![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Area between graphs |

Uses limits in terms of x. More positive value = top, values , step 1 graph. Step 2 find intersects. Step 3. If vertically complex use multiple integrands. Solve |
|
|
Area between graphs in terms of y |

Same as in.terms of x, but limits and differential are in terms of y. Sometimes this will be easier than in terms of x |
|
|
Volume as the integral of cross sectional area |

Step 1, determine the formula for a A(y), a math puzzle. Determine limits |
|
|
Total mass M |

Slice the rod into N pieces. Estimate the mass of each piece. Sum together |
|
|
Total population |

Accounts for size of each ring and population density with each. Sums together population at each circumference. |
|
|
Flow rate |
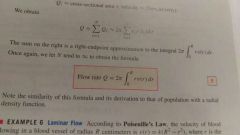
Same logic as for total population. Takes into account the number of particles at each circumference using radius and adjusts for how fast each particle is moving using r(v) |
|
|
Average value |

Really logical. Find the total sum within the length a to b. Then divides by that to get the avg n value within. |
|
|
Mean value theorem |

I'm honestly confused as to how these two things are different |
|
|
Radial density theorem |
Takes the total mass theorem and changes roe to vary with r and then uses circumference to sum values together |

