![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Bradycardia |
Cold: warm pt. Epinephrine titrated to effect or paced rhythm. |
|
|
Tachycardia |
SVT or other narrow ventricular complex rhythms. |
|
|
SVT |
Adenosine 6mg followed by 20 ml fluid bolus (flush). 1-2 minutes second dosage of 12mg by 20 ml fluid bolus. Cardiovert: 50 joules then 100 Joules |
|
|
Narrow Complex Rhythms |
Treat the H's and T's |
|
|
H-ypovolemic |
Dehydrated: fluid bolus Wet lung sounds- CPAP |
|
|
H-ypoglycemic |
Glucagon will only work once and high risk for reoccurrenceD50 with 100 mg Thiamine IV Stabilize with protein and carbohydrate |
|
|
Acidosis/Alkalosis |
Metabolic acidosis - Sodium BicarbonateRespiratory acidosis – Ventilate and increase respirationsRespiratory Alkalosis and metabolic alkalosis – slow pt breathing |
|
|
Toxic Substances |
Give Antidote |
|
|
Narcan |
Narcan Opiod antagonist |
|
|
Romazacon |
Benzodiazepine receptor antagonist Aka Flumazenil |
|
|
Dd |
Dd |
|
|
Atropine |
Organophosphates- parasympathetic agonist |
|
|
Alcohol |
Fluid bolus |
|
|
Vtach with a Pulse |
Antidysrhythmics (lidocaine or amiodarone)- with pulse dosages Synchronized cardioversion starting at 100 J |
|
|
Pulse less Vtach or Vfib |
CPR DefibrillationEpinephrine every 3-5 minutesAmiodarone |
|
|
Asystole PEA |
CPR Epinephrine every 3-5 |
|
|
Torsade’s |
Magnesium! |
|
|
Chest pain |
O2 if under 95% ASA 12 lead IV Nitro if BP over 90 and no right sided. Have IV established. Check for contraindications. |
|
|
12-Lead EKG
|
Rate Rhythm Hemiblock BBB Elevation or Depression |
|
|
Hemiblock
|
Can be Anterior, Posterior, or Ventricular |
|
|
Branches of Heart
|
One Right Two Left Can have right and/or left hemiblock |
|
|
Determine if Hemiblock
|
Leads I, II, and III UP or DOWN? Refer to cheat sheet or MEMORIZE! |
|
|
Hemiblock Cheat Sheet
|
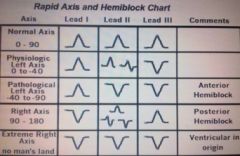
|
|
|
Anterior Hemiblock
|
Lead I: UP Lead II: DOWN Lead III: DOWN |
|
|
Posterior Hemiblock
|
Lead I: DOWN Lead II: UP or DOWN Lead III: UP |
|
|
Ventricular Hemiblock
|
ALL LEADS DOWN Wide QRS without P waves |
|
|
Bundle Branch Block Description
|
Entire left branch is blocked Can also present with a hemiblock Found in V1 |
|
|
BBB- Criteria
|
Wide QRS UP or DOWN means RIGHT or LEFT bundle branch block UP: RIGHT |
|
|
Bifascicular block: Three types
|
Four times at risk for an MI 1. Left BBB 2. Anterior Hemiblock and Right BBB 3. Posterior Hemiblock and Right BBB |
|
|
MI on 12-Lead
|
Elevation or depression in all leads Elevation: Current MI happening, intervene with MI treatments Depression: Former MI or ischemia |
|
|
MI Treatment
|
Aspirin Morphine Nitro (Not in right sided MI) Oxygen if less than 96% TPA- breaks up blood clots |
|
|
MI Elevation |
Anterior: V3, V4 Anterolateral: I, aVL, V3, V4, V5, V6 Anteroseptal: V1, V2, V3, V4 Inferior: II, III, aVF Lateral: I, aVL, V5, V6 Posterior: NONE will show on 15 Lead Septal: V1, V2 |
|
|
MI Elevation Cheat Sheet
|
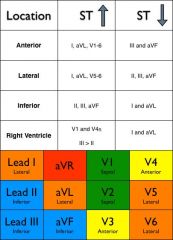
|
|
|
Pericarditis
|
Elevation in all 6 leads Can lead to Tamponade |
|
|
Reading 4 Lead
|
Regularity Rate P waves? 1 for every QRS? QRS wide or Narrow |

