![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Atherosclerosis |
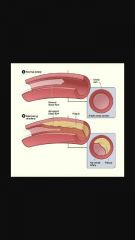
The build-up of fats, cholesterol, and other substances in and on the artery walls |
CAD |
|
|
Arteriosclerosis |
the thickening and hardening of the walls of the arteries, occurring typically in old age. |
|
|
|
4 Chambers of the Heart |
Left and right atrium, left and right ventricles |
|
|
|
The strongest working chamber in the heart? |
Left ventricle |
|
|
|
Cardiac Cycle |
refers to a complete heartbeat from its generation to the beginning of the next beat, and so includes, the systole,the contraction and the diastole, the intervening pause/relaxation. |
|
|
|
Impulse Pattern |
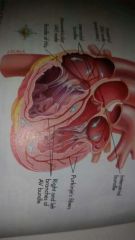
SA node to the VA node to the bundle of his to the right and left bundle branches of A node finally to the Purkinji Fibers. |
|
|
|
Cardiac cycle travel |
Systole,bloods pumps out diastole receives blood in. |
|
|
|
Depolarization |
Electrical activity When the heart contracts . |
|
|
|
Repolarization |
When the heart is relaxed |
|
|
|
Ejection Fraction |
is a measurement of the percentage of blood leaving your heart each time it contracts. During each heartbeat cycle, the heart contracts and relaxes. When your heart contracts, it ejects blood from the two pumping chambers (ventricles). |
|
|
|
Cardiac Output |
The volume of blood pumped per minute by each ventricle of the heart. Cardiac output is equal to the stroke volume (the amount of blood pumped from a ventricle in a single heartbeat) times the heart rate. |
|
|
|
Refactory period |
a period immediately following stimulation during which a nerve or muscle is unresponsive to further stimulation. |
|
|
|
Myocardio infarction |
A blockage of blood flow to the heart muscle. |
|
|
|
CAD Symptoms |
fast heart rate or heart attack heartburn or vomiting nausea, sweating, chest pain shortness of breath |
|
|
|
Acute Coronary Syndrome |
is a term used for any condition brought on by sudden, reduced blood flow to the heart. Acute coronary syndrome symptoms may include the type of chest pressure that you feel during a heart attack, or pressure in your chest while you're at rest or doing light physical activity (unstable angina). |
|

