![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How much blood does the heart beat per minute (when resting and when exercising)? |
When resting- 5 liters When exercising- 30 liters |
|
|
The right side of the heart carries ___ blood and the left side of the heart carries __ blood. |
deoxygenated, oxygenated |
|
|
Veins bring blood from the ___ to the ___ |
Body, heart |
|
|
Arteries bring blood from the ___ to the ___. |
heart, body |
|
|
The general size of the heart is __. |
5 1/2 inches X 3 1/2 inches |
|
|
Where is the heart located in? |
The pericardial cavity within the mediastinum. |
|
|
The right chamber of the heart is situated slightly ___ and points to the ___ |
anteriorly, left |
|
|
The base is also known as the ___ and sits between the __ and the ___. |
superior border, atria, great vessels |
|
|
The base is situated deep to the ___ ___. |
3rd rib |
|
|
The ___ is the point of the heart |
Apex |
|
|
The apex is on the ___ ventricle |
left |
|
|
The apex is situated deep to the ___ ____ ___ |
5th intercostal space |
|
|
What are the three layers of the heart? |
1. Epicardium 2. Myocardium 3. Endocardium |
|
|
The epicardium is AKA the ___ ____. |
Visceral pericardium |
|
|
What are cardiac muscles cells AKA? |
Myocardiocytes |
|
|
Myocardium has what other type of cells besides heart muscle cells? |
Nodal cells and conducting cells |
|
|
The endocardium is continuous with the __ and __. |
Valves, vessels |
|
|
How are adjacent heart muscle cells joined by? |
Intercalated discs |
|
|
Intercalated discs have shared ___ from adjacent cells |
Z-lines |
|
|
What is the bands of fibro-elastic connective tissue interwoven with myocardium and what layer of the heart is it found in? |
Fibrous skeleton, found in myocardium |
|
|
What is the function of the fibrous skeleton? |
1. Shapes chambers 2. Prevents overfilling 3. Electrically separates atria from ventricles 4. Forms frame for valves |
|
|
Which chambers of the heart of the receiving chambers? |
Atria |
|
|
What type of blood and from where does the left atrium receive? |
oxygenated blood from the lungs |
|
|
What type of blood and from where does the right atrium receive? |
Deoxygenated from the body |
|
|
What are the names of the pacemaker cells and where are they found? |
SA node and AV node are found on the right atrial wall |
|
|
What chamber is the pumping chamber of the heart? |
The ventricles |
|
|
Which chambers of the heart has the thicker walls? |
Ventricles |
|
|
The ventricles are separated by what? |
The ventricular septum |
|
|
The right ventricle pumps ___ blood to the ___ |
deoxygenated, lungs |
|
|
The left ventricle pumps ___ blood to the ___ |
oxygenated, body |
|
|
Which ventricle has the thickest wall? |
Left |
|
|
Which major vessel carried deoxygenated blood from body tissues to right atrium? |
Superior and inferior vena cava |
|
|
Which major vessel carried deoxygenated blood from right ventricle to lungs? |
Pulmonary artery |
|
|
Which major vessel carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium? |
Pulmonary vein |
|
|
Which major vessel carries oxygenated blood from left ventricle to the body? |
Aorta |
|
|
Which valve is found between atria and ventricles? |
Atrioventricular valves |
|
|
The right atrioventricular valve is AKA? |
Tricuspid |
|
|
The left atrioventricular valve is AKA? |
Bicuspid/mitral |
|
|
What are the valves between the ventricles and vessels called? |
Semilunar valves |
|
|
How do the AV valves open? |
When blood returns to the atria, valves are forced open |
|
|
How are the AV valves close? |
When ventricles contract, AV valves forcibly close |
|
|
What role does the chordae tendineae play? |
They tighten and prevent AV valve flaps from everting into atria |
|
|
How do the semilunar valves open? |
When ventricles contract, blood is pushed through and forces semilunar valves open |
|
|
How do the semilunar valves close? |
As ventricles relax, blood from arteries begin to fall back and close the semilunar valves |
|
|
What is a heart attack AKA? |
Myocardial infarction |
|
|
Heart attack is the death of ___ |
heart tissue |
|
|
What necessary substance becomes insufficient and causes a heart attack? |
Blood |
|
|
What node begins the atria contraction? |
SA node |
|
|
What node begins the ventricle contraction |
AV node |
|
|
Describe the electrical activity of the intrinsic conduction system. |
Begins at SA node to internodal pathway, AV node, AV bundle (bundle of His), bundle branches, and the purkinje fibers |
|
|
What two "holes" do fetuses have in their heart to assist circulation in utero and what is their purpose? |
Foramen ovale and ductus arteriosus. They are there to bypass the lungs |
|
|
The foramen ovale brings blood from the ___ ____ to the ___ ___. |
Right atrium, left atrium |
|
|
The ductus arteriosus brings blood from the ___ ___ to the ___ |
pulmonary artery, aorta |
|
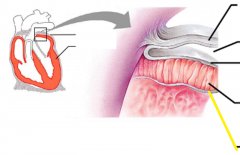
|
Endocardium
|
|
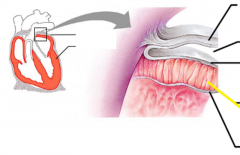
|
Myocardium
|
|
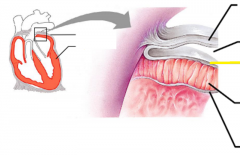
|
Epicardium
|
|
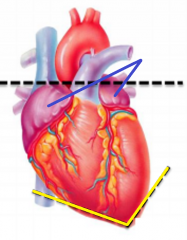
What is in blue?
|
Auricles
|
|
|
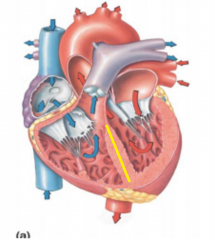
Interventricular septum
|
|
|
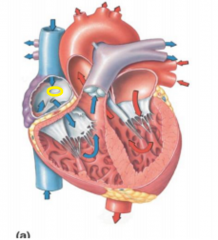
Fossa ovalis
|
|
|
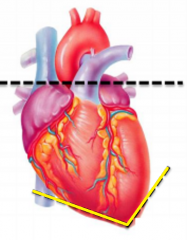
Apex
|
|
|
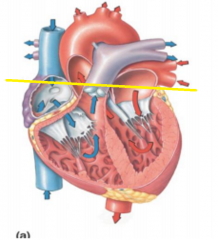
Base
|
|
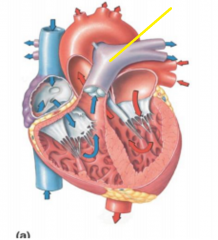
|
Pulmonary artery
|
|
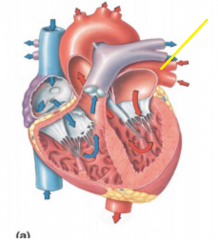
|
Pulmonary vein
|
|
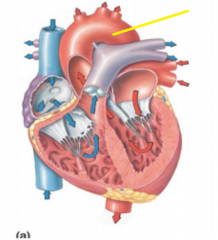
|
Aorta
|
|
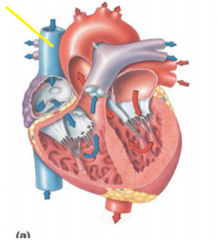
|
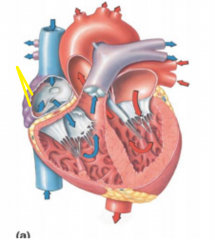
Superior vena cava
|
|
|
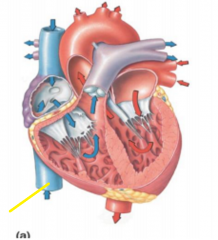
Inferior vena cava
|
|
|
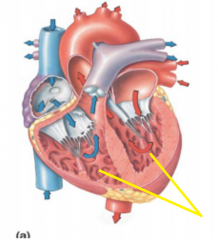
Trabeculae carneae
|
|
|
Pectinate muscles
|
|
|
Systole
|
contraction
|
|
|
Diastole
|
relaxation
|
|
|
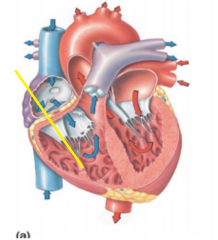
Papillary muscles
|
|
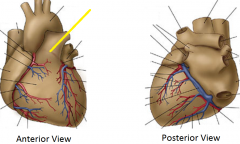
|
Left coronary artery
|
|
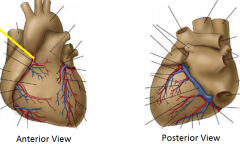
|
Right coronary artery
|
|
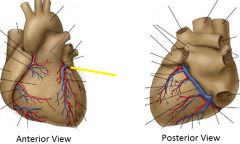
|
Circumflex artery
|
|
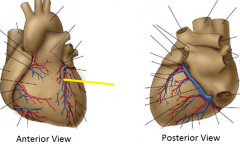
|
Great cardiac vein
|
|
|
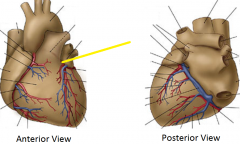
Anterior interventricular artery
|
|
|
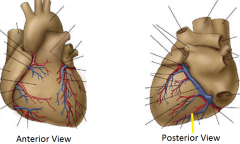
posterior interventricular artery
|
|
|
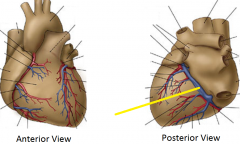
Coronary sinus
|

