medulla] XI - accessory [medulla] XII - hypoglossal [medulla] |
|
|
brain accounts for ___% of total O2 consumption
|
20%
|
|
|
what is "Respirator brain"
|
1) Brain was dead and basically starting to decompose but was on respirator
2) Marked necrosis/edema/widespread destruction of the brain 3) From recurrent cycles of edema/vasocompression 4) → result - autolysis/softening of brain - prevents fixation in formalin |
|
|
this is Morphology of cerebral ____________
i. Swollen brain ii. Widened gyri iii. Narrowed sulci iv. Possible herniation v. Ischemia and hemmorrhage associated with herniation |
this is Morphology of cerebral ischemia
i. Swollen brain ii. Widened gyri iii. Narrowed sulci iv. Possible herniation v. Ischemia and hemmorrhage associated with herniation |
|
|
red neurons are a sign of the early stage of what
|
ischemic injury to the brain
|
|
|
what 2 cell types/areas of the brain are particularly susecptible to early stage ischemic injury in the brain
|
a) Pyramidal cells - of the hippocampus
b) Purkinje cells - of the cerebellum |
|
|
Pseudolaminar necrosis
is seen in subacute brain ischemia (24hrs - 2 wks) what is it |
Pseudolaminar necrosis - uncontrolled death of cells in cerebral cortex in BAND-LIKE pattern
|
|
|
what micro changes happen during the subacute stage (24hrs-2wks) of ischemic brain injury
|
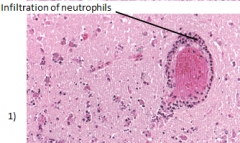
- macrophages
- neutrophils |
|
|
what is the difference btw thrombotic and embolic strokes
|
embolic (red stroke) can be lysed and bloodflow re-established
thrombotic - thrombus reforms |
|
|
what is a white stroke?
other name |
thrombotic stroke
1) ↓ oxyhemoglobin in affected area of brain (turns pale) a) From lack of perfusion 2) Thrombus may be lysed but quickly reforms (b/c of atherosclerotic changes in the vessel) |
|
|
what is a lacunar stroke
|
hyaline narrowing of small branches of blood vessels (seen w/HTN)
- small infarcts → undergo liquefactive necrosis → leaves small cavities (lacunae) in basal ganglia |
|
|
what is
Arteritis |
Small / large vessel inflammation
b) Was seen in syphilis and TB c) Now seen in immunosuppressed |
|
|
Notch3 mutation
|
iii. CADASIL (cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy w/subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy)
1) Rare hereditary form of stroke 3) Sx a) Recurrent strokes b) Dementia 4) Gross a) Abnormalities of white matter b) Concentric narrowing of the adventitia / media of leptomeningeal arteries |
|
|
where do emboli usually infarct?
|
middle cerebral arter - direct extension of internal carotid artery
|
|
|
3 types of emboli
|
- fat
- air (puncture or the bends - nitrogen) - tumor |
|
|
5 kinds / causes of suffocation
|
1 - entrapment (displaces O2 out of environment)
2 - smothering - occlude external airway (nose/mouth) 3 - choking - occlude inner airway 4 - mechanical asphyxia - compress chest 5 - gases - displace oxygen or inhibit O2 binding |
|
|
3 kinds of strangulation - which is a type of smothering
|
hanging (own ligaments occlude)
ligature (extension cord) manual strangulation (arm/hands) |
|
|
ruptured blood vessels in the eye may be a sign of what cause of death
|
choke hold
33lbs of force blood goes in but cant leave |
|
|
what kills via this MOA
By competing w/ferric iron of intracellular cytochrome oxidase (last stop of ETC - thing that makes ATP) |
Hydrogen cyanide
|
|
|
Hydrogen cyanide
mech of killing |
By competing w/ferric iron of intracellular cytochrome oxidase (last stop of ETC - thing that makes ATP)
|
|
|
Hydrogen cyanide
smells like what |
almonds
|
|
|
if you smell these 2 smells you should GET OUT OF THERE because it might be what 2 gases
|
almonds - hydrogen cyanide
rotten eggs - hydrogen sulfide |
|
|
put these neuro insults in order of quickness of onset
neoplastic, vascular, degenerative, infectious |
vascular (min)
infection (hrs/wks) neoplastic (days/wks) degenerative (months/yrs) |
|
|
neuro DDx - accronym
MITCH VINDI DO stands for? |
metabolic
infectious traumatic congenital hereditary vascular immune neoplastic drugs idiopathic degenerative/demyelinating other |
|
|
what are the 6 parts of the neuro exam
|
1 - mental status
2 - cranial nerves 3 - motor 4 - reflexes 5 - sensory 6 - gait / coordination |
|
|
6 parts of mental status exam (explain each)
LOC orientation memory sustained mental activity language general knowledge |
LOC
orientation (who, where, when) memory (3/33 min recall (give 3 objects to memorize) sustained mental activity (spell backwards) language (repeat/comprehend) general knowledge (ask about something current) |
|
|
how test each of the 12 cranial nerves
|
1 - alcohol wipe
2 - reactive to light / visual fields 3, 4, 6 - H test (EOMI w/o nystagmus (extra ocular movements intact) 5 - facial sensation / muscles of mastication (clench/open) 7 - facial expression + corneal reflex 8 - can you hear that 9, 10, 11 - gag reflex / say ahhhh (if soft palate deviates on side - then def) 12 - stick tongue out (is it midline) |
|
|
how test each of the 12 cranial nerves
|
1 - alcohol wipe
2 - reactive to light / visual fields 3, 4, 6 - H test (EOMI w/o nystagmus (extra ocular movements intact) 5 - facial sensation / muscles of mastication (clench/open) 7 - facial expression + corneal reflex 8 - can you hear that 9, 10, 11 - gag reflex / say ahhhh (if soft palate deviates on side - then def) 12 - stick tongue out (is it midline) |
|
|
2x tests to test higher cortical function on PE
|
stereognosia (ID object based on touch)
graphesthesia (write number in your hand) |
|
|
what is graphesthesia
what does it test |
write in hand - know what it is
tests higher cortical function |
|
|
what are the levels of tendon reflexes
|
0 - abscent
1 - hypoactive 2 - normal 3 - hyperactive 4 - hyperactive w/clonus (twitching) |
|
|
what is the most important thing when testing tendon reflexes
|
symmetry
|
|
|
in a positive Babinski what happens
and this indicates what |
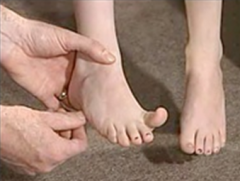
toe goes up
upper motor problem |
|
|
2 main differences btw upper and lower motor neuron pathology in physical exam findings
|
upper - no atrophy, +Babinski
lower - atrophy, -Babinski |
|
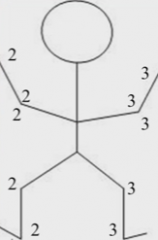
this picture is more typical of an upper or lower motor neuron weakness?
|
upper
|
|
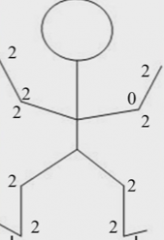
this picture is more typical of an upper or lower motor neuron weakness?
|
lower
|
|
|
what is
Dysdiadakokinesia |
in ability to perform rapid movements
|
|
|
what is
Romberg sign |
iv. Station/balance
1) Romberg sign (Romberg 15s) a) Close eyes b) If break stance after 3s c) Note wavering |
|
|
in 2-3min you should be able to find a neuro problem even in pts w/o neuro Sx - what are the 6 steps and what do you do in each step
|
a. Mental status
i. Level of alertness ii. Appropriatness of responses iii. Orientation to date and place b. Cranial nerves i. Visual acuity ii. Pupillary light reflex iii. Eye movements iv. Hearing v. Facial strength (smile, eye closure) c. Motor function i. Gait (casual, tandem) ii. Coordination (fine finger movements, finger-to-nose) iii. Strength 1) Shoulder abduction 2) Elbow extension 3) Wrist extension 4) Finger abduction 5) Hip flexion 6) Knee flexion 7) Ankle dorsiflexion d. Reflexes i. Deep tendon reflexes 1) Biceps 2) Patellar 3) Achilles ii. Plantar responses e. Sensation i. One modality at toes - can be light touch, pain/temperature, or proprioception |
|
|
what regulates the emotional state
|
limbic system
|
|
|
2 hey limbic structure for emotion/memory
|
hippocampus
amygdala |
|
|
what has these functions
i. Functions 1) Endocrine 2) Autonomic a) Pulse b) BP 3) Regulates a) Hunger b) Thirst c) Response to pain d) Sleep wake cycle e) Levels of pleasure |
hypothalamus
|
|
|
what does the hypothalamus do
|
regulates
autonomic - pulse / BP hunger thirst pain response sleep/wake cycle level of pleasure |
|
|
what does the hippocampus do
|
memory
|
|
|
what does the amygdala do
|
emotion
|
|
|
Lesions in the prefrontal cortex leads to?
|
i. Interrupts inhibitory control on amygdala
ii. Disinhibition of emotional responses iii. Leads to socially inappropriate behavior and impulsivity |
|
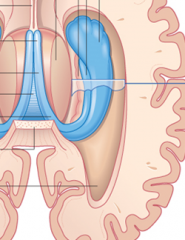
what is the blue thing
|
hippocampus
|
|
|
what are the 3 zones of the hippocampus
|
i. Hippocampus proper
ii. Dentate gyrus iii. subiculum |
|
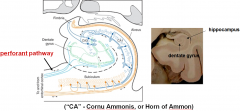
what is the
Perforant pathway |
major input to the hippocampus
i. In the entorhinal cortex ii. Connects the hippocampus to parts of the cerebral cortex |
|
|
a lesion in what would lead to:
i. Inability to learn new information ii. Loss of declarative memory (facts) - "amnesia" iii. Associated w/epilepsy - partial complex seizures |
hippocampus
|
|
|
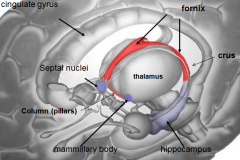
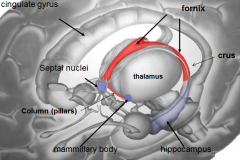
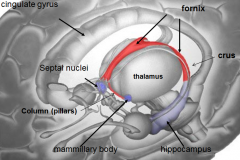
[Key fiber tracks of the limbic system]
short term memory |
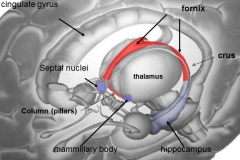
Fornix -- hippocampus
|
|
|
[Key fiber tracks of the limbic system]
Input of emotional responses |
Stria terminalis -- amygdala
|
|
|
[Key fiber tracks of the limbic system]
whats this do: Stria terminalis -- amygdala |
Input of emotional responses
|
|
|
[Key fiber tracks of the limbic system]
whats this do: Fornix -- hippocampus |
short term memory
|
|
|
whats the mammillary body do?
where / what is it? |
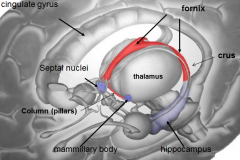
long term memory
nuclei of hypothalamus |
|
|
whats the fornix
whats it do |
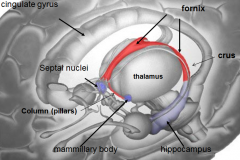
b/l fiber track
takes short term memory from hippocampus and puts it in mammillary body (long term memory) |
|
|
whats the
Stria terminalis do |
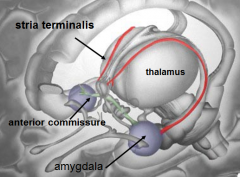
brings info from amygdala (emotion) to
septal area hypothalamus |
|
|
what is the Source of cholinergic input to the hippocampus and amygdala?
|
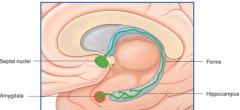
septal nuclei
|
|
|
what is Papez's circuit?
|
Basic layout of how limbic system works
|
|
|
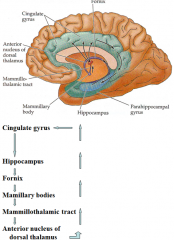
Papez's ciruit describes the circle that limbic emotion goes. what are the 6 parts and their order?
|
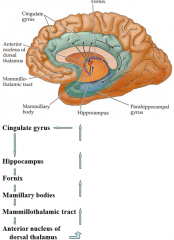
cingulate gyrus (big thing)
hippocampus fornix mamillary bodies mammillothalmic tract anterior nucleus of dorsal thalamus |
|
|
where (2x) are Declarative (explicit) facts stored such as episodic (events) and semantic (facts)
|
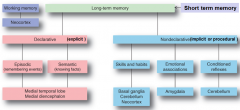
medial temporal lobe
medial diencephalon |
|
|
where are skills and habits stored
|
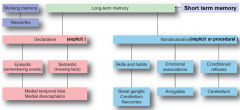
basal ganglia
cerebellum neocortex |
|
|
where are long term emotional associations stored
|
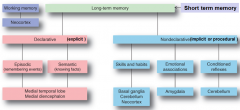
amygdala
|
|
|
what is Korsakoff syndrome
|
loss of memory and confabulation (fabricate imaginary experiences as compensation for loss of memory)
|
|
|
Dx?
athology 1) ↓ neurons in hippocampus & parahippocampal cortex 2) Formation of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles ii. Sx Progressive loss of memory / cognition / orientation / behavior |
Alzheimer;s disease
|
|
|
this syndrome is caused by
a) Chronic alcoholics b) Thiamine (Vit B1) deficiency |
Korsakoff's syndrome
cant form new memories intelligence fine - so fills in gaps |
|
|
what is Kluver-Bucy syndrome
|
destruction of amygdala
no emotional response Compulsion to be overly attentive to all sensory stimuli hypersexuality |
|
|
what is
Hyperthymestic syndrome |
super memory
|
|
|
Dx?
ii. Sx 1) Tremor 2) Muscle rigidity 3) Impairment of postural reflexes 4) Btadykinesia (slow movements) Hypokinesia (few movements) |
Parkinson's disease
|
|
|
what does the Basal ganglia do
|
controls movement
Modulates cortical output from the primary motor cortex |
|
|
what are the 4 main components of the basal ganglia (coordinates movement)
|
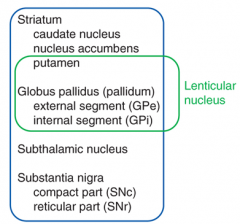
striatum
globus pallidus (pallidum) subthalamic nucleus substantia nigra |
|
|
excitatory = (molecule)?
|
excitatory = glutamate
|
|
|
which of the 4 main parts of the basal ganglia takes most of the basal ganglia's input (which is from the cerebral cortex)
|
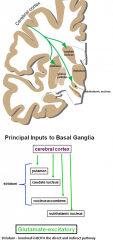
striatum
|
|
|
inhibatory = (molecule)?
|
inhibatory = GABA
|
|
|
output from the basal ganglia comes from which 2 of the 4 parts? what does the ouput pass through on the way out to the cerebral cortex?
|
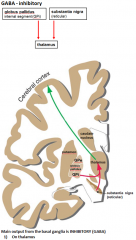
- globus pallidus
- substantia nigra passes through the thalamus |
|
|
output from the basal ganglia is INHIBITORY (GABA) to the thalamus which then excites/inhibits the cerebral cortex? what molecule?
|
excites (glutamate)
|
|
|
summarize the ins/outs of the basal ganglia
|

|
|
|
The basal ganglia influence is to modulate the_____________ OF THE THALAMIC NUCLEI
|
The basal ganglia influence is to modulate the level of EXCITATION OF THE THALAMIC NUCLEI
|
|
|
what is the difference btw direct and indirect basal ganglia pathways
|
- indirect inhibits the globus pallidus (which is outside the ganglia)
- which then stims the globus pallidus (which is part of the basal ganglia) which then INHIBITS the thalamus (same) which then STIMS the cortex (same) |
|
|
functional difference btw direct/indirect basal ganglia pathways (in terms of the result, not how they work)
|
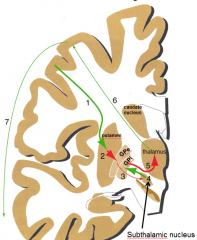
direct - facilitates movement
indirect - inhibits/damps down movement |
|
|
what doe the
Substantia nigra (compact part of basal ganglia) do? what molecule does it use to do this? |
* the substantia nigra modulates the striatum - with DOPAMINE (stims direct / inhibits indirect pathways)
|
|
|
If you lose dopamine - lose modulation = (disease)
|
Parkinsons
|
|
|
too much inhibition from the (indirect) basal ganglia results in what
|
Parkinsons disease
|
|
|
too much stim from the (direct) basal ganglia results in
|
Huntingdon's chorea
Hemiballism |
|
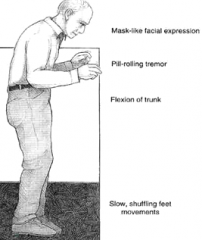
Dx?
|
Parkinsons
|
|
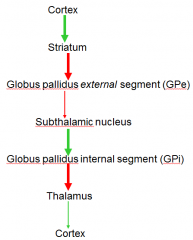
direct or indirect pathway of basal ganglia
|
indirect = inhibatory
|
|
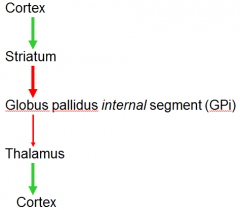
direct or indirect pathway of basal ganglia
|
direct
|
|
|
what does
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) - pacemakers for the brain Tx? |
Parkinsons
restores excitation and inhibition to the thalamus Relief from tremors/rigidity/slowness of movement/stiffness/balance |
|
|
Dx?
decreased inhibition - which leads to too much stim of cortex from basal ganglia |
Huntingdon's disease of "Chorea"
|
|
|
what is
Huntingdon's disease of "Chorea" |
decreased inhibition - which leads to too much stim of cortex from basal ganglia
|
|
|
how does Basal ganglia interact w/cerebellum
|
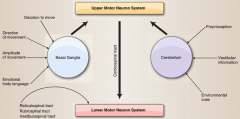
through upper motor neuron
|
|
|
Any abnormality of the brain resulting from a pathologic abnormality of the blood vessels or their contents
|
Cerebrovascular disease
|
|
|
Sudden neurologic deficit resulting from cerebrovascular disease
|
Cerebrovascular accident (CVA) = stroke
|
|
|
what is CVA
|
Sudden neurologic deficit resulting from cerebrovascular disease
|
|
|
what are the 2 types of stroke
|
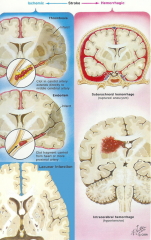
ischemic (white)
hemorrhagic (red) |
|
|
3 kinds(causes) of ischemic stroke
|
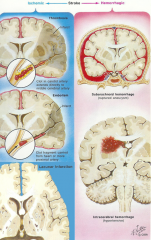
- thrombosis (clot forms there)
- embolism (clot got stuck there - formed somewhere else) - lacunar infarct (thrombi in small vessel) |
|
|
2 types of hemorrhagic stroke
|
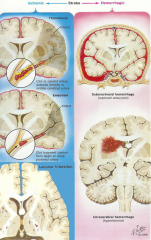
subarachnoid
intracerebral |
|
|
what happens
↑ pCO2 → vessel ___________ |
↑ pCO2 → vessel dilates
|
|
|
↓ pCO2 → vessel _______________
|
↓ pCO2 → vessel constricts
|
|
|
↓ SBP → vessel ____________
|
↓ SBP → vessel dilates
|
|
|
on the humunkulus of the motor cortex, where is face?
|
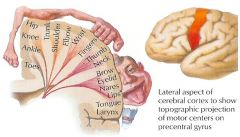
lateral
|
|
|
on the humunkulus of the motor cortex, what is midline before the cortex goes down
|
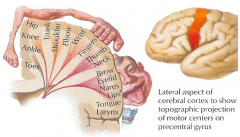
hip
|
|
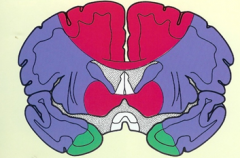
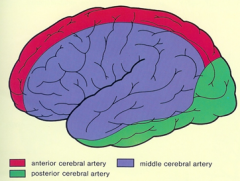
what is the vascular supply for each color
|
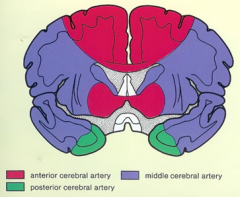
|
|
|
language is usually dominant in the _________ hemisphere
|
Language = Left
|
|
|
strokes in the middle cerebral artery are more likely to cause hemisensory deficit in ________ the most
|
face > arm > leg
|
|
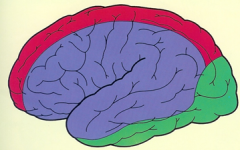
what is the vascular supply for each color
|
|
|
|
what is the blood supply (artery) for occipital and posterior temporal lobes
|
posterior cerebral
|
|
|
what is the blood supply (artery) for
pons midbrain occipital lobes |
basilar artery
|
|
|
what is
Locked-in syndrome |
awake and conscious - cant move anything other than vertical eye movement
|
|
|
what is a TIA (stand for and definition)
|
transient ischemic attack
- old term - < 24hrs - recover completely - lasts 10-15min - > 6hrs = stroke (neuron death) now called a stroke with resolving deficits |
|
|
for a TIA
If even within 72 hrs and ABCD2 > __ (score) → ADMIT |
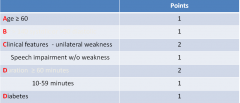
If even within 72 hrs and ABCD2 > 3 → ADMIT
|
|
|
what are the ABCDs of determining (score) of the risk of a stroke after a TIA?
|

|
|
|
what is TSI
|
transient Sx associated with infarct
|
|
|
Better than warfarin for cardioembolic stroke
|
Dabigatran (Pradaxa) / Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
|
|
|
what is
Endarterectomy for |
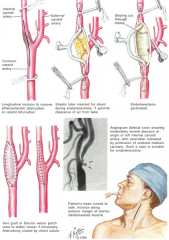
surgical Tx for atherosclerotic stroke
place shunt (tube) |
|
|
what is a
Watershed infarction |
ischemia, or blood flow blockage, that is localized to the border zones between the territories of two major arteries
iv. Watershed = most distal area - most sensitive to ↓ in blood flow 1) This why you don’t ↓ BP in hypertensive pt with signs and Sx of cerebral ischemia |
|
|
Tx - acute ischemic stroke?
|
Do NOT ↓ BP acutely!
(will kill the watershed areas! - will extend dead zone) 3) Aggressive Tx of hyperglycemia and hyperthermia a) To prevent spread of zone Is the pt a candidate for thrombolysis? |
|
|
how work/Tx suspected embolic stroke (start with a test)
|
CT to see if there is blood
if not - anticoag (heparin then coumadin long term NOT anticoagulating this stroke - anticoag against next stroke |
|
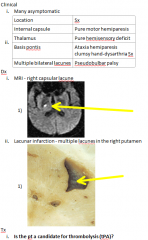
Dx?
|
lacunar infarct
|
|
|
tPA for ischemic stroke must be given within _____hrs of Sx onset
|
4.5hrs
|
|
|
AHA (America heart) says that for ischemic stroke when giving statins you want LDL below what
|
70mg/dL
|
|
|
what 2 things can cause
Carotid / vertebral artery dissection which can cause stroke |
trauma
sneezing |
|
|
5 kinds of stroke - fill in
Ischemic 1) ____________ 2) ____________ 3) ____________ Hemorrhagic 1) ____________ 2) ____________ |
Ischemic
1) Thrombotic 2) Embolic 3) Lacune Hemorrhagic 1) ICH (intracerebral hemorrhage) 2) SAH (subarachnoid hemorrhage) |
|
|
name for
multiple or single small cavitary infarcts |
lacunar infarct
|
|
|
what is a
slit hemorrhage |
i. Rupture of small penetrating vessels → small hemorrhages
ii. Make slit like cavity (lacunar is round lake) 1) Surrounded by brownish discoloration iii. Micro 1) Focal tissue destruction 2) Pigment laden macrophages 3) Gliosis (remember - like fibrosis) |
|
|
Onion skinning of vessel (means malignant ___)
|
Onion skinning of vessel (means malignant HTN)
|
|
|
what is
Binswanger disease |
Pattern of injury - large areas of the subcortical white matter with myelin and axon loss
from Hypertensive encephalopathy |
|
|
Caudate nucleus constitutes a system that is responsible largely for _____________________
|
voluntary movement
|
|
|
*what are the 3 basic structure that make up the basal ganglia
|
- putamen
- globus pallidus - caudate nucleus |
|
|
what is
* Duret's hemorrhage |
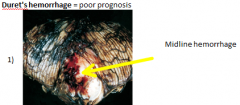
hemorrhage of the pons (midline)
2) ALWAYS secondary hemorrhages 3) When brainstem pushed down arteries at 90 rupture causing this 4) → death |
|
|
3 branches of the trigeminal
|
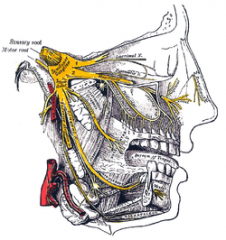
ophthalmic
maxillary mandibular |
|
|
facial skin infections, sinusitis, and dental abscess can cause dural sinus thrombosis where
|
cavernous sinus
|
|
|
birth control, malnutrition, dehydration, and cancer can cause dural sinus thrombosis where
|
superior sagittal sinus
|
|
|
what is the largest and most dangerous cerebral vascular malformation?
|
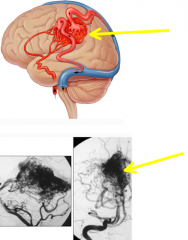
AVM (arteriovenous malformation)
|
|
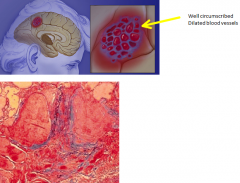
Dx?
i. Cerebral subcortical white matter - most commonly ii. Up to few cm in diameter iii. Frontal lobe - most common site iv. May be multiple v. Well circumscribed vi. Dar red to brown vii. Micro 1) Vascular channels a) Many b) Closely packed c) Thin fibrous walls - w/o muscularis |
Cavernous hemangiomas (malformation/tumor)
which is a Cerebral vascular malformation |
|
|
where are berry aneurysms most commonly found
|
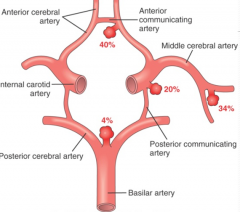
branch points
|
|
|
having what 3 things increase the incidence of berry aneurysms
|
- adult polycystic kidney disease
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome - Marfan syndrome (collegen production) also - smoking - HTN - cocaine |
|
|
what is
CAA (cerebral amyloid angiopathy) |
superficial hemorrhage in ppl over 60 where
Amyloidogenic peptides deposit in the wall of medium/small meningeal/cortical vessels |
|
|
word for:
outside coverings of the brain |
epidural
|
|
|
2 mechanisms of stroke
|
- block an artery (ischemia)
- rupture an artery (hemorrhage) |
|
|
what are the components of the Circle of Willis
|
Anterior communicating artery
Anterior cerebral artery (left and right) Internal carotid artery (left and right) Posterior communicating artery (left and right) Posterior cerebral artery (left and right) |
|
|
what does the
pineal gland do |
makes melatonin
|
|
|
what is the most common source of the embolis in an embolic stroke
|
heart
from afib valve disease |
|
|
90% of pts who get an Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH)
also have |
HTN
|
|
|
*** most common place for ICH (intracerebral hemorrhage) is?
|
PUTAMEN
|
|
|
*** most common place for ICH (intracerebral hemorrhage) is?
|
PUTAMEN
|
|
|
study of choice for suspected ICH
|
CT
|
|
|
Thrombosis of small deep penetrating arteries
is called what |
lacunar stroke
|
|
|
what is the
Monro-Kellie doctrine |
- volume of head is fixed
If volume ↑ must = loss or → ↑ pressure |
|
|
main Tx for ↑ ICP
|
ELIMINATE THE CAUSE = SURGERY
|
|
|
for increased cranial pressure - when do you remove
1) Small hemorrhages (< ___cc) DO NOT need to be removed 2) Not enough ICP to cause herniation syndromes |
dont remove if < 30cc
|
|
|
what is
Decompressive hemicraniectomy |
open the box
large 10x10cm flap to relieve pressure |
|
|
who came up with
Bio-psycho-social |
Engel (MD)
|
|
|
integration of behavior and relationships =
|
personality
|
|
|
1st textbook about mental illness - published 1586 by Timothy Bright
|
The Treatise of Melancholie
|
|
|
what is
The Treatise of Melancholie |
1st textbook about mental illness - published 1586 by Timothy Bright
|
|
|
what did
Benjamin Rush do |
i. Philadelphia physician - signed declaration of independence
ii. Hospital for Tx of psych pts |
|
|
who?
i. Philadelphia physician - signed declaration of independence ii. Hospital for Tx of psych pts |
Benjamin Rush
|
|
|
who?
i. Superego? ii. Psychoanlalysis |
Freud
|
|
|
who?
i. Thought Freud overemphasized sexuality ii. Coined "inferiority complex" iii. Birth order 1) Oldest vs youngest sibling |
Alder
|
|
|
who?
i. Unconscious - not just individual 1) Collective unconscious a) Social / cultural group ii. Derived idea of persona 1) How you project yourself |
Carl Young
|
|
|
what did Carl Young do?
|
- collective unconsious
- derived idea of persona (how you project yourself) |
|
|
* name for this theory:
Ppls behavior not determined by internal events - rather by external events |
social learning theory
|
|
|
* what is the
social learning theory |
- Ppls behavior not determined by internal events - rather by external events
Ex - behavior that is rewarded or punished - To make change (NOT by gaining insight or understanding -- But by changing their behavior) - Not governed by the unconscious - but by something that is learned |
|
|
who?
a. How ppl react to particular stimuli b. Salivating dogs c. Conditioned stimulus i. Disappears without unconditioned stimulus (ring bell enough w/o food) |
Pavlov
|
|
|
what is
operant conditioning |
Behaviors are part of personality
i. Reinforced / strengthened w/ reward ii. Go away if associated w/ something negative b. Can use to desensitize to fears Variable reinforcement - Sometimes get + reinforcement - sometimes no - Don’t know when its going to get it Continuous reinforcement - Always get Observational learning - Watching how someone else does it |
|
|
Who?
Systematic desensitization - to overcome anxiety / fears |
Wolpe
|
|
|
name of this therapy:
a. Ppl react to stimuli and how they react to stimuli b. And how they incorporate that into whats going on in their lives c. Eric Beck d. Ppl are depressed b/c negative view of themselves |
cognitive therapy
|
|
|
what is
Catatonia |
complete cessation of motor activity
|
|
|
what is the definition/difference btw
illusion hallucination |
illusion = mistake in perception
hallucination = false perception |
|
|
what is a
Persecutory delusion |
Object of plot of someone trying to harm you
|
|

|
Body of the corpus callosum
|
|
|
name the structure
a. The little brain b. c. 10% of brains total weight d. Largest structure in the posterior fossa e. Behind brainstem at level of the pons f. Attached by peduncles: i. Superior, middle, inferior peduncles |
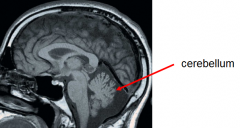
cerebellum
|
|
|
what coordinates voluntary movements
|
cerebellum
|
|
|
what does these things:
a. Coordination of voluntary movements b. Equilibrium c. Muscle tone d. Postural control e. Cognitive functions |
cerebellum
|
|
|
what part of the cerebellum is most important
|

midline
|
|

|
cerebellar peduncles
|
|

|
vermis
|
|

|
tonsil
1) On either side of the pyramids of the medulla 2) Herniation compresses medulla → dead |
|
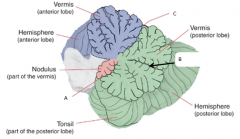
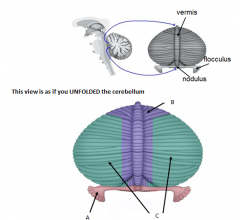
A
|
posterolateral fissure
|
|
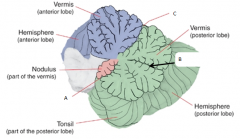
B
|
horizontal fissure
|
|
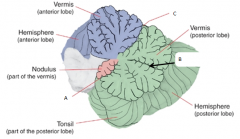
C
|
primary fissure
- divides ant/post lobes |
|
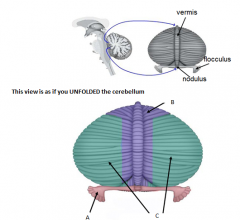
A
name what does it do |
Vestibulocerebellum or flocculonodular lobe
1) Balance and gait |
|
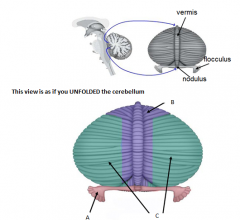
B
name what does it do |
Spinocerebellum
1) Coordinating adjustment of limb musculature 2) Comparator btw intended and actual movements |
|
C
name what does it do |
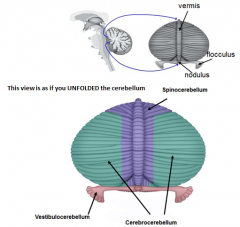
Cerebrocerebellum
1) Coordination of voluntary motor activities 2) Motor planning |
|
|
what part of the cerebellum compares btw intended and actual movements
|
spinocerebellum
|
|
|
what part of the cerebellum creates balance
|
vestibulocerebellum or flocculonodular
|
|
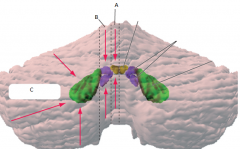
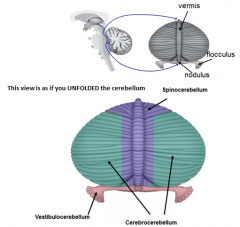
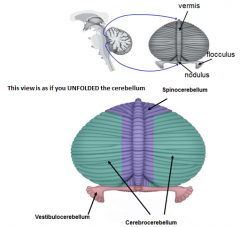
* A
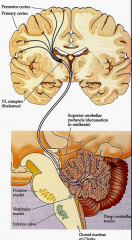
- what zone (longitudinal) - what deep cerebellar nucleus does it contain (colored structures) - what is its function |

vermis
fastigial nucleus - balance (eye movements) |
|
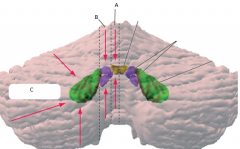
* B
- what zone (longitudinal) - what deep cerebellar nucleus does it contain (colored structures) - what is its function |
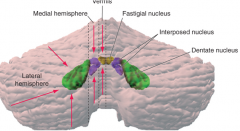
medial hemisphere (intermediate or parvermal zone)
interposed nucleus (emboliform + globose nucelus) - adjusting limb movements |
|
* C
- what zone (longitudinal) - what deep cerebellar nucleus does it contain (colored structures) - what is its function |
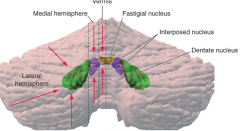
lateral hemisphere
dentate nucleus - planning initiation & control of voluntary movements |
|
|
vermis = ? *
|
vermis = balance *
Fastigal nucleus |
|
|
what deep cerebellar nucleus and what is it in that does:
planning initiation & control of voluntary movements |
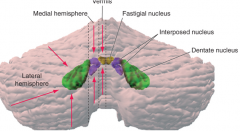
dentate nucleus
in the lateral hemisphere |
|
|
what is the major cell type of the cerebellum
|
Purkinje cells
|
|
|
what are the 3 layers of the cerebellum
|
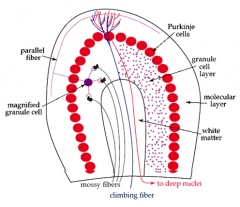
- molecular layer (axons + dentrites from the purkinje cells)
- purkinje layer (purkinje cells) - granular layer (unmyelinated axons + interneurons) |
|
|
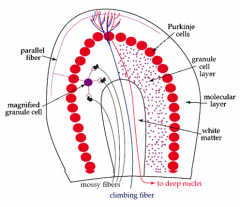
climbing fiber
- what structure - where synapse - originate from |
cerebellum
- synapse on purkinje cell dendrites (molecular layer - outer layer) - originalte in the contralateral inferior olivary nucleus (medulla oblongata is the lower half of the brainstem) |
|
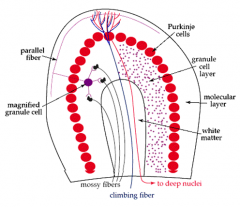
Mossy fibers
- what structure - where synapse - originate from |
cerebellum
- synapse on dendrites of the granule cells - originate from brainstem nuclei & spinal cord nuclei |
|
|
describe the 4 steps of information flow into/out of the cerebellum
- structures - inhibitory (GABA) or excitatory (glutamate) |
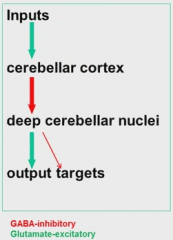
Input stim causes inhibition of deep cerebellar nuclei which causes mostly output stim
|
|
|
describe the 4 steps of information flow into/out of the cerebellum
- structures - inhibitory (GABA) or excitatory (glutamate) |
Input stim causes inhibition of deep cerebellar nuclei which causes mostly output stim
input (stims) - cerebellar cortex (inhibits - w/GABA) - deep cerebellar nuclei (which mostly stim) - output targets |
|
|
what molecule is inhibatory stimulation
|
GABA
|
|
|
what molecule is excitatory stimulation
|
glutamate
|
|
|
*********** purkinje job is to
|
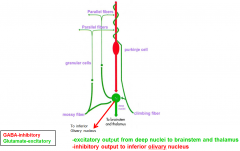
purkinje job is to modulate output to the deep cerebellar nuclei
|
|
|
most dysfunction in the superior cerebellar peduncle (main output) is ipsilateral or contralateral?
|
ipsilateral
crosses TWICE - caudal midbrain - pyramid |
|
|
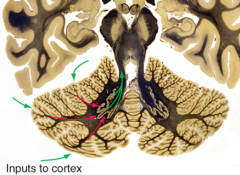
3 brainstem and 1 spinal cord nuclei that send inputs into the cerebellar cortex
|
brainstem
- pontine nuclei - vestibular nuclei - inferior olivary nucleus (origin of climbing fibers) spinal cord - Clarks nucleus (C8-> L2-3) - proprioceptive information [to spinocerebellar] |
|
|
3 brainstem and 1 spinal cord nuclei that send inputs into the cerebellar cortex
|
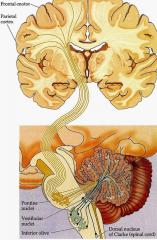
brainstem
- pontine nuclei - vestibular nuclei - inferior olivary nucleus (origin of climbing fibers) spinal cord - Clarks nucleus (C8-> L2-3) - proprioceptive information |
|
|
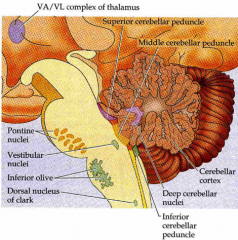
output pathway from cerebellar cortex to?
|
cerebellar cortex ->
deep cerebellar nuclei -> (decussation (passes to)) brainstem - travels to thalaumus -> motor/pre-motor cortex |
|
![[cerebellar cortex inputs]
pontocerebellar pathway
- terminates (2x)
- peduncle
- function (2x)](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/62/89/47/3628947_m.png)
[cerebellar cortex inputs]
pontocerebellar pathway - terminates (2x) - peduncle - function (2x) |
![pontocerebellar pathway
- terminates (2x)
[Contralateral anterior AND posterior cerebellar lobes]
- peduncle [middle cerebellar]
- function (2x)
[- Cortical info relevant to motor commands
- Planned motor activities (walking)]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/62/89/50/3628950_m.png)
pontocerebellar pathway
- terminates (2x) [Contralateral anterior AND posterior cerebellar lobes] - peduncle [middle cerebellar] - function (2x) [- Cortical info relevant to motor commands - Planned motor activities (walking)] |
|
![[cerebellar cortex inputs]
Olivocerebellar pathway
- terminates (2x)
- peduncle
- function (2x)](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/62/89/74/3628974_m.png)
[cerebellar cortex inputs]
Olivocerebellar pathway - terminates (2x) - peduncle - function (2x) |
![Olivocerebellar pathway
- terminates (2x)
[Inferior olivary nuclei
accessory olivary nuclei]
- peduncle [inferior cerebellar]
- function (2x)
[Motor coordination
Motor learning]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/62/89/77/3628977_m.png)
Olivocerebellar pathway
- terminates (2x) [Inferior olivary nuclei accessory olivary nuclei] - peduncle [inferior cerebellar] - function (2x) [Motor coordination Motor learning] |
|
![[cerebellar cortex inputs]
Posterior spinocerebellar pathway
- terminates (2x)
- peduncle
- function](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/62/89/89/3628989_m.png)
[cerebellar cortex inputs]
Posterior spinocerebellar pathway - terminates (2x) - peduncle - function |
![Posterior spinocerebellar pathway
- terminates (2x)
[Ipsilateral vermis
Intermediate zone]
- peduncle [inferior cerebellar]
- function [proprioceptive information]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/62/89/92/3628992_m.png)
Posterior spinocerebellar pathway
- terminates (2x) [Ipsilateral vermis Intermediate zone] - peduncle [inferior cerebellar] - function [proprioceptive information] |
|
|
what are the 3 cerebellar input pathways and what they carry?
|
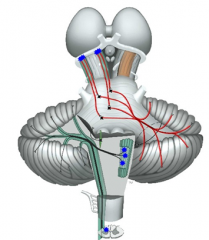
- pontocerebellar (planned - walking)
- olivocerebellar (coordination) - posterior spinocerebellar (proprioceptive) |
|
|
what are the 3 output cerebellar pathways and what information do they carry?
|
- dentate nucleus (planning initiation - control voluntary)
- interposed nucleus = emboliform + globus nucleus (comparator - adjust limb position) - fastigial nucleus (balance / gait) |
|
![[cerebellar cortex outputs]
Dentate nucleus
- terminates (2x)
- peduncle
- function](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/62/91/06/3629106_m.png)
[cerebellar cortex outputs]
Dentate nucleus - terminates (2x) - peduncle - function |
![Dentate nucleus
- terminates (2x) [contralateral red nucleus and thalamus]
- peduncle [superior cerebellar]
- function [PLANNING inititation - control voluntary movements]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/62/91/09/3629109_m.png)
Dentate nucleus
- terminates (2x) [contralateral red nucleus and thalamus] - peduncle [superior cerebellar] - function [PLANNING inititation - control voluntary movements] |
|
![[cerebellar cortex outputs]
Interposed nucleus = emboliform + globus nucleus
- terminates
- peduncle
- function](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/62/92/77/3629277_m.png)
[cerebellar cortex outputs]
Interposed nucleus = emboliform + globus nucleus - terminates - peduncle - function |
![Interposed nucleus = emboliform + globus nucleus
- terminates [interposesed nucleus]
- peduncle [superior cerebellar - descending limb]
- function [comparator - adjusts limb position]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/62/92/80/3629280_m.png)
Interposed nucleus = emboliform + globus nucleus
- terminates [interposesed nucleus] - peduncle [superior cerebellar - descending limb] - function [comparator - adjusts limb position] |
|
![[cerebellar cortex outputs]
Fastigial nucleus
- terminates
- peduncle
- function](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/62/92/92/3629292_m.png)
[cerebellar cortex outputs]
Fastigial nucleus - terminates - peduncle - function |
![Fastigial nucleus
- terminates [bilateral to vertibular nuclei - reticular formation]
- peduncle [inferior cerebellar peduncle]
- function [balance and gait]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/62/92/95/3629295_m.png)
Fastigial nucleus
- terminates [bilateral to vertibular nuclei - reticular formation] - peduncle [inferior cerebellar peduncle] - function [balance and gait] |
|
|
Most common form of ataxia (Aberrant regulation of limb movements w/poor coordination btw limbs)
- from dysfunction in cerebellum - or afferent / efferent pathways |
Cerebellar ataxia
|
|
|
what is ataxia
|
Aberrant regulation of limb movements w/poor coordination btw limbs
|
|
|
what is
Posterior lobe syndrome |
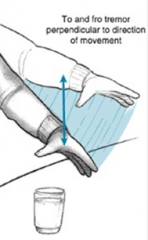
Loss of coordination of voluntary movements
↓ muscle tone Back-forth movements perpendicular to intended direction of movement |
|
|
what is anterior lobe syndrome
|
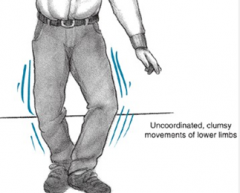
gait messed up - all over - like your drunk
from malnutrition in chronic alcoholism |
|
|
what is
Flocculonodular lobe syndrome |
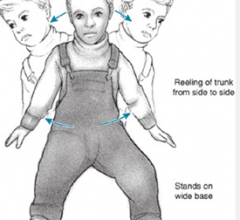
Truncal ataxia
Lesion in flocculonodular lobe AND posterior VERMIS Seen in children w/medulloblastomas in roof of 4th ventricle |
|
|
in coordinating movement - what role do the basal ganglia and cerebellum play generally
|
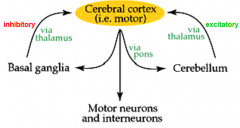
basal ganglia - inhibitory (via thalamus)
cerebellum - excitatory (via thalamus) |
|
|
where does the neuron that leaves the motor cortex synapse?
|
anterior horn cell
|
|
|
what 1950s neurosurgeon that tried to fix epilepsy make maps of the brain?
|
Wilder Penfield
|
|
|
Visual cortex is in what lobe
|
occipital
|
|
|
auditory is in what lobe
|
temporal
|
|
|
olfactory is in what lobes
|
inferior frontal
medial temporal |
|
|
which hemisphere does language
|
the dominant one
|
|
|
how many layers does the cerebral cortex have?
|
6
|
|
|
what are the 3 formal and 2 additional parts of a mini mental status exam (Folstein exam)
|
orientation (person-you / place-floor,country,state / time)
registration (remember 3 words apple/ball/tree - check in 3 min) attention (getting what you say to them) _____________________________________________ calculation (how many quarters in $3.75) visuo-spatial - draw clock |
|
|
what lobe is Wenikies area in?
do? |
posterior 1/3 of superior temporal gyrus
like dictionary for word meanings |
|
|
what lobe is Broca's area in?
do? |
frontal lobe
coordinates motor parts of language (speaking) |
|
|
Wernies aphasia
- where is problem? - what happens (Sx) |
temporal lobe
- sub in wrong word or letter - or make up new word |
|
|
what is
apraxia |
cant do learned movement correctly
|
|
|
what is
transitive apraxia |
use toothbrush instead of spoon
|
|
|
what is
ideomotor apraxia |
dont know the mechanics of how to eat the corn
|
|
|
what is agnosia
|
no knowledge / cant recognize
|
|
|
what is
Anosognosia |
doesnt know they are sick
|
|
|
what is
Aprosopagnosia |
Cant ID face - ID person based on facial features
|
|
|
what happens in pts w/ neglect agnosia?
what is usually caused by |
neglect one side of the body
usually from visual field defect |
|
|
what is
Asomatagnosia |
Asomatagnosia
|
|
|
what is this:
i. Lesion of the NON dominant parietal lobe ii. 4 parts to it 1) Acalculia - cant calculate anything 2) Finger agnosia - cant distinguish anything 3) Right-left confusion - cant distinguish btw right and left 4) Agraphia - cant write |
Von-gerstmann
|
|
|
what is
Agraphia |
cant write
|
|
|
where would the lesion be
- talk forever - hypersexuality |
temporal lobe
|
|
|
where would the lesion be
- cant get calm - dont care how they look |
frontal lobe
|
|
|
left of right brain?
musical, artistic, big picture |
right
|
|
|
left of right brain?
logic |
left
|
|
|
left brain is?
|
logic
|
|
|
right brain is?
|
music / art / big picture
|
|
|
the hippocampal gyrus does what
|
short term memory
|
|
|
what transfers information L/R btw hemispheres (structure)
|
corpus callosum
|
|
|
4 main parts to bedside neuro exam
|
orientation
aphasia corital sensory (put object in hand) |
|
|
match the problem (motor/cognitive)
with cerebral palsy mental retardation |
motor = CP
cognitive = MR |
|
|
what causes
Cerebral palsy generally |
Brain injury btw fertilization & infancy
|
|
|
sensory or motor?
anterior horn cell |
motor
|
|
|
how long is the spinal cord?
|
22 inches
|
|
|
how many levels in each of the 5 sections of the spinal column
|
cervical - 8
thoracic - 12 lumbar - 5 sacral - 5 coccygeal - 1 |
|
|
ascending spinal cord tracts are long and
- do? - project to (3x) |
- sensory
project to - thalamus - cerebellum - brainstem nuclei |
|
|
descending spinal cord tracts are long and
- do? - project from(2x) - to? |
motor
from - cerebral cortex - brainstem nuclei - spinal gray matter |
|
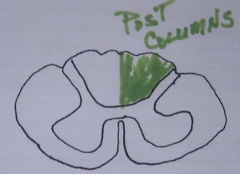
posterior columns - of spinal cord
- ascending or descending - carry (3x) - ipsi or contra lateral? - how many neurons |
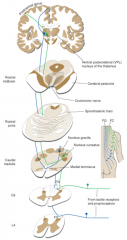
ascending
carries - position - vibratory senses - touch sensations ipsilateral 3 neurons |
|
|
what track?
fasiculus cuneatus (nucleus cuneatus in medulla) what does it carrier |
posterior columns
fibers from sacral/lumbar/thoracic legs thorax trunk |
|
|
what track?
fasiculus gracilis (nucleus gracilis in medulla) what does it carrier |
posterior columns
fibers from cervical levels hand arms neck |
|
|
what does the Corticospinal tract
- do? - how many neurons? - ipsilateral or contralateral |
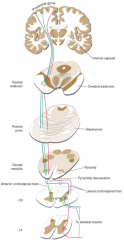
corticospinal tract
- voluntary motor (descending pathway) - 2 neurons (precentral gyrus to anterior horn to muscle) - ipsilateral (crosses before cord - in the medulla |
|
|
where does the corticospinal tract cross?
is it ipsilateral or contralateral |
crosses in the the pyramidal decussation of the medulla
considered ipsilateral (same side) because it crosses before the cord |
|
|
where are the face fibers in the internal capsule?
|
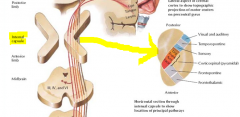
at the bend (genu)
|
|
|
what is the
corticobulbar |
connects cerebral cortex and brainstem
|
|
|
what are upper and lower neurons
|
NOT level in spine
upper - precentral gyrus to anterior horn (in brain) lower - anterior horn to muscle (in spinal cord) |
|
|
big MOTOR nerve to face
|
CN VII - facial
|
|
|
Babinski's sign - bottom of foot
if + is a sign of upper/lower motor neuron problem |
upper
|
|
|
fasiculations (muscle twitch) is a sign of upper/lower motor neuron problem?
|
lower
|
|
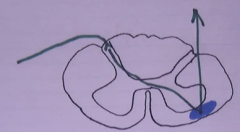
name the tract
|
spinothalamic tract
|
|
|
what is
Brown Séquard syndrome |
half the spinal cord is crushed
|
|
|
3 parts of the
Equilibrial triad |
1 - proprioceptive system
2 - visual system (CN II) 3 - vestibular system (CN VIII) |
|
|
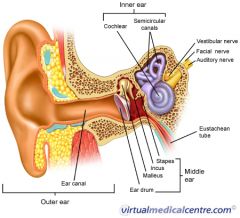
what are the 3 parts of the bony labyrinth
|
- vestibule
- semicircular canals - cochlea embeded in the petrous portion of the temportal bone |
|
|
what part of what bone does the bony labyrinth reside in
|
petrous portion of the temportal bone
|
|
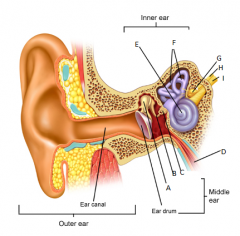
A
|
malleus
|
|
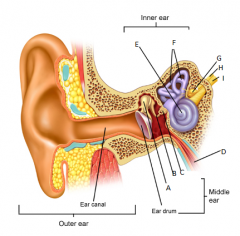
B
|
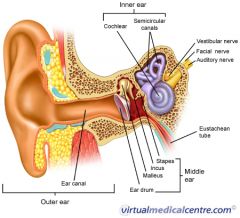
incus
|
|
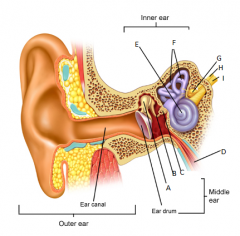
C
|
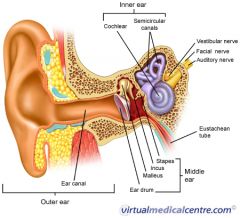
stapes
|
|
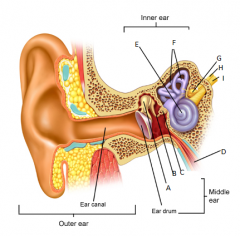
D
|
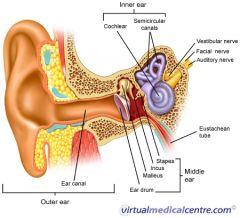
eustachean tube
|
|
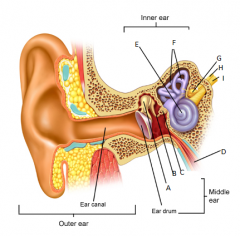
E
|
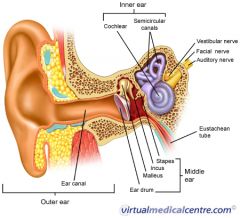
cochlear
|
|
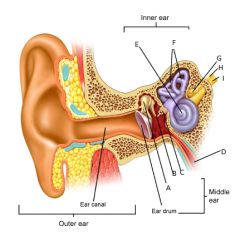
F
|
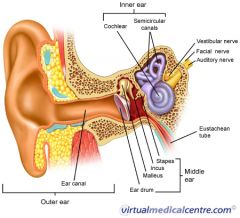
semicircular canals
|
|
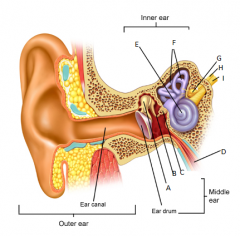
G
|
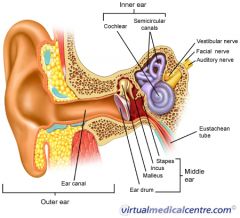
vestibular nerve
|
|
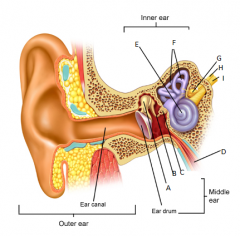
H
|
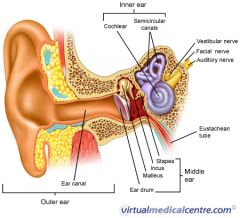
facial nerve
|
|
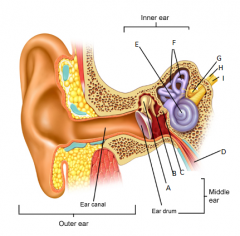
I
|
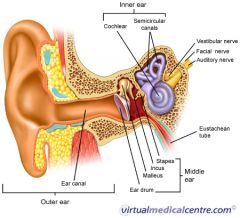
auditory nerve
|
|
|
what is the ampulla in the semicircular ducts and where are they found
|
there are 3 - one at the end of each semicircular duct
- horizontal - anterior - posterior they are where the crista or actual sensors are |
|
A
|
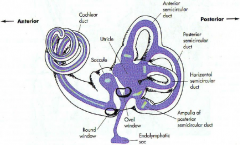
cochlear duct
|
|
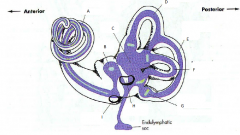
B
|
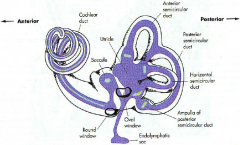
saccule
|
|
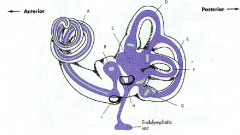
C
|
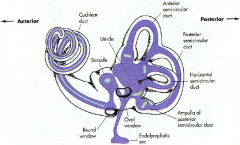
utricle
|
|
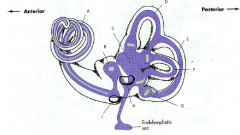
D
|
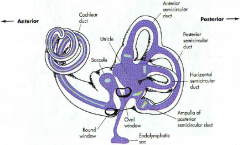
anterior semicircular duct
|
|
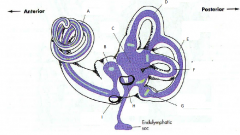
E
|
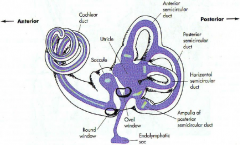
posterior semicircular duct
|
|
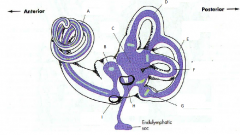
F
|
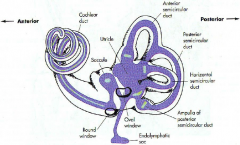
horizontal semicircular duct
|
|
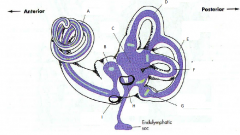
G
|
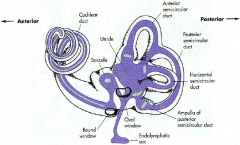
ampulla
of posterior semicircular duct |
|
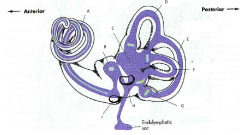
H
|
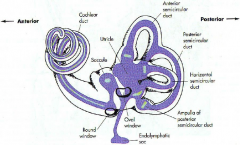
oval window
|
|
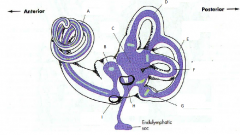
I
|
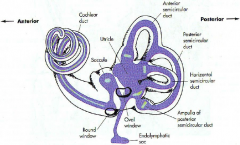
round window
|
|
|
what is the bony labyrinth filled with (its like CSF)?
what electrolytes are high/low - Na / K |
perilymph
- like normal extracellular fluid - high [Na] - low [K] continuous w/subarachnoid space |
|
|
what / where is the membranous labyrinth?
|
closed tube inside bony labyrinth
(purple in pic) |
|
|
what is the membranous labyrinth filled with?
what are [Na and K] |
endolymph
like intracellular fluid - high [K] - low [Na] bony labyrinth : perilymph - like normal extracellular fluid - high [Na] - low [K] |
|
|
what do the Semicircular ducts do?
|
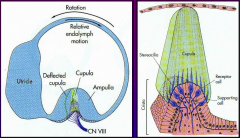
detect motion (by rotation in the 3 planes)
|
|
|
what are the / what do they do?
- crista - cupula what are they in specifically? which is at the end of what? which do what? |
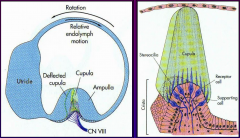
crista - bump that holds the receptor cells
cupula - is the thing that moves in the fluid (endolymph - high K, low Na) this is in the ampulla which is at the end of the semicircular tubes which sense movement |
|
|
what is a tip link?
what is it on? what does it do - specifically and as part of what generally |
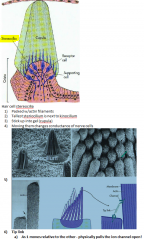
connects stereocilia in the cupula which connect to the crista and sense motion in the semicircular ducts which is part of the inner ear
|
|
|
what are the specific steps to the mechano-electrical transduction of movement in the ampulla of the semicircular ducts
|
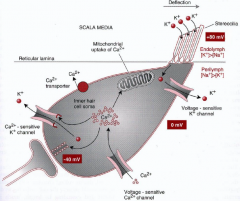
1 - deflection
2 - tip link pulls open K channels 3 - K enters from endolymph 4 - HAIR CELL depolarizes 5 - voltage-gated Ca channels open 6 - release neurotransmitter glutamate (CN VIII - vertibular nerve) - afferent |
|
|
the utricle and saccule detect what?
|
linear motion
|
|
|
what are the otoconia?
what are they part of / do? |
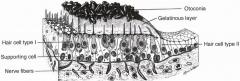
crystals (calcium carbonate) that sit on gel layer - gives mass to the gel and hair cells
otolithic organ - detects linear motion |
|
|
what is the actual cell type that detects the motion of the gel in the otolithic organs (linear) and semicircular ducts (rotation)?
|
hair cells
|
|
|
the macula of the
saccule detects acceleration in the __________ plane |
sagittal
saccule = sagittal |
|
|
saccule = ?
|
saccule = sagittal
|
|
|
the macula of the
utricle detects acceleration in the __________ plane |
horizontal
|
|
|
detects motion in what plane
saccule = utricle = |
saccule = sagital
utricle = horizontal |
|
|
what ganglion does information from the utricle / saccule (linear), and semicircular ducts (rotation) go through?
|
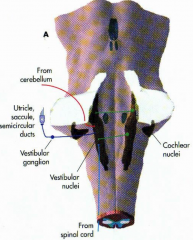
vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
|
|
|
what 2 things does the MVST (medial vestibulospinal tract) do
|
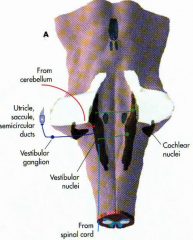
- stabilizes head position
- coordinates eye movement |
|
|
what does the LVST (tract) - lateral vestibulospinal tract - do?
|
postural compensation
|
|
|
what function does the
Vestibuloocular reflex allow for? |
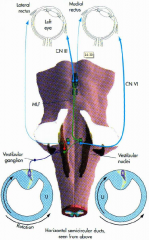
Gaze can stay fixed on an object while the head is moving; Doll's Eye Movement
|
|
|
what is nystagmus
|
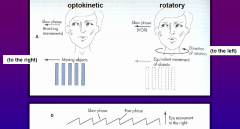
eyes keep tracking an object / movement that is no longer moving
|
|
|
if you squirt COLD water into right ear (of comotose pt), which way will eyes go if brainstem intact
* if lying supine |
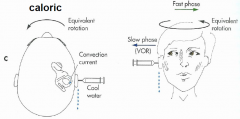
cold in right
think head is going left eyes rotate right for direction head thinks its going COWS = cold opposite / warm same |
|
|
if you squirt WARM water into right ear (of comotose pt), which way will eyes go if brainstem intact
* if lying supine |
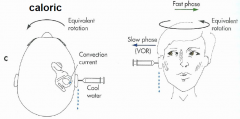
cold in right
think head is going right eyes rotate left for direction head thinks its going COWS = cold opposite / warm same |
|
|
what is
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV)? what causes it? Tx? |
feels like moving when not
caused by - otoconia (crystals) being dislodged - moves to semicircular ducts (usually posterior) - bumps the cupula Tx - canalith repositioning procedure (CRP) - drugs for Sx |
|
|
why / how (MOA) does alcohol cause vertigo?
|
changes blood density
- alcohol enters endolymph (causes cupula to float) - then alcohol leaves - cupula sinks - feels like rotation |
|
|
what is
Proprioception |
sense of position
|
|
|
what is kinesthesia
|
sense of movement
|
|
|
what structure
monitors the strength of muscle contraction |
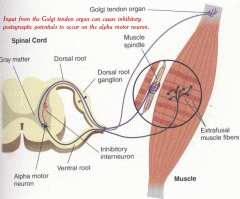
golgi tendon organs
|
|
|
what mechanoreceptor senses vibration and pressure
|
Pacinian corpuscles
|
|
|
what do Pacinian corpuscles do?
|
mechanoreceptors that sense vibration and pressure
|
|
|
what do Muscle spindles sense?
|
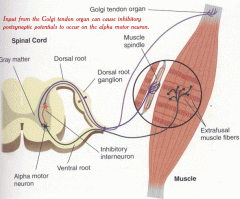
STRETCH
|
|
|
what is this:
a) In SERIES with muscle fibers b) When the muscle contracts they bunch up and do nothing c) They are STRETCH receptors |
muscle spindle fibers
|
|
|
name the mechanoreceptor
- stretch - strength of contraction |
- stretch (stretch)
- strength of contraction (golgi tendon) |
|
|
where does CONTROL of muscle movement come from
|
spinal cord
regulation is farther up |
|
|
1 alpha motor unit = _____________ + ______________
|
1 alpha motor unit = neuron + all muscle fibers it innervates
|
|
|
describe the general steps of a spinal motor reflex
|
i. Produces 1 motor response - same 1 over and over
1) Begins w/stim to a sensory receptor (ex: muscle spindle) 2) An afferent pathway to the CNS 3) 1+ synapses in the CNS 4) An efferent pathway to the periphery 5) An effector (the muscle) |
|
|
what mechanoreceptors sense
velocity length of stretch |
muscle spindles
|
|
|
what mechanoreceptors sense
load force being applied to muscle |
golgi tendon organs
|
|
|
how do distal limb and proximal limb motor nuclei spatial relate in the spinal cord?
|
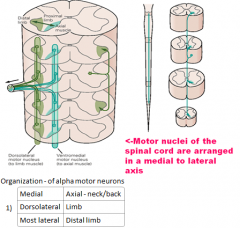
medial = proximal
lateral = distal |
|
|
what are
intrafusal muscle fibers |
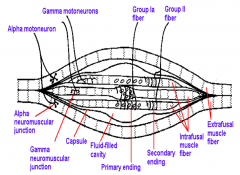
all muscle fibers (cells) that are INSIDE the muscle spindle (group Ia, group II)
|
|
|
what are
extrafusal muscle fibers |
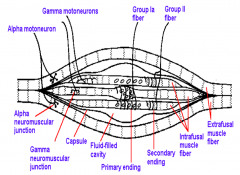
all (most) muscle fibers that are outside the spindle
|
|
|
what are
Group Ia fibers where are they found? |
FAST adapting
signal RATE of stretch |
|
|
what are
Group II fibers where are they found? |
slow / long firing
only innervates nuclear chain fibers |
|
|
for motor efferent (input)
compare alpha and gamma motorneuron input both - are lower motor neurons - have cell bodies in the anterior horn |
alpha
- east to stim - innervates EXTRAFUSAL fibers - when fires => tension / shortens fibers gamma - only gets stim from HIGHER brain centers - innervates INTRAFUSAL muscle fibers - keep the sensing fibers taught |
|
|
what does the static stretch reflex do?
|
increases muscle tonw
also - if bone grows - causes muscle to grow and activates group II sensory fibers |
|
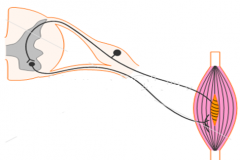
what is this
|
stretch reflex
|
|
|
what do each measure
Group Ia Group II |
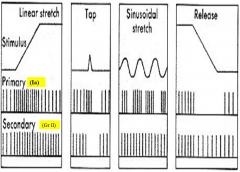
Group Ia - Rate of stretch
Group II - Length of fiber |
|
|
what do gamma efferents do
|
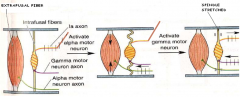
since the intrafusal fibers slacken when the muscle contracts - the gamma efferents tell them to tighten so they can sense changes again
|
|
|
where do gamma fibers that keep the intrafusual sensory fibers taught get their stim from?
|
cerebellar (CNS)
|
|
|
what specific neuron types are involved in a stretch reflex like the patellar reflex
|
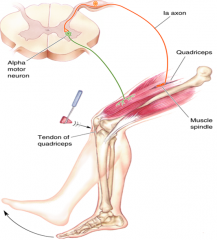
group 1a - sends signal through posterior horn
synapses with alpha motor neuron in the anterior horn |
|
|
what is feed forward inhibition
|
relaxes antagonist muscle
|
|
|
what do golgi tendon organs do?
|
- prevents muscle from being torn
- sensory information of heaviness/resistance to CNS |
|
|
what fiber group does golgi tendon organs use to send info to cord
|
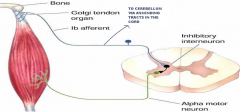
group Ib
|
|
|
how does a golgi tendon reflex work
|
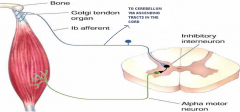
through an inhibitory interneuron
which inhibits the alpha motor neuron telling it to relax so it doesnt tear |
|
|
where is the center of mass in the human body
|
S2
|
|
|
what are the 5 antigravity muscles
|
- gastroc-soleus
- quadriceps - hip extensors - paraspinals - neck extensors |
|
|
what is the crossed extensor reflex
|
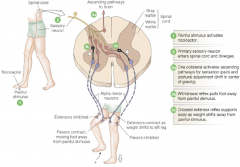
ex - step on tack
inhibits one sides hip extensor, and stims the other side |
|
|
relating to vertigo
Of those who fall (sustain hip fracture __% will die) |
relating to vertigo
Of those who fall (sustain hip fracture 49% will die) |
|
|
#1 complaint pts 70+
|
vertigo
|
|
|
true vertigo
|
vestibular disorder
- sensation of spinning - from asymmetrical impulses from vestibular system - nystagmus (rapid jerking of eyes) |
|
|
Most common peripheral vertigo
|
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV)
|
|
|
what is the mechanism that causes
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) |
Abnormality in association of otoconia to the cupula - in the membranous labyrinth
→ resulting in abnormal responses to endolyph movement with head motion |
|
|
Dix-Hallpike test
tests for? |
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV)
|
|
|
THE Tx for BPPV?
|
Gans repositioning maneuver
brings debris back to neutral hold each of the 3 positions for 30s |
|
|
Dx?
i. Sudden episode of vertigo 1) w/o hearing loss or tinnitus 2) Single or mult 3) Herpes simplex II virus 4) Spring/early summer a) From/with upper respiratory tract infection 5) n-v 6) Followed by BPPV |
Vestibular neuronitis/neuritis
|
|
|
Dx?
i. Sudden profound loss in 1) Auditory 2) Vestibular function ii. Old ppl 1) Young = w/ atherosclerotic or hypercoagulation disorders iii. Episodic vertigo - may be precede complete occlusion iv. After complete occlusion 1) Vertigo subsides 2) Leaves unsteadiness/dysequilibrium - several months while compensates |
Labyrinthian infarction
|
|
|
a Sx triad of:
- vertigo - tinnitus - hearing loss suggests what disease that has too much endolymph (too much production or too little resorption) 20's and 30's |
Meniere's disease
|
|
|
* how Dx Meniere's disease
|
cold air into ear = opposite
|
|
|
a migraine with aura - what is aura
|
hallucinations
- abnormal sensory perceptions (visual most common) |
|
|
what is
Mal de Debarquement |
motion (swaying/rocking) after disembarkment
|
|
|
* what is the gold standard Dx for acoustic neuroma (schwannoma of the 8th CN)
|
MRI of IACs w/gadolinium
|
|
|
what is #1 complaint of pts over 70 y/o
|
dizziness (vertigo)
|
|
|
* when you have less than 3 of the fall factors what is the changes you are going to fall?
|
12%
|
|
|
* spinning inside the head is/is not a vestibular problem
|
is NOT
is a psych problem |
|
|
* best way to test for position vertigo (what test)?
|
Hallpike test
|
|
|
* best Tx for BPPV
|
Gans (Canalith) repositioning maneuver
|
|
|
word?
Any restriction resulting from an impairment of an ability to perform a normal activity |
disability
|
|
|
what is the difference btw impairment, disability, and handicap?
|
impairment - loss / abnormality of pysch / physical / anatomical function
disability - restriction from impairment handicap - disadvantage from impairment / disability |
|
|
4 musculoskeletal uses of heat Tx
|
tendonitis
tenosynovitis bursitis capsulitis |
|
|
what is
Contracture |
a permanent shortening of a muscle or joint.
It is usually in response to prolonged hypertonic spasticity in a concentrated muscle area, such as is seen in the tightest muscles of people with conditions like spastic cerebral palsy. |
|
|
what does each neuromuscular fiber group carry
group 1a group 2 group 1b |
group 1a - muscle length, as well to change in velocity, rapidly adapting
group 2 - position sense group 1b - Golgi tendon organ (tenses spindle fibers) |
|
|
compare the effects of hot and cold Tx
|

|
|
|
main uses of heat Tx (x)
|
- chronic inflammation
- tendonitis - tenosynovitis - bursitis - capsulitis |
|
|
* who (roles/titles) of the 4 team members in occupational therapy. name who does each of the listed
- hygienic factors, meds management, safety - counseling, testing - total living situation, coordinate return to home - assess level of social capability / educate in leisure activities |
rehabilitation nurse - hygienic factors, meds management, safety
psychologist - counseling, testing social worker - total living situation, coordinate return to home recreational therapis - assess level of social capability / educate in leisure activities |
|
|
what is the difference btw an abrasion and a laceration?
|
abrasion - scrape on skin
laceration - NOT cut wound - blunt object breaks / tears skin |
|
|
what is a contusion
|
bruise
|
|
|
name for bruise / black and blue
|
contusion
|
|
|
name for:
a. Blunt object tears soft tissue b. NOT a cut wound |
laceration
|
|
what is this
|
laceration
- irregular margins - skin torn from being hit by a blunt object |
|
|
what is a
spectacle hematoma what is it commonly seen with |
bleeding around eyes
commonly seen w/gunshot wound to head - pressure wave from bullet blows out orbital plates |
|
|
what are
terminal fall injuries caused by |

from the impact of a fall after LOSS OF CONSCIOUSNESS
|
|
|
what are the 5 types of facial fractures
|
- dentoalveolar
- LeFORT I - LeFORT II - LeFORT III - sagital |
|
|
what is a dentoalveolar facial fracture?
|
fragments mandible / teeth
- direct force anterior / lateral |
|
|
what is a LeFORT I facial fracture?
|
![TRANSVERSE fracture of the MAXILLA
above teeth
through nasal septum / maxillary sinuses / palatine bone of the sphenoid bone
[red line]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/64/70/10/3647010_m.png)
TRANSVERSE fracture of the MAXILLA
above teeth through nasal septum / maxillary sinuses / palatine bone of the sphenoid bone [red line] |
|
|
what is a LeFORT II facial fracture?
|
![[blue line]
near zygomatic/maxillary suture
- inferior orbit/orbital floor
- nasal bones / septum](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/64/70/13/3647013_m.png)
[blue line]
near zygomatic/maxillary suture - inferior orbit/orbital floor - nasal bones / septum |
|
|
LeFORT III fracture - where?
|
![[green line]
high transverse fracture
- maxilla
- through nasofrontal suture / medial orbital wall / frontozygomatic suture
- sphenoid bone](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/64/70/19/3647019_m.png)
[green line]
high transverse fracture - maxilla - through nasofrontal suture / medial orbital wall / frontozygomatic suture - sphenoid bone |
|
|
where is sagital fracture
|
in sagital plane
- through maxilla - high death rate |
|
|
compare / location of
LeFORT I, II, III fractures |
I - red
II - blue III - green |
|
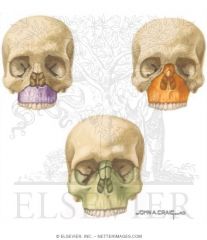
what is this showing?
|
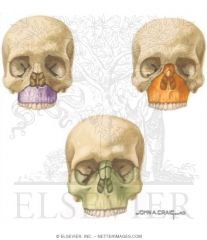
LeFORT facial fractures
I - red II - blue III - green |
|
|
what is a
Subgaleal hematoma |
bleeding under the galea aponeurotica (fiberous layer on top of skull)
|
|
|
name for
bleeding under the galea aponeurotica (fiberous layer on top of skull) |
Subgaleal hematoma
|
|
|
battle sign
- what is it - what does it indicate |
contusion behind the ear
- basilar skull Fx |
|
|
what is
ecchymosis |
a hematoma
- subcutaneous purpura (extravasion of blood) larger than 1 cm |
|
|
periorbital ecchymosis
- what is it - what could it indicate |
bruising around the eye
- Fx of the orbital roof |
|
|
what is a ring Fx
|
jump out of house - spinal column goes up into foramen magnum
|
|
|
what is usually the source of an epidural hematoma (EDH)
|
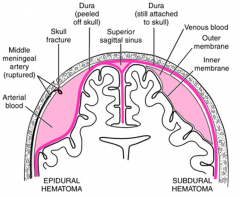
arteriole
skull fractures - meningeal artery ruptures and blood pours in |
|
|
besides above/below the dura, what is the difference(s) btw epidural and subdural hematoma
|
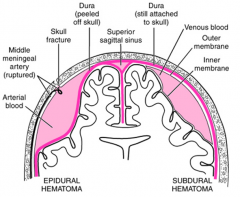
EDH
- from skull Fx that causes arteriole bleed - surface is FLAT SDH - from tears in bridging veins- slowly accumulate blood - has UNDULATING surface |
|
|
what is
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) |
hemorrhage btw arachnoid and cerebral cortex
from berry aneurysm or trauma or AVM (arteriovenous malformation) |
|
|
what is a hemorrhage btw arachnoid and cerebral cortex called
|
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH)
|
|
|
is a coup contusion
|
stationary head is hit
|
|
|
what is
contra coup contusion |
head hits stationary something (ground)
|
|
|
what type of movement causes
Intermediary coup contusions |
rotation
|
|
what type of contusion might this be
|
contra coup (head hit stationary ground)
|
|
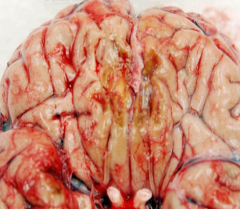
what is the orange spot?
what might this mean |
Hemosiderin = old contra coup contusion
a) Often from falling off barstool backwards b) May impair ability to smell |
|
|
Hemosiderin = old ____________ ______________
a) Often from falling off barstool backwards b) May impair ability to smell |
Hemosiderin = old contra coup contusion
a) Often from falling off barstool backwards b) May impair ability to smell |
|
|
does a concussion cause functional or structural damage to the axon
|
functional
|
|
|
when the brain is accelerated side to side this causes what type of injury to the axons
|
diffuse axonal injury (DAI)
or gliding contusions (glides under dura) |
|
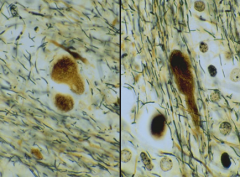
Dx (name of injury type)
- axon swelling - axonal bulbs (Cytoarchitecture and neurofilaments disturbed) - 2-3hrs post injury - beta amyloid precusror protein |
Diffuse axonal injury (DAI)
usually in white matter tracts due to high density of axons |
|
|
Dx?
- SDH (subdural hematoma) / brain swelling - retinal / optic nerve injury (RED FLAG if there - not always there) - may have gripping injury from SQUEEZED - ↑ ICP (from BBB disruption) |
shaken baby syndrome (SSS)
|
|

Dx?
|
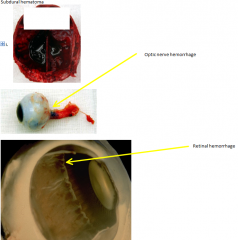
shaken baby syndrome (SSS)
- SDH (subdural hematoma) / brain swelling - retinal / optic nerve injury (RED FLAG if there - not always there) - may have gripping injury from SQUEEZED - ↑ ICP |
|
|
where / what herniates in a transtentorial herniation
why do you observe pupillary dilation on side of lesion from ↑ ICP |
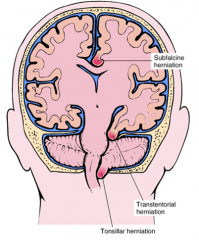
temporal compressed agains tentorum
CN III (occulomotor) compressed) |
|
|
what is respirator brain?
|
hypoxia-ischemia
24-48hrs post insult - swollen necrosis |
|
|
word for:
a. Set of characteristics/traits that distinguish 1 person from the next b. Traits seen consistently 1 day to the next i. Traits established by late adolescence/early adult |
personality
|
|
|
what is
Personality disorder |
when ones characteristic traits become MALADAPTIVE
|
|
|
what is
ego syntonic ego dystonic |
ego syntonic
- when ones maladaptive characteristic traits are NOT DISTRESSING to the individual ego dystonic - when they ARE distressing |
|
|
what are the 3 three letter words that describe the 3 clusters of personality disorders
|
MAD
BAD SAD |
|
|
what are the 2 cluster A
MAD personality disorders |
paranoid personality disorder
schizoid personality disorder |
|
|
what are the 4 cluster B
BAD personality disorders |
antisocial
borderline histionic narcissistic personality disorders |
|
|
what are the 3 cluster C
SAD personality disorders |
avoidant
dependent obsessive-compulsive personality disorders |
|
|
If family Hx alcohol/substance abuse
more likely to have what personality disorder? |
antisocial personality disorder
|
|
|
what is a typical phyiscal exam finding for pts w/personality disorders
|
smooth eye pursuit - eyes shift back and forth
|
|
|
name the personality disorder and name the cluster:
- inappropriate distrust of everyone - ALWAYS guarded - hard to find friends/ significant others |
paranoid personality disorder
MAD |
|
|
name the personality disorder and name the cluster:
- loners - cold and detached - IT ppl - very active fantasy life - may have affection for pet - if stressed - can decompensate and become psychotic |
schizoid personality disorder
MAD - cluster A |
|
|
name the personality disorder and name the cluster:
- illegal acts - social irresponsible - shows Sx <15yo - school late / always in trouble / rules not made for me - criminal in adult life - make up own rules - sopranos / godfather - substance abuse common M > F (3:1) |
antisocial personality disorder
BAD - cluster B for bad |
|
|
name the personality disorder and name the cluster:
- unstable mood - shifts minute to minute - impulsive - feel alone even if not (manipulative so not alone - aloness distressing / depressing / suicidal to get attention) F > M (2:1) - very common / well studied |
borderline personality disorder
BAD - cluster B - all bad one minute - all good the next |
|
|
name the personality disorder and name the cluster:
- focused only on self (appearance / how much attention they are getting) - entire being based on physical attractiveness F > M - seductive in look and speech |
histionic personality disorder
BAD - cluster B |
|
|
name the personality disorder and name the cluster:
- self absorbed - entranced w/own success (always need to be more successful / everyone needs to see how awesome they are) - no apathy for anyone else (cant challenge them) |
narcissistic personality disorder
BAD - cluster B |
|
|
name the personality disorder and name the cluster:
- excessive discomfort in ANY relationship -feel they will be humiliated / rejected if enter relationship - seem shy / awkward - WANTS to have relationship - just too afraid of rejection / humiliation - like women but all fantasy - not in reality |
avoidant personality disorder
SAD - cluster C |
|
|
name the personality disorder and name the cluster:
- turns everything in life over to SOMEONE ELSE - afraid of being alone - will stay in abusive relationship - depressed (esp if separated) - common in medical relationships (no doctor, you tell me what to do) |
dependent personality disorder
SAD - cluster C |
|
|
name the personality disorder and name the cluster:
- perfectionists - standards - little room for compromise - preoccupied w/rules and trivial details - compulsive / organized / structure - inflexible - cant delegate responsibilities - must do self - too focused on 1 thing - interferes w/relationships |
obsessive-compulsive personality disorder
SAD - cluster C |
|
|
what are the 3 SAD - cluster C personality disorders
and generally what are they about |
avoidant - want relationships but fear rejection / humiliation
dependent - turn everything over to someone else / abused will stay obsessive-compulsive - perfectionists / must do self / rules and details |
|
|
what are the 2 MAD - cluster A personality disorders
and generally what are they about |
paranoid - distrust everyone
schizoid - cold detached loner w/active fantasy life |
|
|
what are the 4 BAD - cluster B personality disorders
and generally what are they about |
antisocial - criminal / substance abuse / own rules / me 1st [M 3:1]
borderline - impulsive mood shift minute to minute [F 2:1] histionic - focused ONLY on looks / self appearance narcissistic - entranced w/own success |
|
|
name the personality disorder
- resists authority other people have - EX - have deadline just not going to do it - EX - needs to be done a certain way but does it own way anyway |
passive aggressive
|
|
|
name the personality disorder
- basic personality is just down |
depressive personality
|
|
|
A hydrodynamic disorder of the cerebrospinal fluid that leads to an increase in the volume occupied by this fluid in the central nervous system
|
Hydrocephalus
|
|
|
what is
Hydrocephalus |
CSF takes up more volume in CNS
|
|
|
what are the 5 steps of CSF flow?
|
lateral ventricles
→ foramen of Monro → 3rd ventricle → cerebral aqueduct → 4th ventricle |
|
|
how is hydrocephalus Dx? (radio/Sx)
|
clinically (Sx)
ventriculomegaly can be normal (radio finding) |
|
|
what is communicating hydrocephalus
|
large ventricular system
- no closed ducts - lots of CSF |
|
|
how do pts w/obstructive hydrocephalus present
|
lethargic / comatose - must be relieved (by catheter)
|
|
|
*** how does normal pressure hydrocephalus present
|
clinical triad
- gait disturbance - slow thoughts / actions / dementia - urinary incontinence from resistance to CSF flow |
|
|
these Sx might suggest what type of hydrocephalus:
headache nausea ataxia vision disturbance neck pain |
high pressure hydrocephalus
|
|
|
what is
Hydrocephalus Ex vacuo |
brain shrinks w/age - fills w/fluid
NOT hydrocephalus |
|
|
how Tx hydrocephalus
|
- lumbar puncture
- 3rd ventriculostomy (endoscopic) - remove obstruction - shunting (catheter w/valve) |
|
|
Dx?
a. Clinical Presentation (there will likely be a question about this on the test) i. Headache ii. Nausea iii. Ataxia iv. Disturbance of vision v. Neck pain vi. These are the typical things, and they’re generally not focal neurologic problems that they have – patients just feel lousy |
hydrocephalus
|
|
|
what is the usual cause of hydrocephalus (overproduction or underabsorption or blockage)
|
underabsorption or blockage
|

