![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
treponema
|
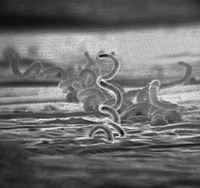
gram-, spirochetes: T. pallidum causes syphillis
|
|
|
borrelia
|

gram-, spirochetes:
B. burgdorferi causes boreliosis (Lyme's Disease) - expanding red rash (erythema chronicum migrans) B. hermsii causes endemic relapsing fever - transmitted by ticks B. recurrentis causes epidemic relapsing fever -transmitted by lice |
|
|
leptospira
|
gram-, spirochetes: causes leptospirosis
|
|
|
campylobacter
|
gram-, aerobic, motile helical/vibroid: causes campylobacteriosis, a common food borne illness
|
|
|
helicobacter
|
gram-, aerobic, motile helical/vibroid; effects some 50% of the world's population with varied, sometimes chronic gastroenteric symptoms.
|
|
|
spirillum
|
gram-, aerobic, motile helical/vibroid: associated with rat bite fever
|
|
|
alcaligenes
|
gram-, aerobic, rod
|
|
|
bordetella
|
1) small gram- aerobic rod
2) B. Pertussis causes pertussis (whooping cough). Pertussis toxin paralyzes cilia. 3) B. parapertussis has a silent copy of the pertussis toxin gene and is a sub clinical disease. 4)B. bronchiseptica: infrequent chronic Resp. T infection in humans, kennel cough, snuffles in rabits, and artrophic rhinitis in swines. |
|
|
brucella
|
gram-, aerobic, rods and cocci: causes brucellosis (Malta Fever)
|
|
|
francisella
|
gram-, aerobic, bipolar staining rod:
F. tularensis causes tularemia (rabbit fever) -transmission is via tick bites -many disease presentations including ulcers, swollen glands, and eye infections. - treat with Tetracycline or streptomycin. |
|
|
legionella
|
gram-, aerobic, rods and cocci: causes legionellosis (Legionnaires' disease)
|
|
|
moraxella
|
gram-, aerobic, rods and cocci
|
|
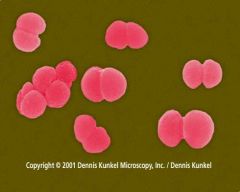
neisseria
|
gram-, aerobic, diplococci: N. meningitidis is one of the most common causes of bacterial meningitis
|
|
|
pseudomonas
|
gram-, aerobic, rods and cocci: Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a nosocmial, opportunistic infection
|
|
|
bartonella (formerly rochalimaea)
|
gram-, aerobic, rods and cocci:
B. quintana causes trench fever - vectored by lice Carrion's disease,cat scratch disease and others |
|
|
bacteroides
|
gram-, aerobic, rods and cocci: Bacteroides fragilis is the most common and most virulent (may also be anaerobic, straight, curved, and helical rods).
|
|
|
escherichia (and related coliform bacteria)
|
gram-, facultatively anaerobic rods: Most common cause of UTIs, can cause diarrhea and meningitis in infants. Enterotoxigenic E. Coli (ETEC) = traveler's diarrhea. E. coli (O157:H7) can cause hemorrhagic colitis and hemolytic-uremic syndrome.
|
|
|
klebsiella
|
gram-, facultatively anaerobic bacilli with mucoid apperance
K. pneumoniae is typically nosocomial - sudden onset, with reddish brown sputum - some strains release extended beta lactamases (ESBL) |
|
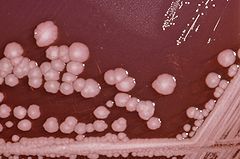
proteus
|
1) gram-, facultatively anaerobic rods
2) P. mirabilis can cause UTIs in women (#2 cause behind e. coli) |
|
|
Serratia
|
Gram negative bacillus.
- S. marcescens can cause nosocomial pneumonia. - serratia infections also include conjunctivitis, pneumonia, and resp. disease. |
|
|
providencia
|
gram-, facultatively anaerobic rods; contributes to urinary tract infections
|
|
|
salmonella
|
gram-, facultatively anaerobic rods: S. typhi (D and Vi antigens) causes typhoid fever
- has characteristic "rose spots" on abdomen and S. enteritidis causes food poisoning and paratyphoid fever. |
|
|
shigella
|
gram-, facultatively anaerobic rods: foodborne illness that causes gastroenteritis and dysentery
|
|
|
yersinia
|
gram-, facultatively anaerobic rods: Y. pestis causes the plague; other infections
|
|
|
vibrio
|
gram-, motile curved rod :
V. Cholerae causes Cholera - 2 virulance factors: cholera toxin and toxin coregulated pilus - has a polar flagellum - rice water stool is chatacteristic Vibrosis causes gastroenteritis from undercooked seafood from V. parahaemolyticus and V. vulnificus |
|
|
haemophilus
|
gram-, facultatively anaerobic rods: Several pathogenic species including H. influenzae and H. ducreyi which causes the STI Chancroid
|
|
|
pasteurella
|
gram-, facultatively anaerobic rods: pathogenesis is from pet bites
|
|
|
fusobacterium
|
gram-, anaerobic, straight, curved, and helical rods: causes the very rare Lemierre's syndrome among other diseases
|
|
|
prevotella
|
gram-, anaerobic, straight, curved, and helical rods: Involved in periodontal disease
|
|
|
rickettsia
|
gram-, obligate intracellular parasite (the reckettsiae and chlamydiae):
R. rickettsii causes rocky mtn spotted fever -rash on palms and soles then spreads...pink macules become maculopapular rash -transmitted by ticks R. prowazeckii causes epidemic typhus - transmitted by lice R. typhi causes endemic typhus - transmitted by fleas |
|
|
coxiella
|
gram-, obligate intracellular parasite (the reckettsiae and chlamydiae):
1) C. burnetii is the causative agent of Q Fever |
|
|
chlamydia
|
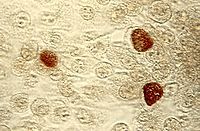
gram-, obligate intracellular parasite (the reckettsiae and chlamydiae)
|
|
|
capnocytophaga
|
gram-, nonphotosynthetic, nonfruiting gliding bacteria
|
|
|
enterococcus
|
gram+, cocci, facultatively anaerobic : a normal inhabitant of the intestinal tract, can cause UTIs and worse. May be highly resistant to antibiotics
|
|
|
peptostreptococcus
|
gram+, cocci, anaerobic: found in normal flora, but may cause disease
|
|
|
staphylococcus
|
gram+, cocci, facultatively anaerobic: Coagulase-positive includes S. aureus (some of which is MRSA) Coagulase-negative includes S. epidermidis and S. saprphyticus. Common cause of food poisoning, nosocomial infections and others.
|
|
|
streptococcus
|
gram+, cocci, facultatively anaerobic: S. pneumoniae is a leading cause of bacterial pneumonia; S. pyogenes, also known as Group A Streptococcus (GAS), causes streptococcal pharyngitis ("strep throat"), acute rheumatic fever, scarlet fever, acute glomerulonephritis and necrotizing fasciitis. S. agalactiae, or GBS, causes pneumonia and meningitis in neonates and the elderly, with occasional systemic bacteremia.
|
|
|
bacillus
|
gram+, endospore forming rod, aerobic:
B. anthracis causes anthrax (woolsorter's disease) - contains a Poly-D glutamic acid capsule which is antiphagocytic -The toxin is a mixture of three proteins: -Protective antigen (PA) -Edema factor (EF) -lethal factor (LF) B. cereus causes a foodborne illness - 2 distinct enterotoxins: diarrhea and abdominal pain...the other is emetic after eating cooked rice. |
|
|
clostridium
|
gram+, anaerobic endospore forming rods: C. botulinum (along with C. barati, C. butyricum have 7 serotypes)
C. difficile, C. perfringens causes gas gangrene and food poisoning with its enterotoxin; C. tetani |
|
|
erysipelothrix
|
1) gram+
2) facultatively anaerobic rod regular, nonsporing; causes erysipeloid |
|
|
listeria
|
1) gram+ coccobacilli, psychrophilic
2) facultatively anaerobic intracellular pathogen 3) L. monocytogenes causes listeriosis, a potentially fatal disease - source of it is contaminated soft cheeses, dairy products, and lunch meats. |
|
|
actinomyces
|
1) gram+
2) facultatively anaerobic irregular, nonsporing, |
|
|
corynebacterium
|
1) gram+,
2) facultatively anaerobic rod (bacillus) 3) C. diphtheriae is the cause of diphtheria C. minutissimum causes erythrasma; C. acnes is commonly found in acne lesions |
|
|
mobiluncus
|
1) gram+
2) anaerobic 3) implicated in bacterial vaginosis irregular, nonsporing, |
|
|
mycobacterium
|
1) "gram+"
2) aerobic 3) M. tuberculosis causes tuberculosis, 4) M. leprae causes(Hansen's Disease) leprosy 5) acid fast stain is indicated in lab. 6) contains mycolic acid in cell wall nasty stuff that can colonize their hosts without the hosts showing any adverse signs. |
|
|
nocardia
|
1) gram+,
2) actinomycetes, 3) aerobic, 4) rod shaped: 5) catalase-positive cause of some opportunistic infections. |
|
|
streptomyces
|
1) gram+,
2) aerobic, notable as the source of various antibiotics, e.g., the tetracyclines actinomycetes: |
|
|
rhodococcus
|
gram+, aerobic, actinomycetes
|
|
|
mycoplasma
|
(gram +) cell wall-less eubacteria, mycoplasmas: a primary cause of atypical pneumonia
|
|
|
ureaplasma
|
(gram +) cell wall-less eubacteria, mycoplasmas: associated with nonspecific urethritis in males and genital tract infections in females
|

