![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name the vaccines available |
-rabies - canine distemper virus - measles virus - canine adenovirus, type 2 ( injection or intranasal) - canine parvovirus - canine parainfluenza virus (Injection or intranasal) - leptospirosis - bordetella bronchiseptica (kennel cough) (Injection or intranasal) - borrelia burgforferi Lyme vaccine - canine influenza
|
|
|
What are the clinical signs of canine distemper virus? |
- decreases appetite/ anorexia - Fever/ biphasic - lethargy - signs of respiratory disease ocular discharge- small and builds into massive amount of mucous Nasal discharge- small and builds into massive amount of mucous Coughing GI signs: diarrhea & vomiting More severe cases: Vomiting Diarrhea Anorexia Dehydration |
|
|
Canine distemper has been associated with neurologic signs? |
Yes! 1. Hypersalivation 2. Muscle twitching 3. Seizures 4. Jaw chomping = looks like their chewing gum - ataxia (can’t move) - paresis - hyperesthesia (extreme sensitivity to the skin or eyes) very painful to pet your dog |
|
|
What clinical signs are associated with canine distemper in a later stage of the disease? |
Hyperkeratosis (thickening of the outer layer of the skin) e.g. calluses |
|
|
What does CDV stand for? |
Canine distemper virus |
|
|
Which age is more susceptible to CDV? |
Dogs of any age |
|
|
Who is more at risk of contracting CDV? |
Puppies and immune compromised dogs are more at risk - disease can also affect wildlife; foxes, raccoons, ferrets, big cats, skunks, wolves, and ferrets. |
|
|
The CDV is shedded from what part of the animal? |
The virus is shed mostly from the respiratory tract. Can be shed through all secretions area. |
|
|
Does CDV survive in the environment for long periods of time? |
No! Not stable |
|
|
Is CDV a core vaccine? |
Yes! |
|
|
The CDV is available in what type of constitution? |
Recombinant Modified live |
|
|
The CDV vaccine is part of vaccine protocol? |
DA2PP Dhpp |
|
|
Core vaccines |
DA2PPV Rabies |
|
|
Core vaccines |
DA2PPV - canine distemper virus - adenovirus- 2 -parvovirus - parainfluenza virus? Parainfluenza is not considered core but it is often in combination with the DA2PPV Rabies |
|
|
Non core vaccine |
Bordetella bronchiseptica - parainfluenza virus Leptospira - leptospirosis Borrelia burgdorferi - Lyme disease Canine influenza virus Crotallus atrox - rattlesnake vaccine Canine Coronavirus |
|
|
Who makes the vaccine guidelines? |
AAHA American animal hospital association |
|
|
What is the name of the organization that is involved with a lot of shelter médecine? |
UCDavis University of California-Davis |
|
|
Is parainfluenza a vaccine by itself? |
No! It usually tags along with other virus in the vaccine. |
|
|
Is CDV a highly contagious virus? |
Be careful if : 1. Work at a clinic that does exotics animals 2. Dogs in a distemper prone area |
|
|
What are the proper precautions to prevent transfer of disease? |
Ppe? |
|
|
What is one area that is prone to CDV? |
Shelters! Non vaccinated dogs! City Puppy mills |
|
|
By the time the dog hits the neurological signs what is probable? |
Death 😭 |
|
|
J |
J |
|
|
If they do survive CDV the ocular discharge to the neurological signs what happens? |
Hyperkeratosis Thickening pass on feet Looks like Dirty/ Stained teeth- not proper covering on them called enamel hypoplasia Puppy- multiple teeth |
|
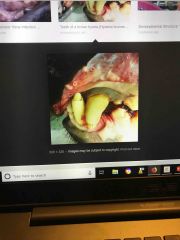
Where would you see a puppy with enamel hypoplasia? |
Mother who was effected (in utero) |
|
|
What is the diagnosis? |
By clinical signs: Nasal discharge. Ocular signs. Neurological signs with a combination with an animal that has no vaccine history. CBC result: - lymphopenia (low lymphocyte count) - leukopenia ( love white blood cell count) Radiographs: It can show pneumonia Confirmation of (outside lab) PCR & IFA: Conjunctival swabs Tracheal swabs CSF or bone marrow aspirated cerebrospinal fluid-General anesthesia Bone marrow aspirates- take a biopsy of the liquid of the soft tissue inside the bone. Necropsy: IFA and PCR
|
|
|
Transition of CDV? |
Aerosolized |
|
|
What is the most common spread of the virus CDV? |
Aerosolized Direct contact with secretions Fomites/ multiple surfaces that virus can stay |
|
|
Which area is prone to be easilly spread of the virus CDV? |
Daycare Shelters Dog parks |
|
|
Treatment for CDV? |
1. Isolation 2. Fluid therapy- diarrhea 3. Antibiotics - treatment and prevention of secondary bacterial infections 4. Maybe- antivirals 5. Nutrition- parenteral/ small frequent meals / highly digestable 6. Symptomatic: Treat the fever ✅ Analgesics- to make them feel better ✅ Antiemetic- stop the vomiting ✅ Anticonvulsants- stop the seizures ✅ Nursing care: High level of nursing care Frequent bedding changes Sponge baths/ cleaning nose and eyes frequently Regular physical assessment IV catheters & fluid maintenance TLC
|
|
|
Things to think about with a seizure dogs and IV maintenance |
They can reap out the IV fluid |
|
|
Prognosis CDV |
Guarded- cautious not the greatest chance Early detection is key! May improve outcome but viral disease no cure Once neurological signs are present- it is often too late and fatal |
|
|
Prevention |
Limiting outdoor exposure to puppies until 16 weeks of age. Vaccinate! |
|
|
Tirers check are? |
Reasonable assessment of protective immunity for distemper |
|
|
The vaccination scheduled for CDV? |
6-8 weeks Every 3 or 4 weeks Until 16-20 weeks A year later Revaccinate every 3 years or tirers check. |

