![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
5 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What do the two cardiac fields divide into? |
1st: the scaffolding of the heart (dorsal aorta) -> left ventricle 2nd: adds to the conus cordis and truncus arteriousus, as well as right ventricle, atria, vena cava and pulmonary |
|
|
The progenitor endoderm of cardiac fields secretes which factor, and what are its effects? |
BMP-2, which induces NK-2 homeobox 5 gene and Mesoderm Posterior 1(Mesp1) |
|
|
What cardiac structure do the neural crest cells contribute to? |
The septa in between cardiac and pulmonary tracts. |
|
|
Describe how the sinus venosus and atrium become incorporated within pericardial cavity |
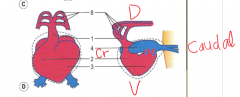
The conus cordis and the ventricle begin to bulge cranially looping the truncus arteriousus caudally. The atria grow towards the bulbus cordis becoming enveloped into the pericardial cavity. With further growth and folding heart becomes more cranial caudal less dorsal ventral |
|
|
How are the atria and ventricle separated? |
Mesenchymal cushions between the atria and ventricle fuse together in the centre. These mesenchymal cells are between the myocardium and encocardium. Divide the heart into left and right atrioventricular openings |

