![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
cardiac output is measured in
|
mls per minute
|
|
|
filling of the heart by blood returning from the veins determines
|
preload
|
|
|
total tension =
|
active tension +resting tension
|
|
|
contractility is defined as the change in
|
peak isometric force at a given intial fiber length (end diastolic volume)
|
|
|
mean arterial pressure =
|
cardiac output X resistance
|
|
|
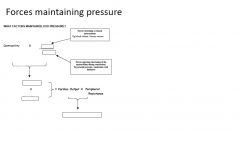
pressure ( mean arterial pressure ) is maintained by modulating
|
cardiac output and arteriolar resistance
|
|
|
MAP (mean arterial pressure)=
|
diastolic pressure +pulse pressure/3
|
|
|
systolic pressure
|
peak pressure as blood is ejected
|
|
|
diastolic pressure
|
pressure when aortic valve is closed
|
|
|

|
|
|
venous return determines.... volume
|
end diastolic
|
|
|
increased stroke volume can be achieved by
|
increasing muscle length ( venous return)
increasing contractility (force generated for any given length) by increasing intracellular Ca during contraction |
|
|
length tension relationship of heart muscle allows for equilization of output from left and right sides of the heart. eg...
|
increased output from Right side of heart leads to increased filling of Left ventricle (increased EDV) and therefore increased stretch of myocardial fibers and increased force development in Left ventricle and increase Left ventricular output
|
|
|
increased arterial blood pressure leads to .... afterload and a ... in volume of blood ejected from the heart with each beat (ejection fraction). the resultant .... in end systolic volume and end diastolic volume.... cardiac muscle stretch, thereby.... force of contraction and... ....
|
higher
reduction increase increases increasing stroke volume |
|
|
venous return determines.... volume
|
end diastolic
|
|
|
increased stroke volume can be achieved by
|
increasing muscle length ( venous return)
increasing contractility (force generated for any given length) by increasing intracellular Ca during contraction |
|
|
length tension relationship of heart muscle allows for equilization of output from left and right sides of the heart. eg...
|
increased output from Right side of heart leads to increased filling of Left ventricle (increased EDV) and therefore increased stretch of myocardial fibers and increased force development in Left ventricle and increase Left ventricular output
|
|
|
increased arterial blood pressure leads to .... afterload and a ... in volume of blood ejected from the heart with each beat (ejection fraction). the resultant .... in end systolic volume and end diastolic volume.... cardiac muscle stretch, thereby.... force of contraction and... ....
|
higher
reduction increase increases increasing stroke volume |
|
|

|
|
|
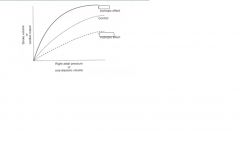
positive inotrope
|
any agent that increases peak isometric tension at a fixed length
|
|
|
inotropes act by modulating
|
Ca levels in cardiac muscle cells
|
|
|
binding of noradrenaline to beta adrenergic receptors on cardiac myocytes leads to
|
-activation of adenyl cyclase
-increased intracellular cAMP - phosphorylation of VOCC -increased inward movement of Ca -increased Ca Release from sarcoplasmic reticulum and over time more stored Ca id SR -increased actino-myosin cross briding -increased force of contraction |

