![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Conducting airways |
Passageway between the ambient environment and the gas exchange units of the lungs (the alveoli). No gas exchange occurs, nevertheless they are important to the overall process of ventilation. divided into the upper airway and lower airway. |
|
|
Upper airway |
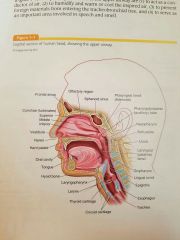
Consist of nose, oral cavity, pharynx and larynx. Acts as a conductor of air, to humidity and warm or cool the inspired air, prevent foreign materials from entering the trachea bronchial tree, and to serve as an important area involved in speech and smell. |
|
|
Outer portion of nose |
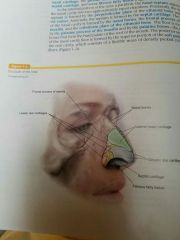
Composed of bone and cartilage. |
|
|
Extubation |
The removal of a tube especially from the larynx after intubation—called also detubation |
|
|
Laryngitis |
Inflammation of the mucous membrane lining the larynx, accompanied by swelling and edema of the vocal cords. |
|
|
Intubation |
insert a tube into (a person or a body part, especially the trachea for ventilation). |
|
|
Edema |
is swelling caused by excess fluid trapped in your body's tissues. Although edema can affect any part of your body, it's most commonly noticed in the hands, arms, feet, ankles and legs. |
|
|
Acute epiglottitis |
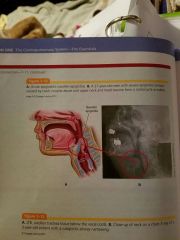
Is a supraglottic airway obstruction. ...resulting from inflammation of the epiglottis, are epiglottitis folds, and false vocal cords.
AND IS A LIFE THREATENING EMERGENCY!
Is almost always caused by a bacterial infection of hemophilia influenza type b. |
|
|
LTB |
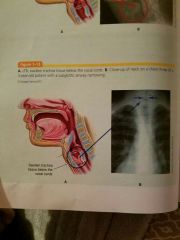
Is Subglottic airway obstruction
Causes edema and swelling of the mucous membrane BELOW the glottis. |
|
|
Master Cells |
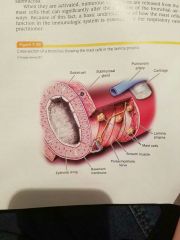
Found in the lamina proprietary. Play an important role in the immunologic mechanism. When activated, numerous substances are released from the master cell that can significantly alter the diameter of the bronchial airways. |
|
|
Antigen |
a toxin or other foreign substance that induces an immune response in the body, especially the production of antibodies |
|
|
Lymphoid tissues |
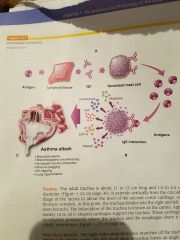
Lymphoid tissue, cells and organs that make up the lymphatic system, such as white blood cells (leukocytes), bone marrow, and the thymus, spleen, and lymph nodes. |
|
|
COPD |
Chronic obstruction pulmonary disease |

