![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 2 ways to classify heart failure? |
1) Systolic Disfunction - unable to contract well
2) Diastolic Disfunction - unable to fill well |
|
|
What is the main manifestation of Left-sided heart failure? |
Pulmonary congestion leading to pulmonary edema and pleural effusions |
|
|
Name the 4 major causes of Left-sided heart failure. |
1) Valvular disease 2) Hypertension 3) Ischemic heart disease 4) Cardiomyopathies |
|
|
What are the main manifestations of Right-sided heart failure? |
Venous Congestion - ascites, dependent pitting edema, hepatospleenomegaly w/ "nutmeg liver" |
|
|
What manifestation is common to both right and left-sided heart failure and causes fluid retention to further complicate heart failure? |
Pre-Renal Azotemia (renal failure due to poor perfusion) |
|
|
What are the 3 causes of Right-sided heart failure? |
1) Left-sided heart failure (most common) 2) Mitral Stenosis 3) Cor Pulmonale |
|
|
What condition always precedes congestive heart failure and why? |
Cardiac Hypertrophy - due to increased number of sarcomeres requiring a larger oxygen demand that cannot be met |
|
|
Which type of of hypertrophy is the result of pressure overload? How does this change the size of the chamber? |
Concentric Hypertrophy - decrease chamber size |
|
|
Which type of of hypertrophy is the result of volume overload? How does this change the size of the chamber? |
Eccentric/Serial Hypertrophy - increases chamber size |
|
|
What is the normal mass of the heart? |
300-350 grams |
|
|
What 2 conditions increase the mass of the heart the most (ie cause the most hypertrophy)? |
Aortic Regurgitation Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (~1,000 g) |
|
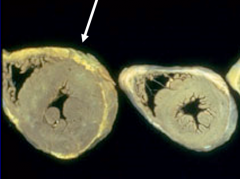
|
Concentric Hypertrophy |
|
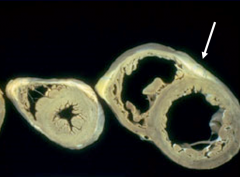
|
Dilated/Eccentric/Serial Hypertrophy |
|
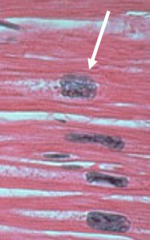
|
Box-Car Nucleus - seen in hypertrophy |
|
|
What is the main criteria to diagnosis a cardiac dysfunction as a "Myocardial Disease" (ie Cardiomyopathy) |
Cardiac dysfunction not linked to CAD, valvular disease, or hypertension |
|
|
Hypertrophic (600+ g), flabby heart with all 4 chambers dilated |
Dilated Cardiomyopathy |
|
|
What type of cardiac dysfunction does dilated cardiomyopathy cause? |
Systolic dysfunction |
|
|
Give the 5 causes for dilated cardiomyopathy. |
1) Genetic mutation in mt. or myocyte cytoskeletal genes (main cause) 2) Viral myocarditis 3) Pregnancy 4) Drugs (mainly chemo and cocaine) 5) EtOH |
|
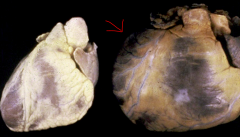
|
Dilated Cardiomyopathy |
|
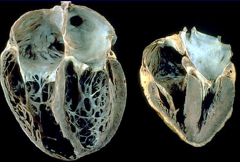
|
Dilated Cardiomyopathy |
|
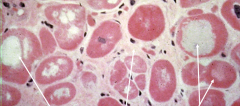
|
Dilated Cardiomyopathy with vacular degeneration (left), interstitial fibrosis (middle), and variation in myocyte size (right) |
|
|
Massive (1000 g) hypertrophic and hypercontracted heart with asymmetric septal hypertrophy |
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy |
|
|
What type of cardiac dysfunction does hypertrophic cardiomyopathy cause? |
Diastolic dsyfunction (and outflow obstruction in 1/3 of cases) |
|
|
What general class of protein mutation cause hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and what 4 specific proteins are effected? |
Sarcomere proteins 1) B-myosin heavy chain (most common) 2) Troponin T 3) alpha-Tropomyosin 4) Myosin-Binding protein C |
|
|
What kind of murmur might occur with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy? |
Harsh systolic ejection murmur (due to outflow obstruction) |
|
|
What are the 3 complication of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy? |
1) focal ischemia 2) A-fib with mural thrombi 3) Sudden death from an arrthymia |
|
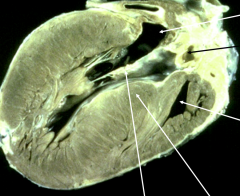
|
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy - septal hypertrophy and functional aortic stenosis that may causes outflow obstruction |
|
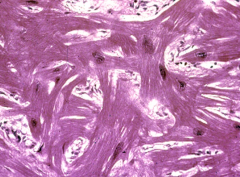
|
Myocardial Disarray from Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy |
|
|
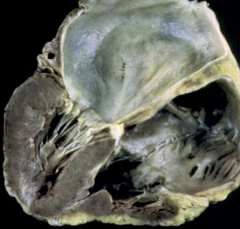
Normal heart size, contractility, and non-dilated ventricles but decreased filling during diastole and bilateral atrial dilation |
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy |
|
|
What are the 3 main causes of restrictive cardiomyopathy |
1) radiation 2) sarcoidosis 3) amyloidosis |
|
|
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy |
|
|
What are the 2 indications for a right atrial cardiac biopsy? |
Suspect myocarditis or amyloidosis |
|
|
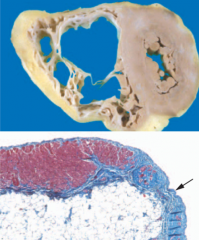
Right heart failure with thinned right ventricular walls and ventricular arrhythmias |
Arrhythmyogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy |
|
|
What syndrome is Arrhythmyogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy associated with? |
Naxos Syndrome - causes hyperkeratosis of soles/palms due a plakoglobin mutation |
|
|
Arrhythmyogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy - thinned right ventricle walls, interstitial fibrosis (blue), fatty infiltration |
|
|
How will a secondary cardiomyopathy heart appear? |
dillated cardiomyopathy |
|
|
What is the most common cause of myocarditis? |
Coxasackie A & B virus |
|
|
What is the most common cause of heart failure in south america? |
Chaga's disease due to infection from Trypansomi cruzi |
|

|
Hemachromatosis - cause of secondary cardiomyopathy |
|
|
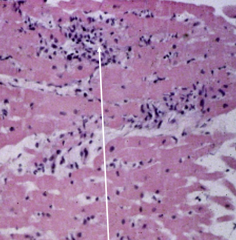
Myocarditis with lymphocyte infiltration and myocyte necrosis |
|
|
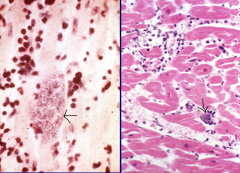
Cysts from parasitic myocarditis |
|
|
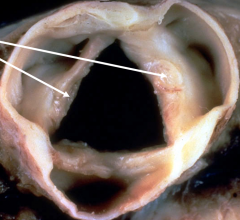
Carcinoid Valvular Disease - due to metastasis of a tumor to the liver that produces cytokines to damage the right heart and form plaques on the tricuspid valve |
|
|
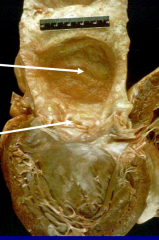
Leuitic (syphillis) Heart Disease - causes aneurisms of ascending aorta, dilation of aortic root, and LVH (cor bovinum) |

