![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
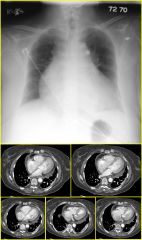
|
Findings:
– Cardiomegaly – Enlarged RA – Tricuspid valve displaced into RV cavity – Small RV – Small pericardial effusion Ebstein’s Anomaly – Massive cardiomegaly – Decreased pulmonary vascularity – Posterior and Septal leaflets of tricuspid valve displaced into RV – RV proximal to valve leaflets is thin (“atrialized right ventricle”) – ASD with R-to-L shunt & cyanosis is common in Ebstein’s patients |
|
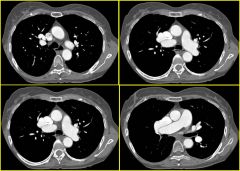
|
Findings:
– Massively enlarged RA – Enlarged RV – Atrial septum intact – Anomalous RUL pulmonary drainage to SVC Partial Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return – R lung 2-10 times more common than L – Atrial septum usually intact |
|
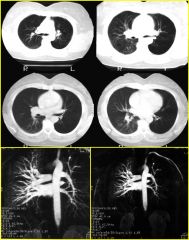
|
Findings:
– Decreased vasculatity of L lung – Hyperlucent L lung on CXR and CT – Mild hyperinflation L lung Swyer-James Syndrome – Oligemic, hyperlucent lung – Often see bronchiectasis on HRCT – Air trapping on HRCT – Acquired in childhood; probably secondary to viral infection – Bronchitis, bronchiolitis, bronchiolitis obliterans, bronchiectasis and destruction of lung parenchyma |
|
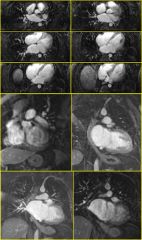
|
Findings:
– Enlarged LA with abnormal septum between pulmonary vein confluence and mitral valve – ASD (PFO) Cor Triatriatum – LA and mitral valve are separated by a constriction or membrane – Separating membrane may have a single or multiple orifices – PAPVR, ASD, VSD, coarct, AV canal common |
|
|
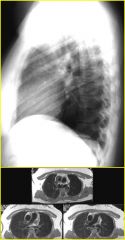
Findings:
– CXR: mass posterior to trachea on lat CXR – MR: L pulm artery originates from R pulm art., courses between trachea and esophagus Pulmonary Sling – Sling leads to airway obstruction; can mimic asthma – High association with tracheal anomalies such as tracheomalacia and complete tracheal rings |
|
|
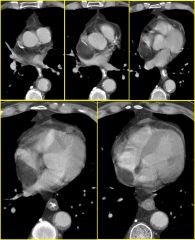
Findings:
– Very low attenuation mass along posterior RA and interatrial septum – Some mass effect on R pulm veins, but no chamber enlargement Atrial Septal Lipoma – Fairly common – Usually incidental finding and of no clinical significance – Fat attenuation on CT – Potential DDx: Atrial Myxoma, Atrial Thrombus, Intra-cardiac neoplasm |
|
|
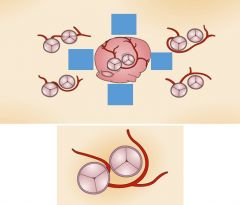
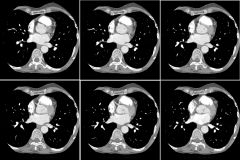
Findings
Left main coronary artery arises from R coronary ostium LMA passes between aorta and pulmonary artery Anomalous Left Coronary Artery “Malignant” anomaly in this case - high risk of sudden death due to LMA compression between Ao and PA |
|

|
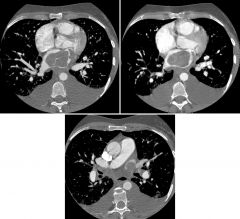
Findings
RA mass, arising from floor of RA. Mass touches tricuspid valve but does not obstruct. Atrial Myxoma (Right) But wait… there’s more… |
|
|
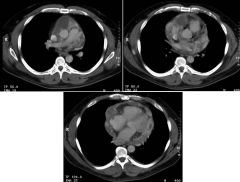
Findings
Space-occupying mass in LA Enhancing vessel within mass Pleural effusions, pulmonary edema Atrial Myxoma (Left) DDx (especially on right) includes thrombus (both bland and tumor thrombus from RCC, HCC, etc), mets, sarcoma, fibroma, lymphoma |
|
|
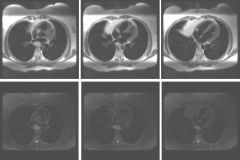
Findings
LA mass High signal on Gd+ T1 and T2 imaging Intraatrial Pheochromocytoma |
|
|
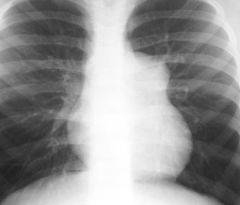
Fingings
Thick, irregular pericardium Multiple cystic/complex areas Pericardial effusion Pericardial Sarcoma DDx includes pericardial mets (esp. lung/breast/esophagus), lymphoma, complex infectious pericarditis/TB |
|
|
Findings
“Mass” near AP window Not in left hilum (can still see hilar vessels) Not posterior mediastinum (can still see aortic arch and it silhouettes the top of the L heart border) ...Thus, must be anteriorly located Partial Absence of Pericardium Partial (localized) absence on left can result in herniation of LA appendage or LV thru defect Can be assoc. w/ chest pain Partial absence on right is very rare. RA appendage or RV, even right lung, can herniate Complete absence usually asymptomatic and benign Here’s another case… |
|
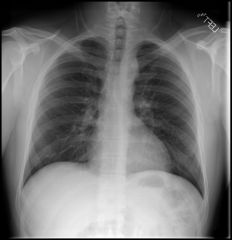
|
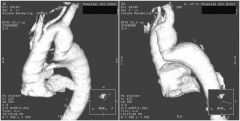
Findings
Extra border above aortic arch, along left paratracheal margin No rib notching or other abnormality Pseudocoarctation of aorta |
|
|
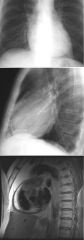
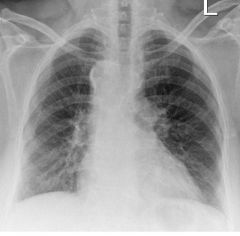
Findings
Calcification of pericardium on CXR Thickened pericardium on MR (normal should be a barely perceptible 3 mm) Bowing of the IV septum in towards the left ventricle (indicates increased R heart pressures) Constrictive Pericarditis Etiologies: Infection, prior surgery, trauma, mixed connective tissue disease |
|
|
Right Arch / Aberrant Lt SCA
|
|
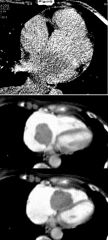
|
Atrial Myxoma
|
|
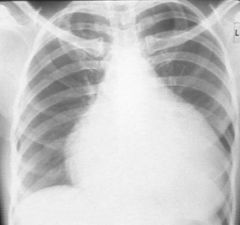
|
Pericardial Effusion
Tuberculous or malignant pericarditis Cardiomyopathy Ebstein's anomaly |
|
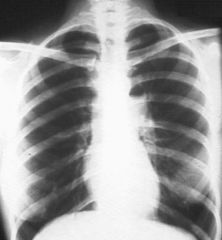
|
Pulmonic Stenosis
|
|
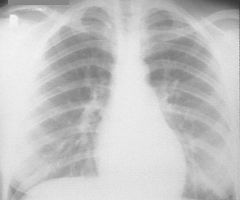
|
PDA
|
|
|
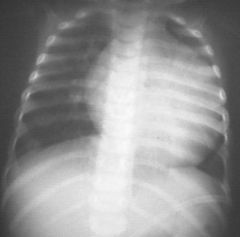
Transposition of Great Vessels
Egg on a string |
|
|
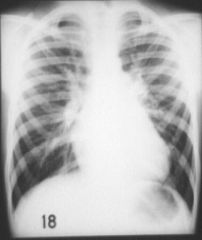
ASD
|
|
|
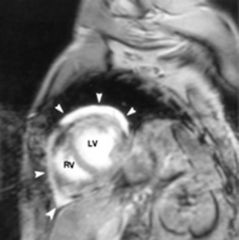
Pericardial Effusion
|
|
|
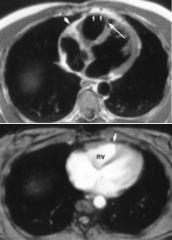
Arrhythmogenic RV Dysplasia
|
|
|
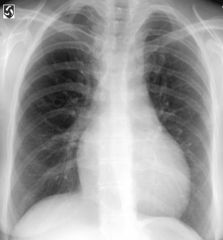
Coarctation
|
|
|
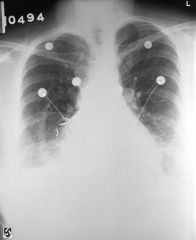
Hypoplastic Lung
Scimitar Syndrome |
|
|
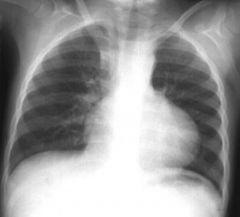
Tetralogy of Fallot
|
|
|
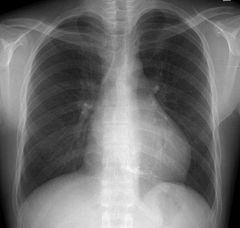
Tetralogy of Fallot
|
|
|
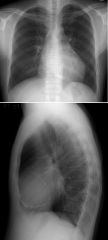
Constrictive Pericarditis
|
|
|
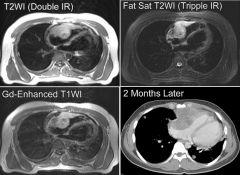
Cardiac Angiosarcoma
|
|
|
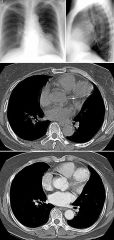
Coronary Artery Aneurysm
|

