![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What diagnostic tool is key in differentiating this classification? |
ECHO |
|
|
|
What is the LVEF in DCM ?
|
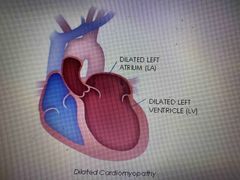
Dilated cardiomyopathy EF less than 40% |
Decreased cardiac output |
|
|
What are the symptoms of DCM? |
Dyspnea on exertion, orthopnea, fatigue, wt gain, syncope, palpitation and chest pain |
|
|
|
assessment findings |
S3,S4, a systolic murmur Crackles Likely, ECG LBBB, |
Heart and lung |
|
|
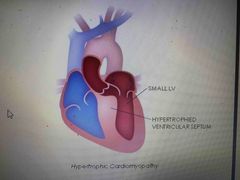
2. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy What are the symptoms of HCM ? |
Dyspnea, chest pain, palpitation, syncope. |
|
|
|
2. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy What are the symptoms of HCM ? |
Dyspnea, chest pain, palpitation, syncope. |
Potential Genetic source (cause) |
|
|
SCD (sudden cardiac death) in HCM. Why ? |
Sudden death like with in an hour due to sudden electrical malfunction of the heart |
|
|
|
Treatment of HCM |
Improving ventricular filling and stroke volume. Reduce obstruction and SCD *ventricular septal myectomy and PASA (septal ablation) |
Warning: avoid inotropes (digoxin, dopamine…) + Add a hint |
|
|
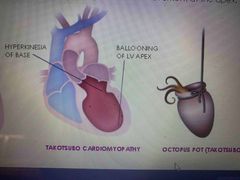
3. Stress induced cardiomyopathy What is the cause and symptoms? |
Cause: sudden temporary dysfunction of the myocardium, ANS and Adrenalin Chest pain, Dyspnea |
|
|
|
Treatment of SICM |
Supportive therapy like oxygen, fluid, prevent complication and monitor dysthymias |
|
|
|
4. Restrictive cardiomyopathy Characterized by |
Rigid myocardial wall that decreases the expansion of chamber walls during ventricular filling |
Amyloidosis (waxy protein builds up) and sarcoidosis |
|
|
What are the Treatments of RCM ? |
Treat dysrhythmias, reduce risk of SCD, relive symptoms. Life expectancy 2 years from Dx consider palliative care support |
|
|
|
Vasoactive medication Milrinone |
High risk/alert medication Category: inotropic, phosphodiesterase-3 enzyme inhibitor |
|
|
|
How is it given? What is it used for? |
Iv drip and used for inotropic support in HF ( decompensated HF) |
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action ? |
A selective phosphodiesterase inhibitor in cardiac and vascular tissue results in vasodilation and inotropic effect with little chronotropic effects. |
|
|
|
Does it require titration |
No fixed rate Loading dose followed by maintenance dose |
|
|
|
What to monitor |
Monitor B/P, HR, lab like CMP for CrCl Watch for hypovolemia, iv site extravasation. |
|
|
|
Warning/Precautions |
Ventricular arrhythmias including v tach. May cause thrombocytopenia, consider alternative if platelet count is lower than 150,000 mm3. |
|
|
|
Adverse effects |
Hypokalemia , ventricular arrhythmia,hypotension, angina, headache |
|

