![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
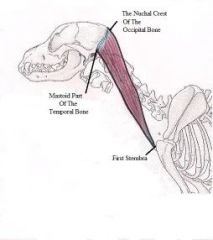
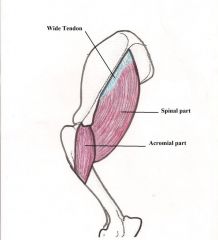
Sternocephalicus muscle
to move the head up and down and from side to side. If the muscles contract together they Move the head up and down in a nod If one muscle contracts on its own it Moves the head to one side on the side that the muscle contracted |
|
|
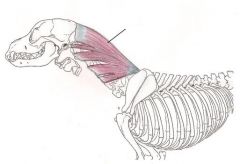
Splenius Muscle
To move the head backwards and forwards If both of the muscles move together then the dog’s neck will lift and its head will extend. If only one of the muscles moves then the dog will only move its head and neck to that side. |
|
|
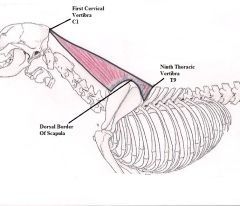
Rhomboideus Muscle
Draws scapula up, backward and forward and lifts neck Pulls the top of the shoulder up, forwards and towards the body When the shoulder is still it can lift the neck. One side can only pull the neck to that side. |
|
|
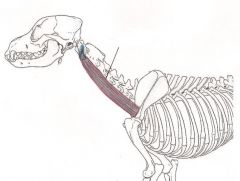
Omotransversarius muscle
Moves the limb forward and the neck to the side |
|
|
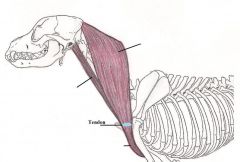
Brachiocephalicus muscle
Pulls leg forwards and neck and head down and to one side Will pull the whole forelimb forwards. The muscle extends the shoulder joint if the neck and head are still. When the muscles pull from both sides of the body, they pull the neck and head down. When the muscles only pull from one side of the body, they pull the head and neck to that side. |
|
|
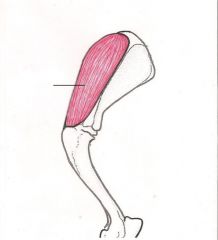
Supraspinatus muscle
Extends and stabilizes the shoulder joint |
|
|
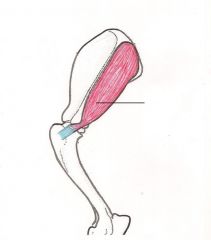
Infraspinatus Muscle
extend or flex shoulder joint, abduct shoulder, rotate arm laterally and stabilize the shoulder joint. Rotates the dogs arm in the outward direction Pulls the leg away from the dogs body Prevents dislocation of the shoulder joint by stabilizing it. |
|
|
Deltoideus Muscle
Makes shoulder joint flex and pulls the foreleg away from the dog’s body |
|
|
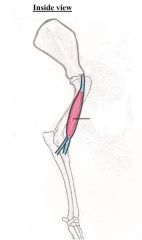
Biceps Brachii Muscles
Flexes elbow joint and extends shoulder joint |
|
|
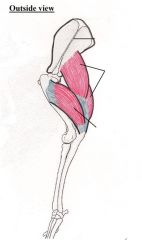
Triceps Brachii Muscles
Extends and flexes elbow joint Long Head – Flexes the shoulder joint and extends the elbow joint Lateral Head – only extends the elbow joint |
|
|
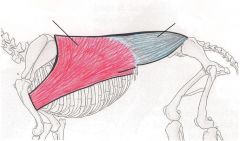
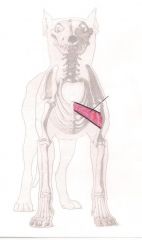
Latissimus Dorsi Muscle
pulls leg backwards Its contraction causes the leg to move backwards. It also is a contributing muscle to making the leg able to rotate towards the middle. |
|
|
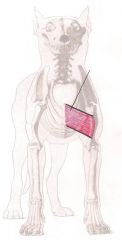
Pectoralis Descendens
Advances forelimb and pulls the forelimb to the center of the body |
|
|
Pectoralis Transversus Muscle
Pulls forelimb towards the middle line of the body |
|
|
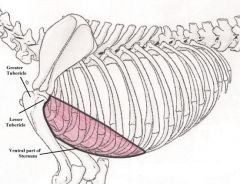
Pectoralis Profundus Muscle
Deep Pectoral Adducts foreleg and moves it backwards with movement When the Pectoralis Profundus muscle contracts and the limb is supporting weight it makes the body pull forwards and the shoulder will then extend. When the limb is not supporting any weight and it contracts it will pull the limb towards the head and flex the shoulder joint. During all movement it will stabilize the foreleg. |
|
|
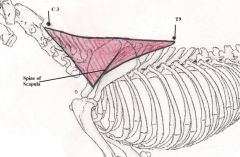
Trapezius Muscle
Draws scapula up, backward and forward and lifts neck The Trapezius muscle as a whole pulls the shoulder blade upwards. It also is able to hold the shoulder against the body. Neck section – Pulls it up and forwards Thoracic section – Pulls it up and backwards |
|
|
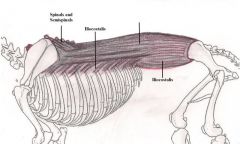
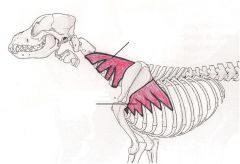
Longissimus Dorsi Muscle
Stretches and straightens back and loins, lateral flexion Stretch the vertebral column. When they contract they will straighten and stabilize the spinal column. When the muscle contracts to one side the spine will bend to that side. |
|
|
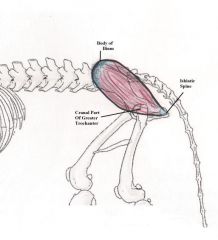
Serratus Ventralis
Pulls the top of the shoulder blade forwards, lifts and bends (neck) Pulls shoulder blade back and down and rotates the blade (chest) Neck - Pulls the top end of the shoulder blade forwards. Causes the neck to bend to one side. Also lifts the neck. Chest – Pulls the top part of the shoulder back and down this can cause the shoulder to rotate which will make it move forwards. Causes an interrupted sling from both of the chest muscles, this keeps the body stable and sturdy and raise the chest. |
|
|
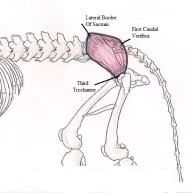
Gluteus Medius
Pulls the limb away from the body and extends the dog’s hip joint. This is an important muscle for the dogs rearing, jumping, kicking and moving forwards as it extends the hip joint. It also pulls the limb away from the dog’s body. |
|
|
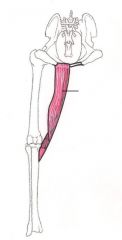
Superficialis Gluteus muscle
Pulls the limb from body and flexes hip joint. The Superficialis gluteus muscle flexes the dog’s hip joint and also pulls the limb away from its body. |
|
|
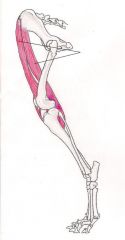
Gracilis Muscle
Pulls limb, extends hip, flexes knee joint, extends ankle joint. flexes the knee joint Extends the ankle joint Pulls the hind limb to the middle of the body Extends the hip joint |
|
|
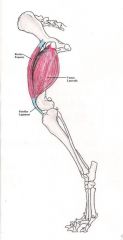
Sartorius Muscle
Flex hip and extend stifle Pulls the limb towards the midline of the body Flexes the hip joint |
|
|
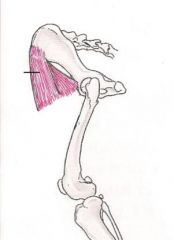
Quadriceps Femoris
Extend stifle and flex hip Vastus Medialis, intermedius and lateralis – Extend the knee joint Rectus Femoris – Extends the knee joint and also flexes the hip joint. |
|
|
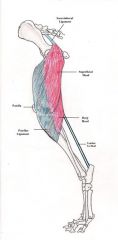
Tensor Fascae Latae Muscle
Extends knee joint, flexes hip joint This muscle flexes the hip joint and because it is attached to the patella and the tibia it will extend the knee joint as well. |
|
|
Biceps Femoris Muscle Hamstring
Extends hip joint, extends and flexes knee joint and extends ankle joint The whole muscle extends the hip joint The knee joint is extended by the upper front fibers. The ankle joint is extended by the lower rear fibers. The lower rear fibers could also flex the knee joint |
|
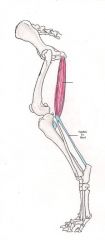
Hamstring
|
Semitendinosus Muscle
Extends hip and ankle joint, flexes knee joint and rotates leg inwards Rotates the dogs leg inwards Flexes the dogs knee joint Extends the dog’s hip joint and also its ankle joint. |
|
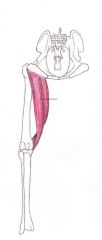
Hamstring
|
Semimembranosus Muscle
Pulls the limb towards the middle of the body, extends hip joint Pulls the dogs hindlimb towards the middle of its body Extends the dogs hip joint |
|
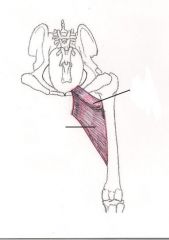
|
Adductor Muscles of the hind limb
Adduct limb and extend dogs hip and stabilizes hind leg The adduct muscles are there to adduct the hind leg of the dog (keep it close to the middle) and to extend its hip. This happens but the contraction of these muscles. All this helps to stabilize the dog’s hind leg while he is moving |

