![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
102 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
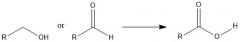
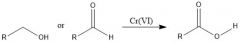
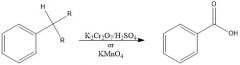
What oxidizing aromatic side-chains, what is required?
|
A C-H benzylic bond and very strong oxidizing agents:
K2CrO7/H2SO4 or KMnO4 |
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
List some ways to synthesize a carboxylic acid.
|
Reducing benzylic side-chains, ozonolysis of alkenes, organometallic addition to CO2, nitrile hydrolysis
|
|
|
How does organometallic additions to CO2 work?
|

|
|
|
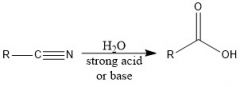
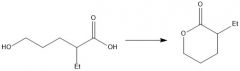
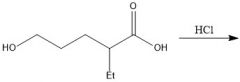
When should you use nitrile hydrolysis to make a carboxylic acid and what are the conditions?
|
When you have a halide that can be substituted with SN2 for a nitrile group
|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
How do you protect an alcohol?
|

|
|
|
How do EWG and EDG affect acidity of carboxylic acids?
|
EWG will increase acidity
EDG will decrease acidity |
|
|
What do carboxylates look like, how are they made, and what are they used for?
|
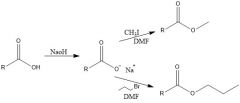
They are made by deprotonating the alcohol. They are used for SN2
|
|
|
How does the reaction between carboxylic acid and diazomethane work?
|
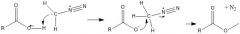
|
|
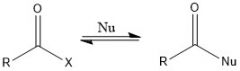
Why does the nucleophilic acyl substitution not have an SN2 mechanism?
|
x = OH, OR, Cl, SR, NR2, etc
There is too much steric hindrance between R and X |
|
|
Mechanism of the neutral nucleophilic acyl substitution?
|
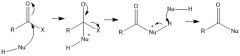
|
|
|
How does base catalyzed nucleophilic acyl substitution work?
|
The base will protonate the C=O, activating it, and it will also protonate the X, making it a better leaving group.
|
|
|
What is the most reactive carboxylic acid derivative and which si the least reactive?
|
acyl chloride > anhydride > ester > CA > amide > nitrile
|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|
Mechanism for acid catalyzed Fischer esterification?
|

|
|
|
Mechanism for acid catalyzed ester hydrolysis?
|

|
|
|
Mechanism for base catalyzed ester hydrolysis?
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
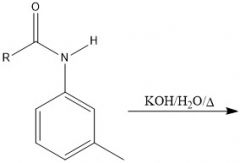
|

|
|

|

|
|
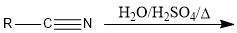
|

|
|

|
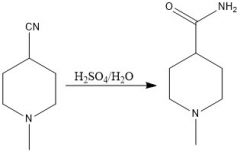
|
|

|

|
|
|
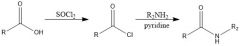
What are 3 reagents used to turn a CA into an acyl chloride?
|
SOCl2, PCl3 and PCl5
|
|
|
How does SOCl2 turn CA into acid chloride?
|

|
|
|
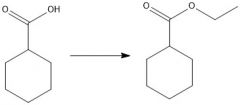
What's a method of forming an ester?
|
Acid chloride + alcohol
|
|

|
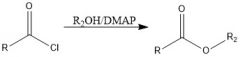
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
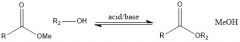
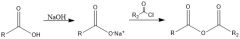
When is transesterification ever useful?
|
When you have lots of R2OH and it's cheap. It is used in excess
|
|
|
What is a bad way to make an amide?
|
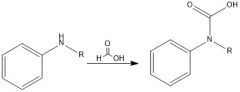
Directly try to put amine and CA together... it will only yield an ammonium salt and a carboxylate
with the exception being formyl derivatives |
|
|
What is a good way to make an amide? Draw the overall scheme
|
ACYL CHLORIDES + CA = AMIDES :D
socl sokkl sokkul |
|
|

|
|

|

|
|

|
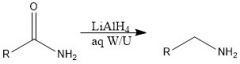
|
|
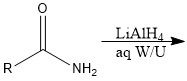
|

|
|
|
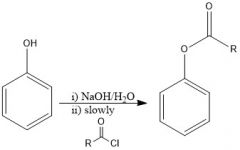
What are Schotten-Baumann conditions and what are they used for?
|
It is when you have an amine in NaOH/H2O, and slowly add your acid chloride. The result amide will precipitate out of your solution. Can also form an ester out of this.
|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
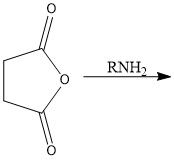
|

|
|
|
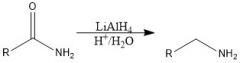
Which reducing agents will and will not reduce a CA?
|
LiAlH4 and BH3 will reduce CA
NaBH4 and H2/Pd will not reduce CA |
|
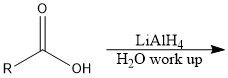
|
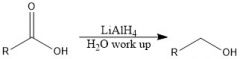
|
|

|
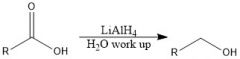
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
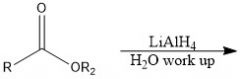
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
How does DIBAL-H reduce carboxylic acids?
|
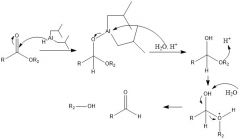
|
|
|
What are the conditions for DIBAL-H reduction?
|
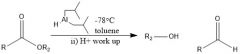
|
|
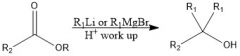
Intermediates?
|
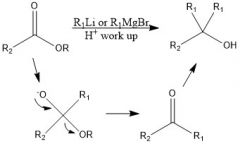
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
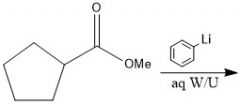
|
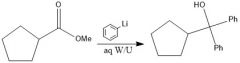
|
|

|
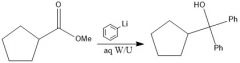
|
|
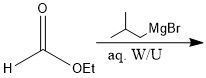
|

|
|
|
When adding to a carboxylic acid, what is the difference between products when using organolithium and Grignard reagents?
|
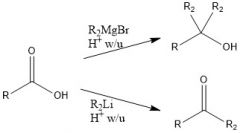
With Grignard, you add the alkyl group twice, and you have an alcohol, but with organolithium, the alkyl group only adds once and the carbonyl stays intact.
|
|
|
How does organolithium reagent reduce carboxylic acids?
|

|
|

|
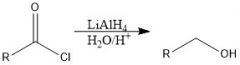
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
What is LiAlH(OtBu)3 used for and how is it made?
|
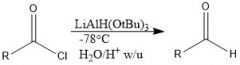
It is a reducing agents which is attenuated, and won't reduce aldehydes. You can use it to reduce acyl chlorides to an aldehyde.
|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|
|
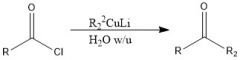
What's so special about organocopper reagents?
|
RCuLi - do not reduce ketones - turn acyl chloride into ketone
|
|

|
NR
|
|
|
How to make organocopper reagent?
|

|
|

|
|
|
|
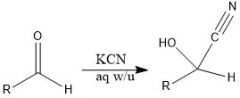
How are nitrile groups oxidized to aldehydes?
|

|
|
|
How are nitrile groups oxidized to ketones?
|

|
|
|

|
|
|
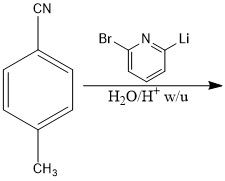
Show a map of how R-CN can be utilized.
|

|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
How to Weinreb?
|
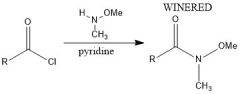
|
|
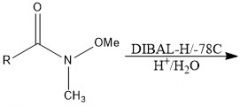
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|

