![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
114 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
how many millimeters is each small box on the ECG?
|
1 mm
|
|
|
how many seconds is each little box on the ECG?
|
.04 s
|
|
|
each big box is how many seconds?
|
.2 s
|
|
|
how many big boxes is 1 second?
|
5
|
|
|
what does the P-wave represent?
|
atrial depolarization
|
|
|
what is the normal amplitude for the P-wave?
|
less than or equal to 2.5 mm (or boxes)
|
|
|
what is the normal duration of the p-wave?
|
.12 seconds (or 3 boxes wide)
|
|
|
in which lead is the p-wave usually biphasic?
|
V1
|
|
|
which leads will the p-wave be upright or positive?
|
I, II, aVL, aVF, V4-6
|
|
|
describe the 3 phases of the p-wave?
|
phase 1: is right atrial depolarization
phase 2: right and left atrial depolarization phase 3: left atrial depolarization |
|
|
what does the PR-interval describe?
|
the conduction time from the SA node to the ventricles
|
|
|
how long does a normal PR-interval last?
|
.12 - .21 seconds (3-5 boxes wide)
|
|
|
if PR-interval is longer than .21 seconds what is the cause?
|
1st degree AV block
|
|
|
if a PR-interval is less than .12 seconds what is the cause?
|
accessory pathway which bypasses the AV node, such as that found in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
|
|
|
what is the the PR-segment?
|
the distance from the end of the P-wave to the beginning of the Q-wave
|
|
|
what does the QRS complex represent?
|
ventricular contraction
|
|
|
what is the duration of a normal QRS complex?
|
.08 - .10 seconds (2-2.5 boxes wide)
|
|
|
what is the length of an abnormal Q-wave?
|
greater than or equal to .04 sec (1 box wide)
|
|
|
leads V1 and V2 represent signals from which ventricle?
|
right
|
|
|
leads V5 and V6 represent signals from which ventricle?
|
left
|
|
|
what is the J-point?
|
the point at which the S and T segments meet
|
|
|
what amplitude does the J-point normally lie?
|
0, a.k.a. the isoelectric line
|
|

what does the st-segment indicate?
|
early repolarization pericarditis
|
|

what does the st-segment indicate?
|
infarction ventricular aneurysm
|
|
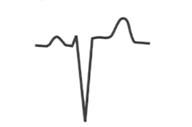
what does the st-segment indicate?
|
injury pattern
|
|

what does the st-segment indicate?
|
strain pattern
|
|

what does the st-segment indicate?
|
strain pattern
|
|
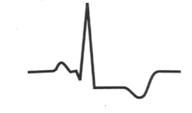
what does the st-segment indicate?
|
subendocardial ischemia
|
|
|
what does the T-wave represent?
|
ventricular repolarization
|
|
|
the T-wave should be upright or positive in which leads?
|
I, II, V3-6
|
|
|
In limb leads the T-wave should be less than or equal to how many mm?
|
5
|
|
|
in precordial leads the T-wave should be less than or equal to how many mm?
|
10
|
|
|
would you rather see a symmetrical or asymmetric T-wave?
|
asymmetric with 2/3 of the width during the rising phase
|
|
|
what does the QT-interval describe?
|
the entire depolarization and repolarization of the ventricles
|
|
|
how do you find the corrected QT-interval (QTc) by taking into account the HR?
|
QTc = QT + 1.75(ventricular rate-60)
|
|
|
what is the range for a normal QTc interval?
|
.42 + or - .02 seconds
|
|
|
where is the U-wave found?
|
in leads V3 and V4 between the T-wave and the P-wave
|
|
|
a abnormally large U-wave represents what?
|
hypokalemia
|
|
|
how do you determine HR by looking at a ECG?
|
divide 300 by the number of big boxes between two similar points such as the peak of the QRS complex
|
|
|
the mean P-wave vector (the combined input of both atria depolarizing) will be in what direction?
|
down and to the left
|
|
|
where is the P-wave usually seen best?
|
lead II
|
|
|
leads V3 and V4 are good for measuring what?
|
the depolarization of the interventricular septum
|
|
|
the negative or positive sign in front of the degree for the hearts depolarization vector is determined in relation to which lead?
|
lead I with the negative pole being the top of the heart and the positive pole being the bottom of the heart
|
|
|
what ECG finding indicates right atrial enlargement?
|
P-wave greater than 2.5 mm, look in limb leads first
|
|
|
what ECG finding indicates left atrial enlargement?
|
P-wave with negative deflection in V1 and a amplitude greater than or equal to 1 mm
|
|
|
how do you know when biatrial enlargement has occurred?
|
the signs of left and right atrial enlargement will be present
Right = P-wave greater than 2.5 mm, look in limb leads first Left = P-wave with negative deflection in V1 and a amplitude greater than or equal to 1 mm |
|
|
what ECG finding is indicative of right ventricular hypertrophy?
|
R-wave is greater than or equal to S-wave in V1
|
|
|
what ECG finding is indicative of left ventricular hypertrophy?
|
S-wave in V1 plus the R-wave in V5 or V6 is greater than or equal to 35mm
|
|

what does this ECG show?
|

left atrial enlargement
|
|
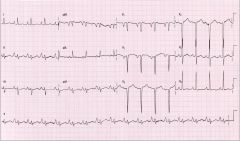
what does this ECG show?
|

right atrial enlargement
|
|

what does this ECG show?
|

right ventricular hypertrophy
|
|

what does this ECG show?
|
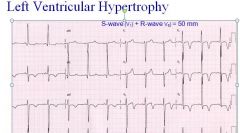
left ventricular hypertrophy - defined as V1 s-wave + V6 R-wave is > 35mm, which in this case is true
|
|
|
a qrs complex greater than .12 seconds usually means?
|
RBBB or LBBB
|
|
|
rSR' in V1 with a wide S-wave in I and V6 indicates?
|
RBBB
|
|

what does the ECG show?
|
RBBB,
notice - the rSR' in V1 - the wide S-wave in V6 - the wide S-wave in I |
|

the patterns shown below are indicative of what?
|
LBBB
|
|
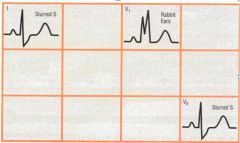
the patterns shown are indicative of what?
|
RBBB
|
|
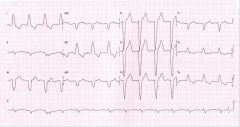
what is shown on this ECG strip?
|
LBBB
Notice - wide S-wave in V1 - QRS > or equal to .12 seconds - large R-wave in I and V6 is not obvious but does not exclude diagnosis of LBBB - There is not rSR' in V1 so this is not RBBB |
|
|
left axis deviation > or equal to -40 degrees, small q-waves in lead I, and rS complex in lead III on and ECG indicate what?
|
Left Anterior Hemiblock
|
|
|
anytime you see a left axis deviation greater than or equal to -40 degrees you know it must be?
|
Left anterior hemiblock
|
|

what does this ECG strip indicate?
|
Left anterior hemiblock
Notice - positive QRS in lead I and negative QRS in lead aVF indicates left axis deviation - aVR closest to equiphasic |
|
|
if QRS axis is > or equal to 120 degrees and/or there are small Q-waves in lead III on ECG, what is indicated?
|
Left posterior hemiblock
|
|
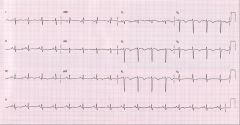
what does this ECG strip indicate?
|
left posterior hemiblock
- notice lower right axis deviation with the most equiphasic lead being lead aVR indicating a greater than 120 degree deviation - also there is a small Q-wave in lead III |
|
|
a prolonged PR-interval is indicative of?
|
1st degree AV block
|
|
|
what are the abnormal rhythms as seen in 2nd degree heart block called?
|
Mobitz 1 (Wenckebach) and Mobitz 2
|
|
|
what causes the missed beats in Mobitz 1?
|
progressive AV-block leads to longer and longer PR-interval which eventually the block is so long that the ventricle doesn't contract because the P-wave happens during the T-wave (refractory period)
|
|
|
describe the PR-interval in Mobitz 2?
|
normal and nonvariable
|
|
|
what causes Mobitz 2?
|
intermittent complete heart block
|
|
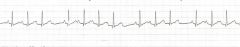
what is shown?
|
2md degree heart block - Mobitz 1
|
|

what is shown?
|
2md degree heart block: Mobitz 2
|
|
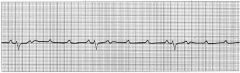
what is shown?
|
2nd degree heart block: Mobitz 2
|
|

what is shown?
|
3rd degree heart block: complete heart block
|
|
|
what will be seen with complete heart block (3rd degree heart block)?
|
atria contracting at a regular rate/rhythm and ventricles contracting at a regular rate/rhythm that is different than the atrial rhythm and usually slower = result of no AV conduction
|
|
|
during 3rd degree heart block if the QRS appears normal looking where is the pacemaker for the ventricles likely found?
|
in the Perkinje fibers close to the AV node
|
|
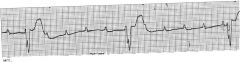
what is shown?
|
3rd degree heart block: complete heart block with pacemaker in ventricular tissue rather than the normal conducting system (ex perkinje fibers) - evidenced by abnormal QRS complex
|
|
|
what are the 3 premature systolic complexes?
|
1. premature atrial complexes
2. premature junctional complexes 3. premature ventricular complexes |
|
|
what causes premature atrial contractions?
|
pacemaker tissue in the atria acting independently of AV node
|
|
|
describe the rhythm of APC's (atrial premature contractions)
|
irregular
|
|
|
describe the PR-interval in APC's
|
variable
|
|

what is shown?
|
premature atrial contraction
notice - variable P-P interval - irregular rhythm |
|

what is shown?
|
premature atrial contraction
|
|
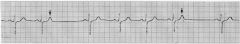
what is shown?
|
premature atrial contraction
notice - the P-wave is so premature it happens during the refractory period thus no ventricular contraction happens and there is a pause in cardiac activity |
|

what is shown?
|
atrial bigeminy
|
|
|
what is the cause of ectopic atrial tachycardia and how does it present?
|
caused by intermittent ectopic pacemaker activity resulting in fast increases in atrial rhythm accompanied by slower rate increase in ventricular rhythm
|
|
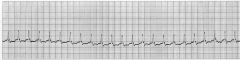
what is show?
|
ectopic atrial tachycardia
notice - ventricular tachycardia is at maximum rate |
|
|
if you see a HR lower than 100 with an irregular irregular rhythm and at least three different looking P-waves, what might be wrong?
|
wondering atrial pacemaker (WAP)
|
|

what is shown?
|
wondering atrial pacemaker
notice - BPM = less than 100 - irregular irregular rhythm - 3 different looking P-waves |
|
|
ECG showing greater than 100 BPM, irregular irregular rhythm, and at least three different P-waves is likely to be what?
|
multifocal atrial tachycardia
|
|

what is shown?
|
multifocal tachycardia
notice - >100 BPM - irregular irregular rhythm - at least 3 different looking P-waves |
|

what is shown?
|
multifocal tachycardia
notice - >100 BPM - irregular irregular rhythm - at least 3 different looking P-waves |
|

what is shown?
|
atrial flutter = 2:1 block, notice that one of the P-waves falls on top of the T-wave so it is not distinguishable
|
|
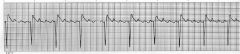
what is shown?
|
atrial flutter - 4:1 block
|
|

what is shown?
|
atrial fibrillation
notice - irregular irregular rhythm - chaotic/indistinguishable P-waves - QRS normal |
|
|
if you see an ECG strip where the rate and rhythm are irregular and there are many small (rate around 300 per minute) or possibly no distinguishable P-waves, what would you consider?
|
atrial fibrillation
|
|
|
when considering lead II, if you see a negative P-wave, no P-wave, or a P-wave which adds to the S-phase of the QRS, you would think of?
|
Premature Junctional Contraction
|
|
|
what is the most common finding with a premature junctional contraction on ECG?
|
P-wave is missing because it is buried in the QRS complex
|
|

what is shown?
|
premature junctional contraction
notice - inverted P-wave |
|

what is shown?
|
premature junctional contraction
notice - missing P-wave (most common finding) |
|
|
what is the name of the rhythm in which atrial depolarization does not happen and after a pause the AV node initiates a ventricular contraction?
|
junctional escape beat
|
|

what is shown?
|
junctional escape beat
|
|

what is shown?
|
junctional rhythm
notice - missing P-wave - rate 40-60 BPM |
|
|
if ECG shows a rate of 40-60 BPM, variable P-waves (absent, retrograde, or anterograde), and regular rythm, what do you have?
|
junctional rhythm
|
|
|
if ECG shows a rate of 60-100 BPM, variable P-waves (absent, retrograde, or anterograde), and regular rythm, what do you have?
|
accelerated junctional rhythm
|
|

what is shown?
|
accelerated junctional rhythm
Notice - distinguished from junctional rhythm by the 60-100 BPM rate |
|
|
if ECG shows an irregular rhythm, periodic wide and abnormal appearing QRS (>.12 seconds), and compensatory pauses between ventricular contractions, what do you have
|
ventricular premature contraction (PVC)
|
|

what is shown?
|
premature ventricular contraction
|
|

what is shown?
|
premature ventricular contraction
|
|
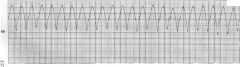
what is shown?
|
ventricular tachycardia
|
|

what is shown?
|
accelerated idioventricular rhythm
notice - 40 to 100 BPM - Wide (> or equal to .12 seconds) QRS with bizarre appearance |
|
|
what looks like v-tach but is slower, usually around 40-100 BPM as compared to 100-200 BPM for V-tach?
|
Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
|
|
|
what is the name of the irregular rhythm without P-waves, and has diamond shaped variation in amplitude?
|
Torsade de Pointes
|
|
|
describe the P-waves in accelerated idioventricular rhythm?
|
there are none
|
|

what is shown?
|
Torsade de Pointes
|
|
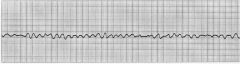
what is shown?
|
ventricular fibrillation
|

