![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Identify the correct lead placement for a 12 lead ECG:
|
RA: right arm
RL: right leg LA: left arm LL: left leg V1: 4th intercostal space, right sternal boarder V2: 4th intercostal space, left sternal boarder V3: Halfway between V2 and V4 V4: 5th intercostal space, left mid clavicular line V5: Anterior auxillary line, left V6: Mid auxillary line, left |
|
|
How to identify a good trace with an ECG:
|
- ask patient to remain as still as possible
- wait approximately 10 seconds for a good trace to emerge |
|
|
What immediate nursing actions should you take if your patient has chest pain?
|
- Sit patient up in bed
- put on O2 mask, 8-10L - request for a GTN order - take vital signs (OBS) - Ask questions about chest pain - ECG - depending on setting - MET call - document later |
|
|
What questions do you ask to confirm that your patient is experiencing chest pain?
|
PQRST Method:
Provokes - What improves it - What makes it worse? Quality - What type of pain is it? e.g stabbing, burning, crushing? Radiates - Does the pain radiate? - Is it localised to one area? - Did it start elsewhere? Severity: - How bad is the pain? (pain score 0-10) Time: - When did the pain start? OTHER: - have you had this pain before? - if yes, what do you normally do to relieve it? - it is worse on inspiration? - Any recent chest trauma? - Any family history of chest pain? |
|
|
Identify normal sinus rhythm:
|
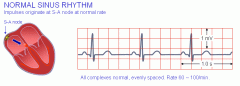
Rate: 60-100 bpm
Rhythm: regular P waves before QRS: yes PR interval: 3-5 small squares QRS complexes look alike: yes |
|
|
Identify Atrial Fibrillation:
|
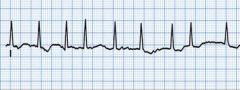
Rate: 350-400 bpm
Rhythm: irregular P waves before QRS: no PR interval: NA QRS complexes look alike: yes |
|
|
Identify Ventricular Tachycardia:
|
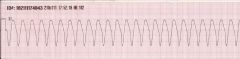
Rate: 101-250 bpm
Rhythm: regular ventricular rhythm P Waves before QRS: no PR interval: not measurable QRS complexes look alike: yes, wide and bizarre |
|
|
Identify Ventricular Fibrillation
|
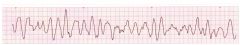
Rate: Not discernable
Rhythm: rapid, unorganised P waves before QRS: no PR interval: none QRS complexes look alike: none |
|
|
Identify Asystole:
|
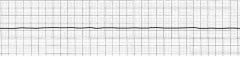
no electrical activity
- appears as a 'flat line' |
|
|
Identify ST Elevation:
|
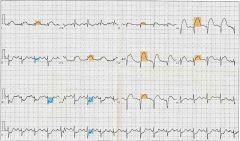
(orange highlights in image)
|
|
|
Identify ST Depression:
|
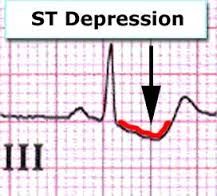
|
|
|
What does it mean is the ECG shows ST elevation?
|
Myocardial infarction
|
|
|
What does it mean if the ECG shows ST depression?
|
Myocardial ischaemia
|
|
|
What is a STEMI?
|
ST elevation myocardial infarction - blockage
|
|
|
What is a NSTEMI?
|
non-ST elevation myocardial infarction - partial blockage
|
|
|
What are some other causes of chest pain?
|
- Pulmonary embolism
- reflex - fractured rib/sternum - chest trauma - anxiety - pneumothorax etc |
|
|
What medications are used to treat cardiac chest pain? How do they work?
|
ACE Inhibitor: vasodilator - decrease resistance
Anticoagulants: prevent clots forming, or existing clots from increasing in size. eg. aspirin Beta blockers: decrease heart contractility and CO Calcium channel blockers: decrease contractility, relax blood vessels Diuretics: reduce volume of blood --> lowered BP Digoxin: slows arrythmias Morphine: Pain managment GTN: vasodilator |
|
|
What observations do you need to take with these medications?
|
- monitor HR
- monitor BP - monitor SP02 |

