![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are 6 types of Cardiac Masses?
|
1.cardiac tumors
2. thrombus 3. vegetation 4. Iatrogenic material 5. Normal variants 6. Extracardiac structures |
|
|
what are the 2 types of Cardiac tumors
|
Primary and Secondary
|
|
|
Which one is more common primary or secondary?
|
Secondary is more common for cardiac tumor
|
|
|
Can you tell on echo if the tumor is benign or malignant?
|
NO, cant definitely distinguish between benign and malignant
|
|
|
On echo how do we assess cardiac tumors?
|
location, extent of mass, size of mass, where it originates.
|
|
|
Are all secondary tumors malignant? why?
|
Yes, bc they metastasis from somewhere else, they occur in 10% of all Fatal malignancy.
|
|
|
What is the the most common primary CA that metastasize (spreads) to the heart?
|
LUNGS, 30% of cardiac tumors are from the lungs
|
|
|
Other Common primary CA that metastasize to the heart?
|
breast, kidney, liver, melanoma, AIDs related Lymphoma, Leukemia, Osteogenicsarcoma (bone CA)
|
|
|
What are the tumors that metastasize to the IVC and as a result spread into the RA?
|
Hypernephroma, Hepatoma, Intravenous leiomyomatosis (rare)
|
|
|
If you see a mass in the RA you need to evaluate?
|
IVC
|
|
|
What are the two types of Primary Tumors?
|
Benign & Malignant
|
|
|
Do we treat benign cardiac tumors?
|
Yes. bc they can be obstructive and break off and cause emboli.
|
|
|
Benign cardiac tumors can cause?
|
systemic symptoms, embolic events, Arrhythmia, chest pain, heart failure.
|
|
|
What are the 4 types of Primary Benign tumors?
|
Myxoma, Fibroma, Rhabdomyomas, Papillary Fibroelastoma
|
|
|
What is the most common Benign cardiac tumor ?
|
MYXOMA, Accounts for 20%-30% of ALL intracardiac tumors
|
|
|
Myxoma is most commonly located?
|
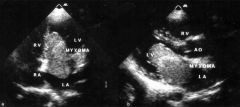
LA, 3X more common in LA than on the RA
|
|
|
What is the most common presentation of myxoma?
|
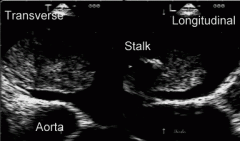
mass attached by a stalk to the middle of IAS
|
|
|
Population of patients who tend to have Myxoma ?
|
young, family hx
|
|
|
Myxoma mimics what type of stenosis?
|
MS bc its obstructive the AV valve
|
|
|
Ventricular myxoma what type of obstruction will you have?
|
LVOT obstruction
|
|
|
What type of obstruction can you have with Myxoma?
|
Impaired ventricular filling, prevents filling, CH won't get filled up.
|
|
|
Fibroma usually located in?
|
LV wall, Ventricular septum, endocardium, Apex
|
|
|
Fibroma presentation?
|
echogenic- multiple calcification, see boarders clearly.
|
|
|
Do you think fibroma has any hemodynamic consequence?
|
No, unless it grows significantly in the LV Cavity. However possibility of conduction abnormalities
|
|
|
What is the most common cardiac tumor in pediatric patients?
|
Rhabdomyomas
|
|
|
Rhabdomyomas commonly seen in patents with
|
tuberous sclerosis
|
|
|
Rhabdomyomas location and presentation
|
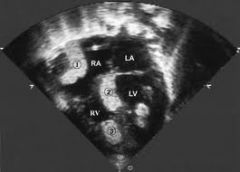
well circumscribed echogenic masses, Multiple masses present in the RV, IVS, Myocardium
|
|
|
Papillary Fibroelastoma Clinical Presentation
|
Irregular shape, echogenic, mimic valvular vegetation,
|
|
|
Papillary Fibroblastoma is commonly found on what valve?
|
Aortic valve
|
|
|
Fear complication of Papillary Fibroblastoma
|
RISK of EMBOLI
|
|
|
What are the 3 types of primary malignant tumors?
|
Angiosacroma, Rhabdomyomasacroma, Fibrosacroma
|
|
|
Angiosacroma located in
|
RA and associated with pericardial effusion
|
|
|
Rhadomyomasacroma & Fibrosacroma occurs
|
anywhere in the heart
|
|
|
what is the most common cause of thrombus in the heart?
|
stasis of blood
|
|
|
what kind of situation will cause stasis of the blood?( 3 scenarios)
|
Dilated CH, Obstruction & stagnation of blood flow, decrease Wall contractility (WMA)
|
|
|
The wall behind the thrombus is a pt with POST MI will be
|
Diskinetic, Akinetic
|
|
|
why is thrombus happening?
|
stasis of blood
|
|
|
most common location for thrombus? why?
|
apex of LV , common : POST MI
|
|
|
what will wall look like behind the thrombus?
|
dead, not moving, does not thicken in systole.
|
|
|
LA thrombus is associated with pts with
|
Rheumatic MS
|
|
|
Iatrogenic material
|
needles, ballons
|
|
|
what are examples of Extracardiac structures
|
diaphragmatic hernia, pericardial cysts, pseudoaneurysm.
|

