![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Identify the 5 good things on a map! |
Title, scale, compass rose, contour lines, and a legend. |
|
|
What is a scale? |
A scale is a measurement upon a map that compares one signifigantly larger or smaller unit to another. |
|
|
Identify three types of scale and provide rules/examples for each. |
Representative Fraction (RF): 1:1000 Verbal Scale: 1cm = 1000m Linear Scale: ___----___ (looks like this but flat) |
|
|
What are contour lines? The rules? |
Contour lines are lines upon a map that indicate dips or rises on landforms. One rule is: follow a specific interval. |
|
|
What is military grid (UTM)? How does it work? |
The military grid is the geocoordinate standard used by NATO militaries for locating points on the earth. It is used for latitude and longitude and is also called eastings/westings, and northings/southings. |
|
|
Define Latitude and longitude. |
Longitude is the North to South lines on the earth. Latitude is the West to East lines. |
|
|
What is the range (^o) for latitude and longitude? |
90^o. |
|
|
What skills are required to examine topographic maps? |
Mapping, math, and an artistic eye. |
|
|
How many time zones exist in Canada? |
Pacific, Mountain, Central, Eastern, Atlantic, and Newfoundland. Six time zones in total. |
|
|
Who invented the international time zone system? |
Sir Sandford Fleming. |
|
|
State the first geologic era along with the significant biological/geological events during the period. |
Precambrian era: the formation of the oceans, the development of the atmosphere and, the evolution of life. The first life forms are thought to have been bacteria, which appeared about 3.6 billion years ago. |
|
|
State the second geologic era along with the significant biological/geological events during the period. |
Paleozoic Era: the colonization of the land by plants and animals and the evolution of sharks, fish, insects, spiders, amphibians, ancestral reptiles, ferns, and early conifers. |
|
|
State the third geologic era along with the significant biological/geological events during the period. |
Mesozoic Era: covers the reign of dinosaurs. Other new life forms of this Era include turtles, crocodiles, ancestral birds, primitive mammals, flowering plants, snakes, lizards and social bees. |
|
|
State the fourth/current geologic era along with the significant biological/geological events during the period. |
Cenozoic Era: the appearance of humans, bats, whales, and primates. |
|
|
What is the tectonic plate theory? |
Plate tectonics is the theory that the outer rigid layer of the earth (the lithosphere) is divided into a couple of dozen "plates" that move around across the earth's surface relative to each other, like slabs of ice on a lake. |
|
|
Identify each of the Canadian Landforms? |
1. Western Cordillera 2. Interior Plains 3. Canadian Shield 4. Great Lakes-St.LawrenceLowlands (where we live) 5. Appalachian 6. Hudson Bay Lowlands - ArcticLowlands 7. Innuitian Mountains |
|
|
How has glaciation affected the physical composition of Canada? |
Glaciation has created landforms and our great lakes. |
|
|
Define weather. |
The state of the atmosphere at a place and time as regards heat, dryness, the sunshine, the wind, rain, etc. |
|
|
Define climate. |
The weather conditions prevailing in an area in general or over a long period. |
|
|
Define growing season. |
The part of the year during which rainfall and temperature allow plants to grow. |
|
|
Define precipitation. |
Rain, snow, sleet, or hail that falls to the ground. |
|
|
Outline the factors affecting climate? |
The climate of any particular place is influenced by latitude, elevation, nearby water, ocean currents, topography,vegetation, and prevailing winds. |
|
|
How many climate regions exist in Canada? |
Eight. |
|
|
Identify three types of precipitation. |
Relief, Frontal, and Convection. |
|
|
Explain Frontal precipitation. |
AKA Cyclonic Precipitation. Cyclonic or Frontal precipitation results when the leading edge of a warm, moist air mass (warm front) meets a cool and dry air mass (cold front). |
|
|
Explain Convectional precipitation. |
Convectional precipitation results when the warm ground heats the air over it. As the air warms, the air molecules separate, thus, the air becomes “lighter” and rises rapidly into the atmosphere. As the air rises, it cools. Water vapor in the air condenses into clouds and precipitation. |
|
|
Explain Relief precipitation. |
Relief rainfall is created as air masses are pushed up and over mountainous or upland areas. Relief rainfall occurs where moist air is forced to rise over a physical barrier such as a mountain range. |
|
|
What is the difference between continental and maritime climate? |
The difference between maritime and continental climate is that there is less of a temperature variation in a maritime climate, while in a continental climate the climate does fluctuate, such that summers can be hot and winters very cold. In a maritime climate, summers can be cool, and the winters are not very cold |
|
|
Define treeline. |
The tree line is the edge of the habitat at which trees are capable of growing |
|
|
What is the dominant vegetation types in Canada? |
Tundra, Grassland, and Forest. |
|
|
What is an ecozone? |
An ecozone is a region that is differentiated from others due to factors such as climate, vegetation, landform, and others. |
|
|
Identify three types of immigration. |
Refugee, independent, and family. |
|
|
Define push and pull factors. |
Push: Factors that push immigrants away from countries. Pull: Factors that pull immigrants to countries. |
|
|
Define Population density and distribution. |
Population density is a measurement of population per unit area or unit volume. Population distribution is the spread of people across the world, i.e. where do people live. |
|
|
What is a census? |
A census is a collection of data based on sex, age, and the number of people in homes. |
|
|
What is urban sprawl? |
Urban Sprawl is large subdivisions that are concentrated in population. |
|
|
What is GDP? |
Gross domestic product. |
|
|
What is the rock cycle? |
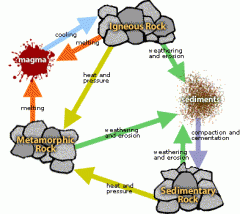
|

