![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Block Nav and Kv channels w/ a moderate off-rate to decrease phase 0 slope and increase refractory and AP duration |
Class Ia antiarrhythmics |
|
|
Block inactivated Nav channels w/ a quick off-rate to mildly decrease phase 0 slope and decrease refractory and AP duration |
Class Ib antiarrhythmics |
|
|
Block Nav channels w/ a long off-rate to signifcantly decrease phase 0 slope w/ little effect on AP duration |
Class Ic antiarrhythmics |
|
|
Class Ia antiarrhythmics |
Quindine Procainamide Disopyramide *(the Queen Proclaims Diso's Pyramid) |
|
|
Class Ib antiarrhythmics |
Lidocaine Mexilitine |
|
|
Class Ic antiarrhythmics |
Flecainide Propafenone *(Can I have Fries, Please) |
|
|
SE = Cinchonism (dizzy, N/V, tinnitus), reversible SLE-syndrome, and Torsades in 2-8% |
Class Ia antiarrhythmics (Quinidine, Procainamide, Disopyramide) |
|
|
Class Ia antiarrhythmics use |
Both atrial and ventricular arrhythmias - especially A-Fib |
|
|
SE = Seizures if infused too fast, tremor, dysarthria, altered consciousness |
Class Ib antiarrhythmics |
|
|
IV Class Ib antiarrhythmic |
Lidocaine |
|
|
PO Class Ib antiarrhythmics |
Mexilitine |
|
|
Class Ib antiarrhythmics use |
Ventricular arrhythmias, Best antiarrhythmic for post-MI ("b" = best) |
|
|
Class Ic antiarrhythmic use |
SVTs, but contraindicated for post-MI or torsades (pro-arrhythmic) |
|
|
Sympatholytics that block B1 and B2 receptors and Nav channels to decrease automaticity and slow conduction throughout entire heart |
Class II antiarrhythmics (beta-blockers) *all end in "lol" |
|
|
Class II Beta-blocker antiarrhythmics use |
SVT, decrease mortality post-MI |
|
|
SE = decreased contractility, Brady, angina when w/drawn suddenly, Bronchospasm in asthmatics |
Class II antiarrhythmics (Beta-blockers) |
|
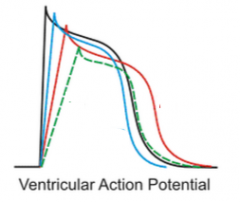
|
- Class Ia - red (prolonged AP and refractory w/ medium decrease in slope) - Class Ib - blue (mild decrease in slope and slightly shorter AP) - Class Ic - green (large decrease in slope, little effect on AP duration) |
|
|
Kv Blockers that delay repolarization and prolong refractory and AP duration |
Class III antiarrhythmics |
|
|
Class III antiarrhythmics |
Amiodarone Ibutilide Dofetilide Sotalol *(AIDS) |
|
|
Clinical use for Class III antiarrhythmics |
A-fib & A-flutter (all class III), VT (Amiodarone and Sotalol only) |
|
|
Class III Non-selective hERG blocker (blocks Kv, Cav, Nav, B-receptors) to cause prolonged AP duration w/out risk of EADs and thus little Torsades risk |
Amiodarone |
|
|
Large Side effect profile: hepatotoxic, thyroid toxic, pulmonary fibrosis, brady, corneal deposits in 100% of pts, photosensitivity |
Amiodarone |
|
|
2 enantiomers: l is a beta-blocker, d & l are Kv blockers. SE = Torsades (5%) |
Sotalol |
|
|
Kv blocker and and activates inward Nav current
SE = Torsades (6%) |
Ibutilide |
|
|
Only "pure" class III antiarrhythmic; must be administered in hospital due Torsades risk (1-3%) |
Dofetilide |
|
|
Block CaV channels to slow AV conduction for use in A-Fib pts |
Class IV antiarrhythmics |
|
|
Class IV antiarrhythmics |
Verapamil & Diltiazem |
|
|
SE = flushing (due to vasodilation effect), decreased contractility, constipation |
Class IV antiarrhythmic (verapamil and diltiazem) |
|
|
Blocks late phase influx through NaV to ensure Na/Ca exchanger works in fwd direction |
Ranolazine |
|
|
Clinical use for Ranolazine |
A-fib, VT, Congenital Long QT syndrome (specifically due to gain-of-fxn mutation in Nav) |
|
|
Increases K+ conductance out of cell to hyperpolarize the cell and decrease Ca2+ current. Released normally by ischemic tissues |
Adenosine |
|
|
What is the drug-of-choice for diagnosing and treating SVT? |
Adenosine |
|
|
SE = flushing, asthma, SA arrest (easily reversed), AV block, effects blocked by caffeine |
Adenosine |

