![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
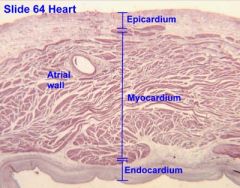
what part of the wall of the heart is made up of a low friction surface made up of mesothelium?
|
Epicardium
|
|
|
What part of the heart wall consists of endothelial lining and CT?
|
Endocardium
|
|
|
What constitutes the visceral layer of the pericardium in the heart wall?
|
Epicardium
|
|
|
The mesothelium of the epicardium is made up of what cell types?
|
simple squamous and cuboidal cells
|
|
|
Where in the heart wall do you see adipose tissue?
|
Epicardium
|
|
|
Increasing pressure across the atrial wall will cause what to happen?
|
ANF will be released to relax cardiac m.
Na and water are released. this decreases blood volume |
|
|
How does ANF relax the cardiac m?
|
by antagonizing vasopressing and angiotensin II
|
|
|
What stimulates diuresis and natriuresis in the right atrial wall?
|
ANF
|
|
|
What prevents hypervolemia and hypertension in the heart?
|
ANF
|
|
|
What are strong junctions between intercalated discs?
|
desmosomes
|
|
|
What is located on the sides of Cardiac M cells and allows the cells to communicate?
|
Gap Junctions
|
|
|
What do you see in aged cardiac muscle?
|
Lipofuscin
|
|
|
Cardiac muscles cells are arranged end to end by what?
|
Intercalated Discs
|
|
|
What two structures hold cardiac m cells together?
|
Desmosomes and Fascia Adherens
|
|
|
Which is longer, desmosomes or fasica adherens?
|
Fascia Adherens
|
|
|
What is modified cardiac muscle that stains light because of rich glycogen?
|
Purkinje cells
|
|
|
What is cholinergic in the heart? (has the ability to release acetycholine)
|
Purkinje Fibers
|
|
|
What innervates norepinephrine release?
|
Symphathetic innervation- Thoracic Spinal Accessory Cardiac Nerves (T1-T6)
|
|
|
What innervates acetycholine release?
|
Parasympathetic: Vagus N
|
|
|
What causes the Coronary A to dilate?
|
Sympathetic Innervation
|
|
|
What causes the Coronary A to constrict?
|
Parasympathetic Innervation
|
|
|
What innervation will cause Tachycardia?
|
Sympathetic
|
|
|
What is the hormonal modulation of the heart?
|
Adrenal Medulla
Epinephrine Norepinephrine |
|
|
What senses high blood pressure in the carotid sinus and aortic arch?
|
Baroreceptors
|
|
|
What senses low blood pressure in the wall of the atria and ventricles?
|
Volume receptors
|
|
|
What senses 02, CO2, and pH in the carotid and aortic bodies?
|
Chemoreceptors
|
|
|
What part of the heart valve is made up of loose CT containing collagen and elastic fibers to absorb vibrations?
|
Spongiosa
|
|
|
Spongiosa of the Aortic and Pulmonary valves are known as what?
|
Arterialis
|
|
|
Spongiosa of the Tricuspid and Mitral Valves are known as what?
|
Auricularis
|
|
|
What part of the heart valve is an extension of theskeletal rings and made up of dense irregular CT?
|
Fibrosa
|
|
|
What are the 3 layers of the heart valves?
|
Spongiosa
Fibrosa Ventricularis |
|
|
What part of the heart valve is dense CT with elastic fibers?
|
Ventricularis
|
|
|
What is made up of multiple layers of elastic lamellae with a relative thick tunica intima and thin tunia adventitia?
|
Large Arteries
|
|
|
What artery has lots of smooth muscle and has less elastin?
|
Medium Arteries
|
|
|
What are 0.5 to 2.0 mm and up to 8 layers thick of smooth muscle cells?
|
small arteries
|
|
|
What is made up of 2-3 layers of smooth muscle?
|
Arterioles
|
|
|
What is absent in arterioles?
|
Internal Elastic Membrane
|
|
|
How do arterioles control blood flow to capillary network?
|
By contraction of smooth muscle cells by precapillary sphincter
|
|
|
With Athersclerosis and Ischemic Heart disease, lesions develop in what layer of the heart muscle?
|
Intima
|
|
|
What consists of a thick laye of fibrous CT with smooth muscle cells, macrophages, foam cells, lymphocytes, cholesterol crystals and cell debris?
|
Lesion in Intima
|
|
|
With developing athersclerosis, macrophages and smooth muscle cells accumulate what?
|
lipid (LDL)
|
|
|
With advanced lesions forming in the Intima of the heart, what type plaques form as well?
|
Fibrofatty Intimial plaques
|
|
|
With Ischemic Heart Disease, when does blood flow become critical?
|
reduced by 90%- this is when you'll develope anginal pain
|
|
|
What is a Coronary Artery Thrombosis?
|
Myocardial Infarct
|
|
|
What are Rouget cells?
|
Pericytes
|
|
|
What type of cell in the capillary wall has a large nucleus and it's basal lamina is continuous with that of the endothelium?
|
Pericytes
|
|
|
Pericytes are precursor cells for what?
|
Endothelial cells and Smooth M cells
|
|
|
What is a vasodilating agent in the capillary?
|
EDRF Endothelial-derived relaxation factor
aka Nitric Oxide |
|
|
Vasodilating agents in the capillary cause the smooth muscles to relax and blood flow increases. If this isn't controlled what can it lead to?
|
Peripheral Edema
|
|
|
What drives Vasodilation?
|
Endothelial derived relaxation Factor and low O2
|
|
|
What are 3 regulations of blood flow?
|
Arteriole
Arteriovenous Shunts Metateriole |
|
|
What is located at the Metarteriole that makes it a regulator of blood flow?
|
Precapillary Sphincter
|
|
|
Contraction of arteriole smooth muscle at the AV shunt would cause what?
|
Blood to go to capillary bed
|
|
|
Relaxation of the arteriole smooth muscle at the AV shunt will cause blood to flow where?
|
bypass the capillary bed and go thru AV shunt
|
|
|
What is the size of Muscular venule diameters?
|
1 mm
|
|
|
What is the size of Postcapillary venule diameters?
|
0.2 mm
|
|
|
Which has thicker Tunica Media, medium arteries or medium veins?
|
medium arteries
|
|
|
What are a characteristic feature of medium veins?
|
valves
|
|
|
The tunica media in medium veins contains what type of muscle cells?
|
circular and longitudinal smooth muscle cells
|
|
|
What size vein contains circumferentially arranged smooth muscle cells, collagen fibers and fibroblasts?
|
Large Veins
|
|
|
What layer of the Large Vein contains collagen, elastic fibers, fibroblasts, and longitudinally arranged smooth muscle cells?
|
tunica adventitia
|
|
What is the epithelium of Epicardium?
|
Mesothelium- Simple squamous/cuboidal epithelium
|
|
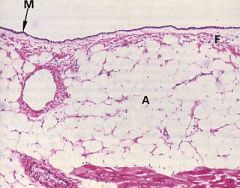
What is this an image of in the heart?
|
Epicardium- notice all the adipose cells, simple squamous/cuboidal epi, and loose CT
|
|
|
Internal elastic membrane is only located in ________.
|
Arteries
|
|
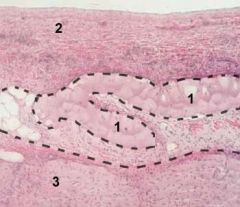
Label each #
|
1. Purkinje Fibers
2. Endocardium 3. Myocardium |
|
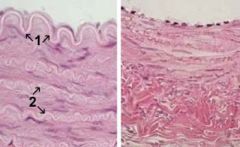
What is the image on the left? label the #s
|
Muscular Artery
#1- Internal elastic lamina #2 elastic membrane (only present in arteries) |
|
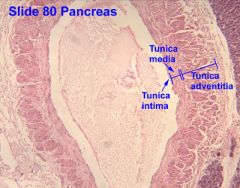
What is this an image of?
|
Large Vein- notice how big the Tunica Adventitia is
|
|
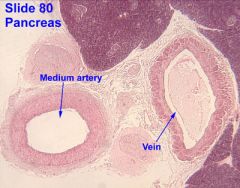
What is unique about medium arteries?
What is unique about medium veins? |
medium arteries- can see prominent elastic membrane
medium veins- circular and longitudinal smooth muscle cells and valves |
|
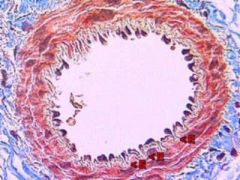
What blood vessels is this an image of?
|
small artery
|

