![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are two causes of cm's?
|
idiopathic (unknown)
autosomal dominant gene |
|
|
What are four alternate acronyms for HCM ?
|
ASH
SAM IHSS HOCM |
|
|
What is the most common cm?
|
ASH
|
|
|
What does ASH stand for?
|
asymmetric septal hypertrophy
|
|
|
What does SAM stand for?
|
systolic anterior motion of the MV
|
|
|
What does IHSS stand for
|
iodpathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis
|
|
|
What other two conditions go along with IHSS?
|
SAM and ASH
|
|
|
What does HCM stand for?
|
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
|
|
|
What does HOCM stand for?
|
hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy
|
|
|
What other two conditions accompany HOCM?
|
SAM and HCM
|
|
|
What will you see in the myocardium with HOCM?
|
myocardial fiber disarray
|
|
|
What chamber will be affected by HOCM?
|
LA
|
|
|
What happens to the LA with HOCM?
|
it's dilated
|
|
|
Why is the LA dilated with HOCM?
|
diastolic dysfunction and/or MR
|
|
|
What happens to the LV with HOCM?
|
becomes noncompliant and you get diastolic dysfunction
|
|
|
What may two things may be seen regarding the septum with HOCM?
|
subaortic septal hypertrophy causing obstruction
septal scarring from MV leaflets striking it |
|
|
What else may cause obstruction with HOCM?
|
anterior MV leaflet motion
|
|
|
What three things may be seen regarding the MV with HOCM?
|
thickening
MAC/fibrosis systolic anterior motion |
|
|
What are five physical signs of HOCM?
|
DOE
angina arrhythmias syncope sudden death |
|
|
What murmur is associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
|
crescendo-descescendo systolic murmur that increases with valsalva or amyl nitrite
|
|
|
What effect does aml nitrite have with HOCM?
|
tachycardia
LVOT gradient increase SAM increase murmur increase |
|
|
What is another type of hypertrophc cardiomyopathy?
|
AHCM - apical hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
|
|
|
What EKG finding is associated with it AHCM?
|
increased QRS voltages and negative T waves
|
|
|
What country is AHCM more prevalent in and what is the incident percentage?
|
Japan
20% of all HCM vs 2% in US |
|
|
What is a term used to describe one view of AHCM on echo?
|
ace of spades
|
|
|
What is ACHM's usual cause?
|
genetic
|
|
|
What might you see on doppler in LVOT with AHCM?
|
flow acceleration in mid lv
late peaking systolic jet |
|
|
What is the ratio for assessing asymmetric hypertrophy?
|
1.3:1
|
|
|
What appearance might the myocardium have with HCM and why?
|
bright from fiber disarray
|
|
|
What will you see in regard to the ventricular walls with HCM?
|
asymmetric or symmetric thickening
|
|
|
What might you see in regard to ventricular contraction and EF with HCM?
|
could be normal or could be hyperdynamic
EF can be elevated, 60-70% |
|
|
What might you see in regard to the AV with HCM?
|
mid systolic closure
|
|
|
How is asymmetric hypertrophy defined?
|
septal to posterior wall > 1.3:1
|
|
|
What will alter septal contact and how?
|
valsalva and amyl nitrite will increase it if patient not on beta blockers
|
|
|
The Venturi effect can be associated with which cardiomyopathy?
a) dilated b) restrictive c) hypertropic d) ischemic |
c) hypertrophic
|
|
|
LVOT obstruction causes the AV to:
a) flutter in diastole b) close in mid-systole c) flutter in systole d) close in late systole |
b) close in mid systole
|
|
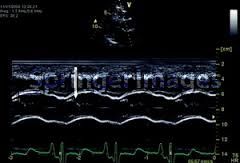
what does this show
|
mid systolic closure or aortic valve
|
|
|
Doppler shows mitral inflow and shows A wave greater than E wave. What does this mean?
|
diastolic dysfunction, impaired relaxation
|
|
|
What are four other doppler findings which might be apparent with HCM?
|
gradient
turbulence mr late peaking systolic jet |
|
|
Does Inderal (beta block) increase SAM?
|
no, decreases heart rate and reduces SAM
|
|
|
What kind of doppler jet goes along with HOCM and IHSS
|
late peaking
|
|
|
61 YO male with IHSS and a resting gradient of 144 mm Hg. Admitted ot hospital with CP. Next day gradient is 15. what happened.
a) LV infarct b) RV nfarct c) a-fib d) post MI VSD |
a) LV infarct
|
|
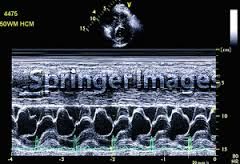
what does this show
|
SAM
|

