![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Size and weight of the heart |
Fist size Approximately 255g in women and 310g in men |
|
|
|
Referred to as its base |
Upper portion/ both atria |
|
|
|
The lower portion or the ventricles are referred to as its... |
Apex |
|
|
|
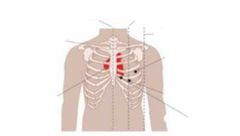
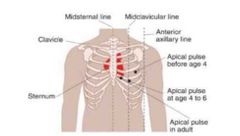
The point where the apex touches the chest wall |
Point of maximal impulse |
|
|
|
Anterior chest area that overlies the heart and great vessels |
Precordium |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Valves located at the exit of each ventricle at the beginning of the great vessel |
Semilunar valves |
|
|
|
What are the 2 semi lunar valves |
Pulmonic valve Aortic valve |
|
|
|
How does heart sound produced |
Valve closure |
|
|
|
Site where it can be auscultate with stethoscope for heart sounds and murmurs |
Precordium |
|
|
|
Arteries that supply oxygen to the neck and head |
Carotid arteries |
|
|
|
Artery that is the only source of blood to the brain, prolong occlusion of these arteries can result in serious brain damage. |
Carotid arteries |
|
|
|
A blowing or swishing sound |
Bruit |
|
|
|
created by turbulence of blood flow due either to a narrowed arterial lumen (a common development in older people) or to a condition, such as anemia or hyperthyroidism, which elevates cardiac output |
Bruit |
|
|
|
Frequently accompanies a bruit, is a vibrating sensation like the purring of a cat or water running through a hose. It, too, indicates turbulent blood flow due to arterial obstruction. |
Thrill |
|
|
|
Veins that drain blood from the head and neck directly into the superior vena cava and right side of the heart. |
Jugular veins |
|
|
|
veins that are superficial and may be visible above the clavicle. |
External jugular vein |
|
|
|
veins that lie deeper along the carotid artery and may transmit pulsations onto the skin of the neck |
Internal jugular vein |
|
|
|
It may indicate right-sided heart failure. |
Bilateral jugular vein distension |
|
|
|
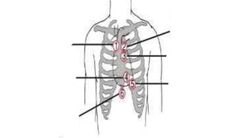
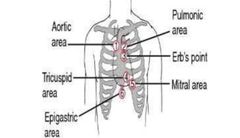
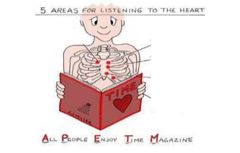
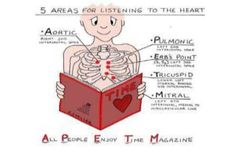
5 areas for listening to the heart |
Aortic Pulmonic Err's Point Mitral Tricuspid |
All People Enjoy Time Magazine |
|
|
Subjective data focus questions |
Chest pain location and radiation Irregular heartbeat, palpitations Family history of heart defect Activity of daily living Usual exercise |
|
|
|
Risk factors for heart disease |
High LDL and Low HDL Family History Upper body obesity Cigarette smoking Diet high in saturated fats and transfatty acid |
|
|
|
Bounding abdominal pulsation |
Aortic aneurysm |
|
|
|
Asymmetric volumes may indicate |
Stenosis or thrombosis |
|
|
|
Decreased pulsation may indicate |
Impaired left cardiac output |
|
|
|
Thickening, hard, rigid, beaded, inelastic walls may indicate |
Arteriosclerosis |
|
|
|
Pulsation Thrills Heaves |
|
|
|
Cardiovascular common symptoms |
Chest pain Breathlessness Ankle swelling Fatigue |
|
|
|
Deficiency of blood in a body part due to construction or obstruction of a blood vessel |
Ischemia |
|
|
|
PMI displaced laterally or lower indicates |
Enlarged heart |
|
|
|
Diffuse lift or heave lateral to apex indicates |
Enlargement or overt activity of left Ventricle |
|

