![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the primary determinant of arterial resistance?
|
Radius of resistance vessels
|
|
|
True or false. The only regulator of cardiac output is the heart itself.
|
False!
Also depends on VASCULAR FUNCTION because the cardiovascular system is a loop. |
|
|
What does the cardiac function curve define?
|
Ventricular output as a function of ATRIAL pressure.
|
|
|
What does the vascular function curve define?
|
Venous return as a function of atrial pressure.
|
|
|
What is steady state cardiac output?
|
Ventricular output occurring in the INTACT system (heart and blood vessles operating together) = VENOUS RETURN.
|
|
|
THE CARDIAC FUNCTION CURVE DETERMINES _________________AS A FUNCTION OF ________________. THUS, IN THE FORMALLY ISOLATED HEART, ATRIAL PRESSURE IS THE______________ AND __________________ IS THE DEPENDENT VARIABLE. HOWEVER, IN THE INTACT SYSTEM, ATRIAL PRESSURE IS NOT AN _________________, BECAUSE IT IS DETERMINED BY THE SIMULTANEOUS ACTIVITY OF THE VENTRICLES AND THE BLOOD VESSELS.
� |
ventricular output
atrial pressure independent variable ventricular output independent variable |
|
|
What is atrial pressure determined by?
Which is determined by.... |
Volume of fluid in the atria
Vascular function (causing blood to return to atria) and by ventricular function (causing blood volume to leave atria) |
|
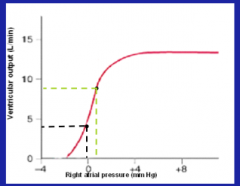
What does this graph show?
|
Ventricular output as a function of right atrial pressure.
The greater the atrial pressure, the greater the ventricular output (up to a certain physiological level). |
|
|
Why is increased atrial pressure associated with increased ventricular output?
|
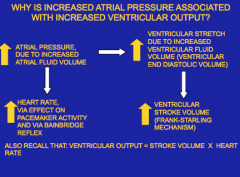
This is why.
|
|
|
What are factors that directly set the cardiac function curve?
|
SYMPATHETIC AND PARASYMPATHETIC ACTIVITY
INTRINSIC VENTRICULAR EFFECTIVENESS AFTERLOAD (AORTIC PRESSURE) INTRAPLEURAL (INTRATHORACIC) PRESSURE |
|
|
What is the influence of sympathetic/parasympathetic activity on the cardiac function curve?
|
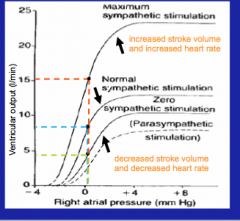
Sympathetic activity at rest is always greater than zero --> the cardiac curve can move up or down with change in activity
Parasympathetic activity changes the cardiac curve opposite to sympathetic activity via effect on heart rate. |
|
|
What is the influence of intrinsic ventricular effectiveness on cardiac function curve?
|
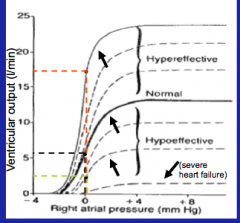
At any right atrial pressure, the ventricular output can change, based on the change of cardiac function curve. HYPEREFFECTIVE OR HYPOEFFECTIVE
There are degrees of intrinsic effectiveness depicted by the various cardiac function curves. Note the severely diminished curve in systolic heart failure. |
|
|
What is the influence of afterload on cardiac function curve?
|
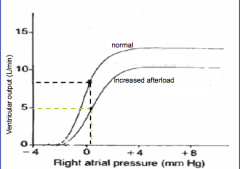
Increase in afterload decreases stroke volume.
|
|
|
What is the influence of intrapleural (intrathoracic) pressure on the cardiac function curve?
What is the net stretch on a ventricle determined by? |
Net stretch = intraventricular pressure (end diastolic pressure) minus extraventricular pressure (intrapleural or intrathoracic pressure)
As pressure outside decreases (deep breathing), net stretch is increase = greater ventricular output *note that flat portion of curve remains the same |
|
|
Why does intrapleural pressure influence the cardiac curve?
|
Net stretching = end diastolic pressure (pressure inside ventricles) - intrapleaural pressure (pressure surrounding ventricles)
Increase intrapleural pressure = decreased ventricular stretch = decrease stoke volume |
|
|
What is the vascular function curve?
|
Defines venous return as a function of arterial pressure
INDEPENDENT OF CARDIAC OUTPUT |
|
|
Draw the vascular function curve and label
Plateau, transitional zone, down slope, mean systemic filling pressure What sets x-axis intercept? What sets the slope of the curve? |
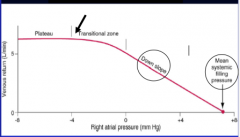
You did it! Yay!
Systemic filling pressure Resistance to venous return |
|
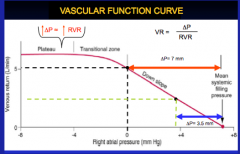
Need some help understanding this one.
|
Maybe it will happen in class?
|
|
|
What is filling pressure (why was this put AFTER the graphs)?
|
Pressure required to fill blood vessels BEYOND their intrinsic volume.
THE FILLING PRESSURE SHOULD REALLY HAVE BEEN TERMED THE “OVERFILLING” PRESSURE, BECAUSE IT IS THE PRESSURE REQUIRED TO FILL THE BLOOD VESSELS BEYOND THEIR INTRINSIC CAPACITY i.e. THE UNSTRESSED VOLUME. |
|
|
What is intrinsic volume?
|
"Unstressed volume"
Volume that just fills the blood vessels completely --> doesn't require "stressing" or stretching them |
|
|
How do you measure the filling pressure?
|
THE FILLING PRESSURE CAN ONLY BE MEASURED AT ZERO CARDIAC OUTPUT, BECAUSE IN THE FUNCTIONING SYSTEM WITH A CARDIAC OUTPUT, THERE IS NO UNIQUE VASCULAR PRESSURE AND THE PRESSURE REFLECTS THE FUNCTION OF BOTH VENTRICULAR OUTPUT AND VENOUS RETURN.
� |
|
|
What components determine filling pressure?
|
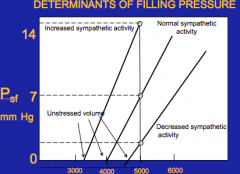
Unstressed volume (at zero at this point) = anything beyond is filing pressure
Compliance of blood vessels Blood volume |
|
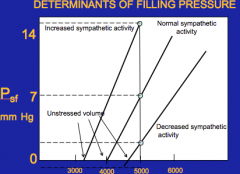
What is the effect of sympathetic activity?
|
The greater the sympathetic activity, the lesser the unstressed volume --> less the compliance due to stiffer blood vessels
Opposite for decreased sympathetic activity Review this slide! |
|
|
What are the physiological determinants of vascular function curve?
|
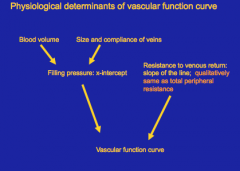
Reproduce this slide!
|
|
|
What is the effect of changing systemic filling pressure without changing peripheral resistance on vascular function curve?
Think about the slope. |
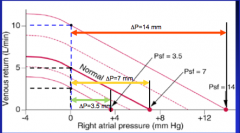
Slope will stay the same because resistance is the same.
If you double filling pressure and keep resistance the same, the flow must double also. Review Hassid's notes on this also. |
|
|
What is we change the total peripheral resistance? What effect does this have on the vascular function curve?
Think about the slope again --> the slope reflects resistance! |
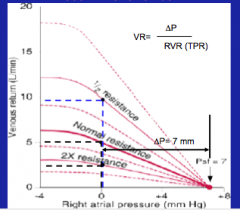
Increase in resistance = decrease in slope (counter clockwise rotation)
Review Hassid's notes on this also. |
|
|
What two things can cause venous return to change?
|
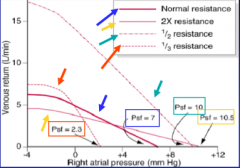
Changes in filing pressure and/or TPR
|
|
|
What are steady state cardiac output, venous return and atrial pressure (end diastolic volume) determined by?
|
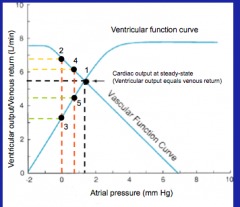
Point of intersection of the cardiac function curve and the vascular function curve.
Review Hassid notes. |
|
|
WHY IS THE INTERSECTION POINT OF CARDIAC FUNCTION CURVE AND VASCULAR FUNCTION CURVE THE STEADY STATE VALUE FOR CARDIAC OUTPUT AND VENOUS RETURN?
� |
BECAUSE AT ANY OTHER ARBITRARY VALUE OF ATRIAL PRESSURE, THE VENTRICULAR OUTPUT (AS DETERMINED BY THE CARDIAC FUNCTION CURVE) IS DIFFERENT THAN THE VENOUS RETURN (AS DETERMINED BY THE VASCULAR FUNCTION CURVE) AND THUS, ATRIAL VOLUME WILL CHANGE AND EVENTUALLY REACH THE INTERSECTION OF THE TWO CURVES. AT THE INTERSECTION POINT, VENTRICULAR OUTPUT IS EXACTLY EQUAL VENOUS RETURN, THUS STABILIZING ATRIAL PRESSURE, (END DIASTOLIC PRESSURE) VENTRICULAR OUTPUT AND VENOUS RETURN.
� |
|
|
What is the effect of moving the ventricular function curve without moving vascular function curve?
From increase in sympathetic nerve stimulation. |
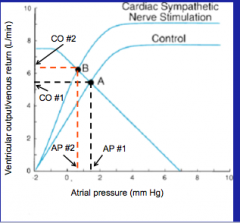
Sympathetic to the heart, move the cardiac function curve upward. We see an increase in ventricular output at lower atrial pressure (which reflects venous pressure).
|
|
|
What does hypervolemia do to the vascular function curve?
|
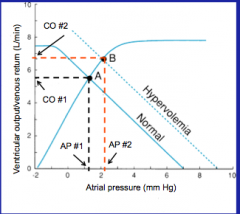
Moves it to the right due to increased blood volume = slope of the line is not changed (TPR remains constant)
|
|

Read through this in the notes.
|
Then update
|
|
|
What is the influence of atrial pressure on pulmonary edema formation?
|
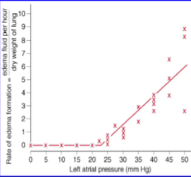
Edema becomes significant when atrial pressure rises about 20 mmHg
|
|
|
What does hemorrhage involve?
Continue making more cards after class! |
Hypovolemia = loss of blood
|

