![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the effect of sympathetic nervous system on pacemaker potential?
|
Increases slope of pacemaker cell potential -> tachycardia
|
|
|
What is the effect of parasympathetic nervous system on pacemaker potential?
|
Decreases slope of pacemaker potential - brachycardia
|
|
|
What is tachycardia and brachycardia?
|
Tachycardia - increased heart rate
Brachycardia - decreased heart rate |
|
|
Where do preganglionic sympathetic fibres arise from?
|
T1-T6
|
|
|
Where do sympathetic preganglionic fibres synapse?
|
Paravertebral sympathetic ganglia
|
|
|
What is the sympathetic neurotransmitter affecting the heart?
|
Noradrenaline on B1 adrenoceptors
|
|
|
Where do parasympathetic pre-ganglionic fibres arise from?
|
Vagal motor nucleus in medulla
|
|
|
Where do preganglionic parasympathetic fibres synapse?
|
Within the heart
|
|
|
Where do sympathetic fibres innervate the heart?
|
Most areas - nodes, atrial and ventricular muscle
|
|
|
Where do parasympathetic fibres innervate the heart?
|
Nodes and atrial muscle
|
|
|
What is the parasympathetic neurotransmitter in the heart?
|
Acetylcholine on M2 muscarinic receptors
|
|
|
Therefore what does the parasympathetic NS not affect?
|
Ventricular contractility
|
|
|
What are chronotropic effects on the heart?
|
Changes in heart rate
|
|
|
What are inotropic effects on the heart?
|
Changes in strength of contraction
|
|
|
What has the most prominent effect on the heart?
|
Vagal tone
|
|
|
How can atropine change the heart rate?
|
Can block M2 receptors, blocks ACh, speeds up heart rate
|
|
|
What influence does the sympathetic NS have on inotropic/chronotropic effects?
|
Increases inotropic and chronotropic effects
|
|
|
What influence does the parasympathetic NS have on inotropic/chronotropic effects?
|
Reduces chronotropic effect
|
|
|
How does acetylcholine decrease chronotropic effect?
|
Leads to hyperpolarising K current out of cell
Harder for potential to reach threshold |
|
|
What is calcium-induced calcium release?
|
Calcium entering the cell can lead to calcium release form sarcoplasmic reticulum stores, leading to contraction
|
|
|
What is the annulus fibrosus?
|
The insulating layer between atria and ventricles
|
|
|
How does the heart act like one big cell?
|
The cardiac cells are connected by intercalated discs - action potentials spread through gap junctions
Also desmosomes connect them |
|
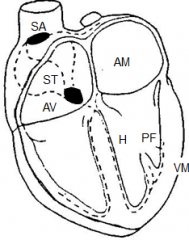
Name the parts of conduction around the heart
|
Sino-atrial node
Special tracts -> atrial muscle contraction Atrio-ventricular node Bundle of His Right & left bundle branch Purkinje fibres -> ventricular muscle contraction |
|
|
Why is atrial excitation complete before ventricular excitation begins? What is the significance of this?
|
There is a delay at the AV node (smaller cells, slower conductance)
Allows atria to top up ventricles before exciting ventricles |
|
|
What is an electrocardiogram?
|
A record of the potential changes at the skin surface that result from depolarisation and repolarisation of heart muscle
|
|
|
How does reduction in calcium in the cell occur and what does it cause?
|
Reuptake of Ca by sarcoplasmic reticulum or mitochondria
Exchange of Ca for Na driven by Na-K pump |
|
|
Does calcium entering the cell cause a contraction?
|
No, calcium entering the cell causes release of calcium from S.R. and mitochondria (CICR) which causes a contraction
|
|
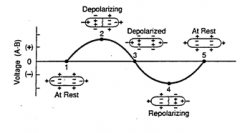
What happens to a cardiac cell when it is depolarising and repolarising?
|
A dipole is set up - part of cell positive, part of cell negative
Fully depolarised - whole cell is positive - returns to 0 mark on voltage because there is no dipole (no difference in charge) |
|
|
In an ECG, what does the voltage recorded depend on?
|
Orientation of electrodes in relation to dipole
Mass of tissue in which dipole is set up |
|
|
What is the triangle created around the heart in an ECG recording called?
|
Einthoven's triangle
|
|
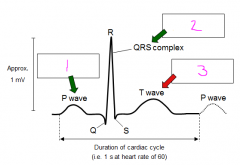
What is represented at each number?
|
1 - depolarisation of atria
2 - depolarisation of ventricles 3 - repolarisation of ventricles (repolarisation of atria not an intracellular reading) |
|
|
What can knowing the P-P interval give you?
|
Atrial rate
|
|
|
What can knowing the R-R interval give you?
|
Ventricular rate
|
|
|
What can ECG give you information about?
|
Anatomy of the heart - muscle thickness in different regions
Evaluates conduction system Cardiac drug treatment assessment |
|
|
Why is the T wave in the same direction as the R wave?
|
Ventricular muscle repolarises before the repolarisation of the bundle branch
|

