![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is Pascals law?
|
A confined body of fluid exerts equal pressure at every point and in every direction in the fluid and acts at right angles to the enclosing walls of the container.
|
|
|
What are the primary and secondary purposes of an accumulator?
|
1. Dampen pressure surges
2. Store an amount of fluid under pressure to assist engine driven pump in times of high workload/fluid demand. |
|
|
What is the purpose of a check valve?
|
Ensures no fluid flows in the wrong direction.
|
|
|
How does a constant displacement pump work?
What are its limitations? |
Pumps fluid and is directly proportional to engine speed. Pressure relief valve regulates pressure.
Limited to about 1500PSI (not enough for large planes) |
|
|
How does a variable displacement pump work?
|
Pumps fluid and regulates pressure.
|
|
|
What is pre-charge pressure?
|
Measured when system is depressurised. Engineers pressurise accumulator to about 40% of normal hydraulic operating pressure.
|
|
|
Which hydraulic system component sense over-pressures and returns excess fluid to the reservoir?
|
Relief valve
|
|
|
Which hydraulic system component is located downstream of the pump and signals pump to kick-in/kick-out?
|
Pressure switch
|
|
|
What causes sludge to build up in hydraulic fluid?
|
Operating outside prescribed temperature limits.
|
|
|
Name the two different types of fluid cooling methods.
|
Tubing heat exchanger
Radiator type heat exchanger |
|
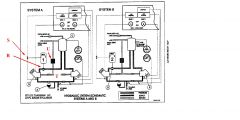
What is the part named "U"?
|
A combination filter and heat exchanger.
|
|
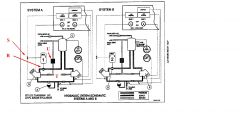
What is the part named "R"?
|
Manually operated isolation valve. Automatic shut off occurs when fire handle is operated by the crew.
|
|
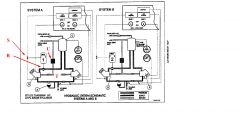
What is the part named "S"?
|
A breaker switch which will automatically extinguish any low pressure light in the cockpit when the isolation valve has been activated.
|
|
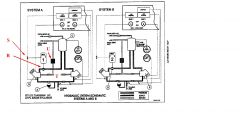
What is the part named "A"?
|
Accumulator
|
|
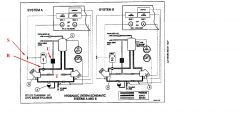
What is the part named "B"?
|
Engine driven pump
|
|
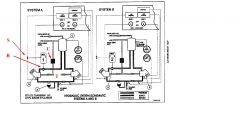
What is the part named "E"?
|
Electrical pump
|
|
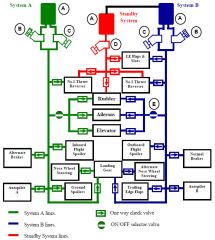
What is the part named "A"?
|
Reservoir
|
|
What is the part named "B"?
|
Engine driven pump
|
|
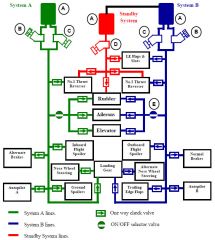
What is the part named "C"?
|
Electrical driven pumps
|
|
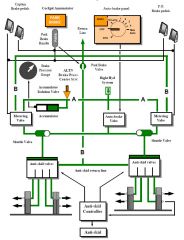
What is the part named "A"?
|
A supply line
|
|
|
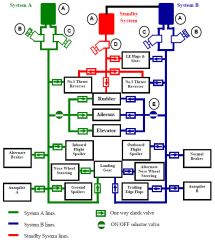
What happens to the braking hydraulic system if the right system depressurises due to a fault?
|
Shuttle valves automatically close off the normal supply and allow the centre system to power the brakes.
|
|
|
What four protections are provided by the anti-skid controller?
|
1. Anti skid
2. Locked wheel 3. Hydroplane 4. Touchdown |
|
|
How does the anti-skid controller work?
|
Regulates hydraulic pressure through each valve, based on eight separate wheel speed transducer inputs.
|
|
|
How can the park brake be set when there is no active hydraulic pressure to both the right and centre systems?
|
A brake accumulator in the normal brake system can apply pressure.
|
|
|
What happens to the brake accumulator in the normal system when the right hydraulic system fails?
|
Brake accumulator pressure is maintained by an isolation valve, preserving accumulator pressure for use should the centre system fail.
|
|
|
What services are available by the brake accumulator only (assuming right and centre system failures)?
|
Several applications of the brakes
Anti-skid protection |
|
|
When will the "Brake Source" light illuminate?
|
When both right system and centre system hydraulic pressure is low. Accumulator is only source of braking power (the reserve system).
|
|
|
What system powers the nose wheel steering?
What happens if this system loses pressure? |
Centre system powers nose wheel steering.
Reserve system provides nose wheel steering in case of failure of centre system. |

