![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
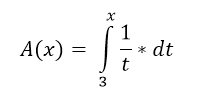
Question 29: |
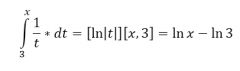
|
|
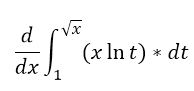
Question 39. Use the second fundamental theorem of calculus to calculate each of the derivatives. |
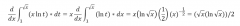
|
|
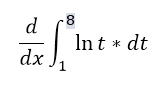
Question 41 |
Constant function derivative is 0 |
|
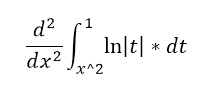
Question 43 |
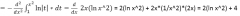
|
|
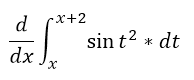
Question 47 |
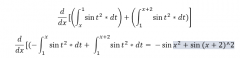
|
|
|
Where should the x always have to be in the integral? |
At the top |
|
|
What is it called when you solve [1,x]? |
It is called the area accumulation function easier to do like a(1) and so forth. |
|
|
What are the conditions for the second fundamental theorem of calculus |
a) F is continuous on [a,b] and differentiable on (a,b) b) F is an antri derivative of f, that is, F'(x) = f(x) |
|
|
What is the second fundamental theorem of calculus? |
The second fundamental theorem of calculus guarentees that we can always construct an antiderivative for any continuous function f simply by defining an area accumulation function for f. |

