![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Pacemaker implantation |
Definitive treatment for: - Sick Sinus Syndrome (Sinus Node Dysfunction) - 3rd Degree AV Block - Atrioventricular Myopathy (uncommon) |
|
|
Vaughan-Williams Anti-arrhythmic drug classification |
Class I - Na+ channel blockers Class II - Beta-adrenergic receptor blockers Class III - K+ channel blockers Class IV - Ca2+ channel blockers |
|
|
Class I - Na+ channel blockers Class IA - Quinidine, Procainaminde Class IB - Lidocaine (IV), Mexiletine (PO) |
- "Membrane stabilizers" - Target phase 0 - Primarily used for ventricular arrhythmias - Use with caution in cats! (glucuronidation) |
|
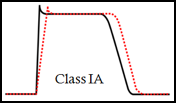
Na+ channel blockers Class IA - Quinidine, Procainaminde |
- Prolong AP duration - Treats supraventricular AND ventricular arrythmias - GI side effects |
|
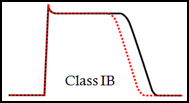
Na+ channel blockers Class IB - Lidocaine (IV), Mexiletine (PO) |
- Shorten AP duration - Lidocaine treats life threatening ventricular tachycardia (cats get 1/10 dose) - CNS side effects (depression, seizures) |
|
|
Class II = Beta-adrenergic receptor blockers - Non-selective (B1 and B2): Propanolol - B1 Cardio-selective: Atenolol (PO), Esmolol (IV) |
-Decrease automaticity (neg. chronotrope) -Decrease conduction (neg. dromotrope) -Decrease contractility (neg. inotrope) - Slow AV nodal conduction = slowed ventricular response rate - Tx supraventricular tachy and atrial fibrillation - First line for ventricular arrhythmias in cats - Treats ventricular arrhythmias associated with Subaortic Stenosis (SAS) - Side effects: negative inotropes, negative chronotropes, worsening of asthma in cats (bronchocontriction) |
|
|
Class III = K+ channel blockers Amiodarone, Sotalol |
- Prolong AP AND refractory period --> interrupt/eliminate re-entry (slows rate of repolarization) - Tx ventricular arrythmias - Side effects: negative inotrope (Sotalol), bradycardia - Sotalol also has non-selective beta-blocker properties |
|
|
Class IV = Ca2+ channel blockers Diltiazem (PO or IV) |
- Blocks the L-type calcium channel - Slow AV nodal conduction --> decrease ventricular response rate (same as beta-blockers) - Reduces myocardial contractility - Tx atrial fibrillation, SVT, re-entry involving AV node - Side effects: negative inotrope, bradycardia, AV block, GI upset (esp. cats - don't tolerate well) |
|
|
Best anti-arrhythmic drugs for cats |
- First line: Beta blockers (Atenolol, Esmolol), though caution with asthma - Then K+ blockers (Amiodarone, Sotalol) -Na+ blockers and Ca2+ blockers not tolerated well |
|
|
Misc. Anti-arrhythmic Drugs |
- Digoxin - Atropine, Hyoscyamine, Propantheline - Isoproteranol, Terbutaline, Theophylline |
|
|
Digoxin |
- Cardiac glycoside, oral administration - Slows AV nodal conduction (AV node filtering) - Positive inotrope (blocks Na/K pump which further activates Na/Ca exchanger) - Tx SVT, atrial fib, atrial flutter - Side effects: GI upset, AV block, VPCs |
|
|
Atropine |
- Anticholinergic (parasympatholytic) - Used to tell wether sinus bradycardia is due to high vagal tone (HR will increase) or structural heart disease (no change) - Used to tell wether sinus arrest is due to high vagal tone (HR will increase) or SA node dysfunction (minimal change) - Temporary (ineffective) medical treatment for sick sinus syndrome - Minimal effect on AV blocks (limited vagal input to ventricular myocytes) |
|
|
Isoproteranol |
- Beta adrenergic agonist (sympathomimetic) - Short term CRI for 3rd Degree AV Block (to increase HR) |
|
|
Treatment options for Supra-ventricular Tachycardia |
1. Control ventricular response rate/slow AV node conduction (for stretch/structural changes) - Digoxin - Class IV Ca channel blocker (Diltiazem) - Class II Beta blocker (Atenolol/Esmolol) 2. Convert to sinus rhythm/prolong AP duration (if no structural heart problem) - Class IA Na channel blocker (Procainamide) - Class III K channel blocker (Amiodarone, Sotalol) 3. For sinus rhythm with frequent single APCs - If asymptomatic, no tx - occasionally digoxin |
|
|
Treating Atrial Flutter |
- Digoxin - Treats SVT, atrial fib, atrial flutter |
|
|
Treatment options for Atrial Fibrillation |
1. Heart rate control (slow ventricular response rate/AV node conduction) = same drugs for SVT - Digoxin - Ca channel blockers (Diltiazem) - Beta blockers (Atenolol/Esmolol) 2. Rhythm control (get back to sinus rhythm) - Electroconversion - Pharmacologic conversion: Lidocaine (1B), Quinidine/Procainamide (1A), Amiodarone (III) |
|
|
Equine A-fib (most common pathologic arrhythmia in horses) |
- No structural heart disease: cardioversion with Quinidine (1A) - Structural heart disease: control ventricular response rate with Digoxin |
|
|
Accelerated Idioventricular Rhythm (AIR) |
- Fast but stable rhythm, not true tachycardia - Commonly seen with non-cardiac diseases (GDV, post-splenectomy) - Anti-arrhythmic tx often unnecessary: aren't hemodynamically compromised, are electrically stable - Do watch to make sure this doesn't degrade into v-tach |
|
|
When to treat Ventricular Tachyarrhythmia |
- Infrequent VPCs = no tx Requires tx: - Multifocal/multiform VPCs - R-on-T morphology - Fast rate - Hypotensive |
|
|
V-tach Tx in Dogs |
Emergency (IV): - Lidocaine (1B) - Procainamide (1A) Oral: - Sotalol (III) +/- Mexiletine (1B) - Atenolol (beta blocker) and Mexiletine (1B) |
|
|
Ventricular Fibrillation |
NO ventricular contraction NO cardiac output Fatal unless electrocardioversion Defibrillate ("D-fibV-fib") |
|
|
Supra-ventricular Tachycardia Review |
Rate control: - Digoxin - Beta-blockers Slow AV nodal conduction: - Calcium channel blockers Rhythm control - Procainamide (IA) OR - Amiodarone/Sotalol (III) |
|
|
Ventricular Tachycardia Review: Dogs |
First line: - Lidocaine (IV) or Mexiletine (PO) - Class IB Second choice: - Procainamide (IV or PO) - Class IA Third choice: - Sotalol (PO) or Amiodarone (PO) - Class III |
|
|
Ventricular Tachycardia Review: Cats |
- Atenolol - Class II - Compounded Sotalol - Class III |
|
|
Ventricular Tachycardia Review: Horses |
Lidocaine |

