![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Two types of carbon compounds |
- aldehyde -ketone |
|
|
|
Aldehyde contain ____ R groups |
1 |
|
|
|
Ketones contain ____ R groups |
2 |
|
|
|
Aldehyde |
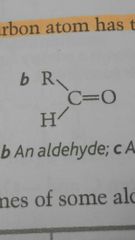
|
|
|
|
Ketone |
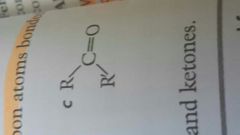
|
|
|
|
Test for Carbonyls |
- Brady's reagent (2,4- dinitrophenylhydrazine) -deep orange precipitate formed in the presence of a carbonyl compound |
|
|
|
Tests to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones |
- Tollen's Reagent - Fehling's Reagent - acidified potassium dichromate/ potassium manganate |
|
|
|
Tollen's Reagent [Ag(NH3)2]+ |
- when warmed with tollen's Reagent aldehydes are oxidized to carboxylic acids - the silver complex ions are reduced to silver atoms - silver mirror is seen on the side of the test tube - ketones do not reacts with tollens' reagent as they cannot be oxidized to carboxylic acids |
|
|
|
How is Fehling's solution made |
- by mixing Fehling's A (which contains Cu2+ (aq) ions) and Fehling's B (contains a complexing reagent and an alkali) |
|
|
|
Reaction with Fehling's solution |
- when warmed with Fehling's solution, aldehydes are oxidized to carboxylic acids. - the blue Cu2+ ions changes to an orange red precipitate of copper (I) oxide -Cu2+ ions oxidize the aldehyde and are themselves reduced to the copper (I) state - ketones cannot be oxidized to carboxylic acids |
|
|
|
Reactions with acidified potassium manganate or potassium dichromate |
- this reaction is done under reflux with excess oxidizing agent -aldehydes are oxidized to carboxylic acids - the purple potassium manganate decolourizes and turns brownish (MnO4-(purple) -------> Mn2+(very pale pink) / MnO2 (brown) - in the case of potassium dichromate, the solution changes from orange to green. ( Cr2O72-(orange) -----> Cr3+(green) ) - ketones are not oxidized |
|
|
|
Nucleophilic addition reactions with carbonyl compounds |
..... |
|
|
|
The C=O bond in aldehydes and ketones are polarized due to the electronegative oxygen atom |
.... |
|
|
|
Nucleophiles which attack carbonyls |
- CN- and HSO4- |
|
|
|
Overall reaction |
- partially positive C atom in C=O bond is attacked by a nucleophile - nucleophile forms a bond with C atom - negatively charged intermediate formed ( negative charge found on O atom ) - H+ ion from acid/water in the reaction mixture bonds to the O atom
|
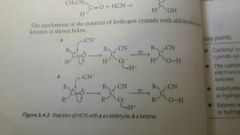
Example |
|
|
Aldehydes are reduced to |
Primary alcohols |
|
|
|
Ketones are reduced to |
Secondary alcohols |
|
|
|
Reduction of aldehyde and ketones |
This is also a nucleophilic addition. H-H from reducing agent adds across the = |
|
|
|
Reducing agent for reduction of aldehydes and ketones |
Lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4) |
|

