![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Pericardium |
Fibroserous sac that encloses the heart and roots of the great vessels |
|
|
Anatomy of the heart |
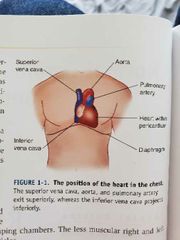
|
|
|
Ventricles |
Right and left ventricles are the main pumping chambers |
|
|
CT |
Computed tomography. Diagnose disease of the great vessels (aortic dissection, pulmonary embolism). Assess pericardial disease and myocardial abnormalities. Detect coronary artery calcification and stenoses |
|
|
CTA |
Computed tomography angiography - CT angiography is a type of medical test that combines a CT scan with an injection of a special dye to produce pictures of blood vessels and tissues in a part of your body. The dye is injected through an intravenous (IV) line started in your arm or hand. |
|
|
Why to have a CTA |
To find an aneurysm (a blood vessel that has become enlarged and may be in danger of rupturing)To find blood vessels that have become narrowed by atherosclerosis (fatty material that forms plaques in the walls of arteries) |
|
|
Ischemic heart disease |
Imbalance between myocardial oxygen supply and demand results in myocardial hypoxia and accumulation of waste metabolites. |
|
|
Angina pectoris |
Uncomfortable sensation in the chest produced by myocardial ischemia |
|
|
Stable angina |
Chronic pattern of transient angina pectoris. Precipitated by physical activity or stress. |
|
|
Variant angina |
Typical angina discomfort, usually at rest, develops because of coronary artery spasm rather than an increase in myocardial oxygen demand |
|
|
Silent ischemia |
Asymptomatic episodes of myocardial ischemia, detected by ECG and other lab techniques |
|
|
Unstable angina |
Pattern of increased frequency and duration of angina episodes produced by less exertion or rest. High frequency to MI if untreated |
|
|
Myocardial infarction (MI) |
Region of myocardial necrosis (death) usually caused by cessation of blood supply; most often results from acute thrombus at site of coronary atherosclerotic stenosis |
|
|
Thrombus / thrombosis |
Blood clot |
|
|
Atherosclerosis |
Atherosclerosis refers to the buildup of fats, cholesterol and other substances in and on your artery walls (plaque), which can restrict blood flow. |
|
|
Stenosis |
Generic term meaning the narrowing of a passage in the body |
|
|
Cardiomyopathy |
disease of the heart muscle that makes it harder for your heart to pump blood to the rest of your body. |
|
|
CMR |
Cardiac MRI - used for evaluating congenital anomalies, such as shunts, and diseases of the aorta, including aneurysms. Also used to assess left / right ventricular mass, intravascular thrombus, cardiomyopathies |
|
|
Coronary MRA |
Coronary magnetic resonance angiography - contrast free angiographic imaging. High sensitivity and accuracy for the detection of important CAD in the left main coronary artery and in the proximal and midportions of the three major coronary vessels. Also useful in delineating coronary artery congenital anomalies |
|
|
Contrast enhanced MRI |
Contrast added MRI to identify infarcted (irreversibly damaged) myocardium and to differentiate it from impaired (but viable) muscle segments |
|
|
Chest radiography |
Detect chamber dilation, identify consequences of stenotic and regurgitant valve lesions and intracardiac shunts. Visualize pulmonary signs of heart failure |
|
|
Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) |
Assess global and segmental ventricular contraction. Identify valvular abnormalities and vegetations. Diagnose consequences of MI. Identify myocardial, pericardial, and congenital abnormalities |
|
|
Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) |
Similar to TTE but higher resolution. Viz intracardiac thrombus, evaluate prosthetic valves |
|
|
Cardiac catherization |
Gold standard to assess intracardiac pressures and to identify and trade coronary artery stenoses. Evaluate intracardiac pressures, viz ventricular contractile function and regurgitant valve lesions. Identify coronary anatomy vans severity if stenosis |
|
|
Nuclear SPECT imaging |
Detect, quantify and localize myocardial ischemia. Perform stress testing in patients with ECG abnormalities. Distinguish viable myocardium vs scar tissue |
|
|
Positron emission tomography (PET) |
Distinguish viable myocardium from scar tissue. Evaluate contractile function |
|
|
MRI |
Assess myocardial structure and function (e.g., ventricular mass and volume, neoplastic disease, intracardiac thrombus, cardiomyopathies). Diagnose aortic and pericardial disease. Detect areas of ischemic vs infarcted myocardium |
|
|
Vasodilation |
Widening of blood vessels |
|
|
Atherogenesis |
the formation of fatty plaques in the arteries. |
|
|
Ischemic heart disease |
Condition in which imbalance between myocardial oxygen supply and demand results in myocardial hypoxia. Most often caused by atherosclerotic disease of coronary arteries |
|
|
Angina pectoris |
Uncomfortable sensation in the chest and neighboring anatomic structure produced by myocardial ischemia |
|
|
Clopidogrel |
Platelet P2Y ASP receptor antagonists. Can be used with aspirin to prevent platelet activation and aggregation. Can be used in place of aspirin and has been shown to be better in combination with aspirin in reducing death and ischemic complications |
|
|
Lipid regulation therapy (statins etc) |
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, aka statins, lower MI and death rates in patients with established coronary disease and those at high risk of developing CAD. Current national guidelines say everyone should receive high intensity statin with a goal of 50% reduction in LDL |
|
|
ACE Inhibitors |
Angiotensin-converting enzyme. Some trials have shown reduced rates of death, MI, and stroke |
|
|
Revascularization |
Pursued if patients angina symptoms don't respond to antianginal drugs or the patient is found to have high risk for coronary disease for which revascularization is known to improve survival |
|
|
Revascularization techniques |
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) |
|
|
Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty |
Balloon tipped catheter inserted and maneuvered to the stenotic segment. Balloon inflates and basically compresses the atherosclerotic plaque. Can insert a coronary stent for more long term benefits as 33pct of patients develop recurrent symptoms |
|
|
Coronary stents |
Developed for implantation during PCI. Shown to significantly reduce rate of restenosis. They are thrombogenic so often aspirin + clopidogrel is crucial to prescribe |

