![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Position of the heart
Lies in the |
mediastinum ( the partition between the right and left pleural cavities) enclosed within its pericardial sac
Usually situated between the third and sixth ribs |
|
|
Dorsal boundary of the heart
|
Lies on a horizontal plane through the center of the first rib
|
|
|
Caudal boundary of the heart
|
Is the dome of the diaphragm
|
|
|
Ventral boundary of the heart
|
Is the sternum
|
|
|
The long axis of the heart is
Essentially vertical in... Almost vertical in... Progressively more oblique in the... |
horses
ruminants pig, dog, cat |
|
|
Shape of the heart
|
Cone shaped
Slightly flattened on the left and right sides, to conform to other similar compression of the thorax |
|
|
Base of the heart
|
Most dorsal part of the heart, low dome formed by the left and right atria
|
|
|
Great veins
Systemic and pulmonary, |
enter the base of the heart
|
|
|
Great arteries
Aortic and pulmonary, |
emerge from the base of the heart
|
|
|
The heart is held in position by
|
the great vessels but otherwise lies entirely free within the pericardium
|
|
|
Apex of the heart
|
Tapered portion of the cone, formed by the left ventricle, lies close to the sternum
|
|
|
Long axis of the heart
|
Extends from middle of the base to the apex
|
|
|
Cranial aspect of the heart
|
Extensively relates to thymus in young animals
|
|
|
Right and left lateral surfaces
of the heart |
Face the corresponding lungs
|
|
|
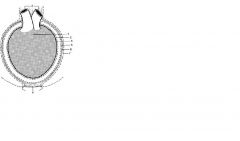
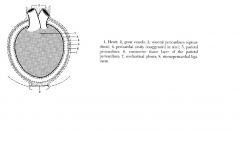
The pericardium
|
A serous sac deeply invaginated by the heart
Closed and is lined by simple squamous epithelium |
|
|
Function of the pericardium
|
Protect the heart
Maintain the heart in its position Minimize friction Possibly prevent heart from becoming overly distended |
|
|
Pericardial cavity
|
Occupied by a thin film of serous fluid, a lubricant
Enables visceral and parietal layers of pericardial member to slide over each other during the cardiac cycle |
|
|
Visceral pericardium
|
Inner wall of the pericardial sac, coats the outer surface of the heart
|
|
|
Parietal pericardium
|
At the neck of the sac, the visceral pericardium continues onto the outer wall of the sac.
|
|
|
the fiberous pericardium
|
parietal pericardium is reinforced by a strong later of fibroelastic tissue
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dorsally the fiberous layer of parietal pericardium continues over the
|
great vessels
|
|
|
Ventrally the fiberous pericardium continues on and attaches to the sternum in
Ruminants- Horse- In carnivores and the pig it attaches to the diaphragm as |
as paired sternopericardiac ligaments
as a single midline sternopericadiac ligament the phrenico-pericardiac ligament |
|
|
Base of the heart is formed by the thin walled
|
atria, separated from the ventricles by the encircling coronary groove
|
|
|
Each atrium has a blind diverticulum (or free appendage) called the
|
auricle
|
|
|
The... is the wall dividing the left and right internal chambers of the ventricle
It is marked externally by the ... on the left side of the heart and the ....on the right side of the heart |
INTERVENTRICLAR SEPTUM
left interventricular groove right interventricular groove |
|
|
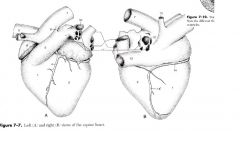
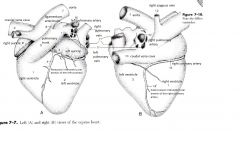
The left surface of the heart ( or auricle surface)
Formed mainly by |
left atrium and left ventricle
Right ventricle and right auricle extend round the cranial border contributing to the left side |
|
|
The right surface ( or atrial surface)
Is formed mainly by the |
right atrium and right ventricle
Left ventricle extends around the caudal border contributing to the right side |
|
|
|
|
|
The right atrium
|
Chamber into which principal systemic veins discharge
|
|
|
The right atrium
Four main openings |
Cranial vena cava
Caudal vena cava Coronary sinus Right atrioventricular orifice guarded by the right A-V valve |
|
|
pectinate muscles
|
Wall of auricle is interlaced with muscular ridges
|
|
|
Vestiges of fetal circulation
|
Fossa ovalis
Intervenous tubercle |
|
|
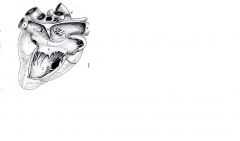
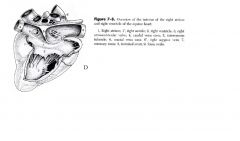
Right ventricle
|
Receives blood from the right atrium
Pumps blood to the pulmonary trunk |
|
|
|
|
|
...separates right and left ventricles
Has two components: |
Thick muscular interventriuclar septum
larger muscular part is thick myocardium formed by the combining walls of the two ventricles. the collagenous but thin membranous part is a small inconspicuous area in the extreme dorsal part of the septum |
|
|
right atrioventricular or TRICUSPID valve
|
guards opening of right ventricle
Valve cusps composed of layer of collagen fibers sandwiched between two layers of endothelium Three thin flap like cusps Free edge of cusp= retained chordate tendineae Chordate tendineae arise from papillary muscles |
|
|
Left atrium
|
Receives atrial blood from the lungs via the pulmonary veins.
Small coronary veins also empty into left atrium Left auricle has pectinate muscles as in the right atrium |
|
|
Left ventricle
|
Connected to left atrium via the left A-V opening guarded by the left A-V valve or MITRAL valve.
This has two cusps and is aka the bicuspid valve. Wall of left ventricle 2-3 times as thick as right |
|
|
aorta
3 major segments |
Ascending aorta
Aortic arch Descending aorta |
|
|
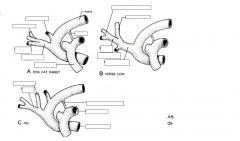
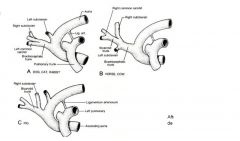
In thorax two major vessels arise from aortic arch
|
Brachiosphalic trunk and left subclavian artery
Both vessels give rise to branches that supply the head, beck, thorax and thoracic limbs |
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
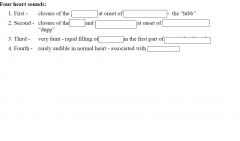
|

|

