![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the main amino acid neurotransmitters? (3)
|
Gamma-amino butyric acid (GABA)
Glutamine (Glu) Glycine (Gly |
|
|
What are the main amine neurotransmitters? (5)
|
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Dopamine (DA) Noradrenaline (NA) Histamine Serotonin (5=H%) |
|
|
What are the main peptide neurotransmitters? (9)
|
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
Dynorphin Enkephalins (Enk) N-Acetylaspartylglutamate Neuropeptide Y Somatostatin Substance P Thyrotropin releasing hormone Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) |
|
|
What are the two components of the central nervous system (CNS)?
|
Brain
Spinal Chord |
|
|
What are the main components of the peripheral nervous system (PNS)?
|
Somatic division
- 12 pairs of cranial nerves - 31 pairs of spinal nerves Autonomic nervous system (ANS) Enteric Nervous System |
|
|
How many pairs of cranial nerves are there in the somatic division of the PNS?
|
12
|
|
|
How many pairs of spinal nerves are there in the somatic division of the PNS?
|
31
|
|
|
In the CNS myelinated tissue is white/grey matter.
|
White matter
|
|
|
In the CNS non-myelinated tissue is white/grey matter.
|
Grey matter
|
|
|
In the CNS, myelin is formed by what kind of cell?
|
Oligodendrocytes
|
|
|
What is an oligodendrocyte?
|
A type of cell that forms myelin in the CNS
|
|
|
In the PNS, myelin is formed by what kind of cell?
|
Schwann cells
|
|
|
Sensory nerves terminate in the CNS/PNS
|
CNS
|
|
|
Synapses appear in the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) T/F
|
F
|
|
|
How are the 31 pairs of spinal nerves divided?
|
8 pairs Cervical
12 pairs Thoracic 5 pairs Lumbar 5 pairs Sacral 1 paired Coccygeal |
|
|
*A*fferent nerves bring information into a centre - so the *a*ffect it in some way
|
*E*fferent nerves take information away from a centre - so they have an *e*ffect
|
|
|
Each spinal nerve passes through its ______________ foramen
|
intervertebral
|
|
|
The spinal cord is longer than the vertebral column T/F
|
F
|
|
|
An area of the skin supplied by nerves from a single spinal root
|
Dermatome
|
|
|
Define 'dermatome'
|
An area of the skin supplied by nerves from a single spinal root
|
|
|
Which disease causes a 'band like rash' revealing a dermatome?
|
Shingles, caused by herpes zoster virus
|
|
|
Associated with thoracic and
lumbar segments Soma of postganglionic neurons mostly in sympathetic chain of ganglia Some postganglionic neurons in collateral ganglia |
Sympathetic division of the ANS
|
|
|
They sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions combine to form the _________ nervous system
|
Autonomic
|
|
|
Clusters of neuronal cell bodies and their dendrites and are essentially a junction between autonomic nerves originating from the central nervous system and autonomic nerves innervating their target organs in the periphery
|
Autonomic Ganglia
|
|
|
What are 'Autonomic Ganglia'?
|
clusters of neuronal cell bodies and their dendrites and are essentially a junction between autonomic nerves originating from the central nervous system and autonomic nerves innervating their target organs in the periphery
|
|
|
Axons from parasympathetic
neurons in the brain pass through cranial nerves III, VII, IX and X. Axons from parasympathetic neurons in the sacral region of the spinal cord pass through S2 – S4 All terminate on neurons in terminal ganglia |
Parasympathetic division
|
|
|
On which ganglia do neurones of the parasympathetic division of the ANS terminate?
|
The terminal ganglia
|
|
|
Intrinsic to the gut
Contains as many neurons as the spinal cord Co-ordinates peristalsis and digestion Under control of the Sympathetic and Parasympathetic divisions of ANS |
Enteric nervous system
|
|
|
The enteric nervous system is a subdevision of which other NS?
|
The peripheral nervous system
|
|
|
This NS coordinates peristalsis and digestion
|
The enteric nervous system
|
|
Enzymatic inhibitors
|
Alpha glucosidase inhibitors
Acarbose |
|
|
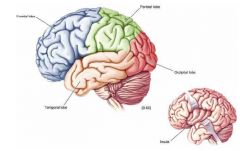
Which parts of the brain are important in learning and memory?
|
Amygdala and Hippocampus
|
|
|
The amygdala and hippocampus are important in...
|
Learning and memory
|
|
|
Define 'decussate'
|
Cross or intersect each other to form an X
|
|
|
Cross or intersect each other to form an X defines..
|
Decussate
|
|
|
.
|
|
|
What is a dorsal root ganglion?
|
A nodule on a dorsal root that contains cell bodies of neurons in afferent spinal nerves.
|
|
|
A nodule on a dorsal root that contains cell bodies of neurons in afferent spinal nerves.
|
Dorsal root ganglion
|
|
|
Clusters of neuronal cell bodies and their dendrites and are essentially a junction between autonomic nerves originating from the central nervous system and autonomic nerves innervating their target organs in the periphery.
|
Autonomic ganglion
|
|
|
What is an autonomic ganglion?
|
Clusters of neuronal cell bodies and their dendrites and are essentially a junction between autonomic nerves originating from the central nervous system and autonomic nerves innervating their target organs in the periphery.
|
|
|
What is a dorsal root?
|
The afferent sensory root of a spinal nerve.
|
|
|
The afferent sensory root of a spinal nerve.
|
Dorsal root
|
|
|
At the distal end of the dorsal root is the...
|
Dorsal root ganglion, which contains the neuron cell bodies of the nerve fibres conveyed by the root
|
|
|
If the dorsal root of a spinal nerve were severed it would lead to numbness in certain areas of the body.
|
.
2311041210 |
|
|
What sort of axons run through the dorsal root?
|
Sensory spinal nerves
|
|
|
What sort of axons run through ventral roots?
|
Motor nerves
|
|
|
What is a ventral root?
|
The efferent motor root of a spinal nerve.
|
|
|
The efferent motor root of a spinal nerve.
|
Ventral root
|
|
|
How is the sympathetic chain connected to the spinal cord?
|
It interacts with the spinal nerves or their ventral rami by way of rami communicantes.
|
|
|
What is the rami communicantes?
|
The term used for a nerve which connects two other nerves.
|
|
|
The term used for a nerve which connects two other nerves.
|
Rami communicantes
|
|
|
Which sort of muscle do somatic motor nerves supply?
|
Voluntary skeletal muscle
|
|
|
Voluntary skeletal muscle is supplied by which type of nerve?
|
Somatic motor nerves
|
|
|
Autonomic nerves supply which sort of muscle?
|
Smooth muscle
|
|
|
Which dermatome coincides with the umbilicus, and what is its importance?
|
T10 (important for early appendicitis pain)
|
|
|
Dermatome T10 coincides with the...
|
umbilicus
|
|
|
What is a preganglionic parasympathetic motor neurone?
|
One that synapses with the postganglionic parasympathetic neurons that synapses CLOSE TO TARGET ORGANS
|
|
|
What is a preganglionic sympathetic neurone?
|
One which usually synapses with their postganglionic sympathetic neurones close to the NEURAXIS
|

