![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Series |
An infinite set of numbers being added together |
|
|
|
Geometric series |

a - coefficient, r - ratio |
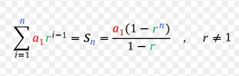
|
|
|
What happens when r (ratio) of a series is between -1 and 1? ( -1 < r 1 ) |
The limit of the sequence is 0 and the series is a/(1-r) |
|
|
|
What happens If r > 1 or r <= -1? |
The series and sequence is divergent |
|
|
|
Example 1 of Series Problem |

|
|
|
|
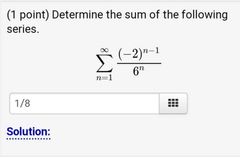
Example 2 of Series problem |
|
|
|
|
How to find the sum of a geometric series |
1) identify it as geometric, usually all terms will have an exponent of n 2) find the first term (a) and the common ratio (r)**, the ratio is the leading nth terms of the problem 3) if the absolute value of the common ratio is greater than 1 it will diverge, if less than 1 it will converge at a point 4) find the point it converges with the formula : a/(1 - r) **dont simplify common ratio fraction |
|
|
|
What makes a series absolutely convergent? |
If a series of absolute values are convergent |
|
|
|
(ratio test) what happens If lim n-> inf |a(n+1)/a(n) | = L < 1? |
The series is absolutely convergent. |
|
|
|
(ratio test) what happens If lim n-> inf |a(n+1)/a(n) | = L > 1? |
The series is divergent |
|
|
|
(ratio test) what happens If lim n-> inf |a(n+1)/a(n) | = 1? |
Ratio test is inconclusive, could be convergent or divergent |
|
|
|
Example 1 of convergence problem |

|
|
|
|
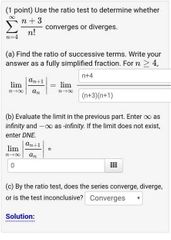
Example 2 of Convergence problem |
|
|
|
|
Example 3 of Convergence problem |

|
|
|
|
How do you find the limit of a sequence? |
Divide all the terms with the leading terms then evaluate what happens when it goes to infinity. |
|
|
|
What do you do for series equations that have 2 terms over one? |
Break it into 2 series problems, evaluate both sums separately then add the two sums together at the end |
|
|
|
How do you find the interval of x in a series problem? |
1) find the first term (a) and the common ratio (r) 2) set up equation for |r| < 1 once you have found r and solve for it. |
|
|
|
How do you solve a convergence problem? |
Use the ratio test |
|
|
|
What do you do if the ratio test is inconclusive? |
Find the sum by dividing all terms by the leading term in the denominator and evaluating it to infinity. |
|
|
|
What is a power series? |
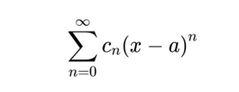
A series with this form |
|
|
|
What do you find in a power series problem? |
The interval of convergence and radius of convergence. |
|
|
|
Example 1 of Power Series problem |
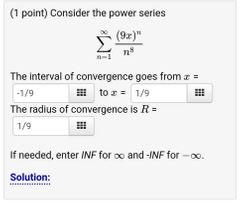
|
|
|
|
Example 2 of Power Series Problem |
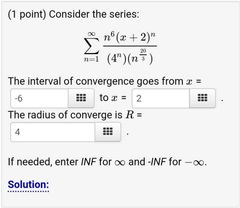
|
|
|
|
Example 3 of a power series problem |

|
|
|
|
How do you solve a power series problem? |
1) Do the ratio test and separate the coefficients and x terms from the n terms 2) If the limits taken at the n term part of the problem evaluate to one then the radius of convergence is the inverse of the coefficient of x. 3) set up the inequality -1 < (x terms) < 1 and solve for x to get the interval of convergence. |
|
|
|
What is a partial sum for a power series? (Section 8.4) |
A specific interval of n in the power series that creates an approximation of the function used. |
|
|
|
What is the radius of convergence for a power series? |
Its half the distance of the interval of convergence |
|
|
|
What form does the function have to be in to be represented as a power series? |
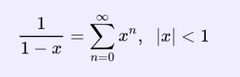
|
|
|
|
Example 1 of representing functions as power series |
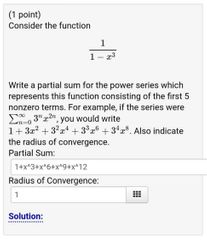
|
|
|
|
Example 2 of representing a function as a power series |
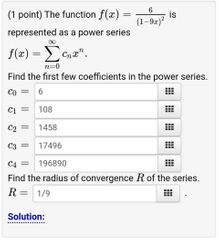
|
|
|
|
Example 3 of representing a function as a power series |
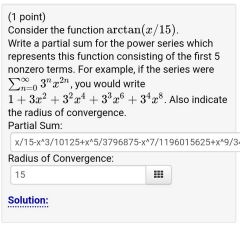
|
|
|
|
How do you solve a representing a function as a power series problem? |
1) put the function into the form: 1/(1-x). You may have to modify the function by pulling a term or constant and/or manipulating x 2) you can then change the form to x^n (distribute n to the coefficients of x) 3) use this form to find the amount of terms specified 4) find the radius of convergence by setting up an inequality problem |x|< 1. This will give you the interval and the radius is half the size of the interval |
|
|
|
What is a taylor polynomial? |
One that follows the form (f^n(x))/n! |
|
|
|
What is the maclaurin polynomial for sin(u)? |
u - (1/3!) u ^3 + (1/5!) u ^5 - (1/7!) u ^ 7 |
|
|
|
What is the Maclaurin series for e^x? |
1 + x + x^2 / 2! + x^3 / 3! |
|
|
|
What is the expression for the series : ((-1)^n(1/3)^(2n+1)) / (2n+1) |
Arctan(1/3) |
|
|
|
What is the expression for the series ((-1)^n(1/3)^(2n))/(2n)! |
Cos(1/3) |
|
|
|
What is the expression for the series: (1/3)^n/n! |
E^(1/3) |
|
|
|
What is the expression for this series: ((-1)^n(1/3)^(2n+1))/(2n+1)! |
Sin(1/3) |
|
|
|
What is the pattern of a maclaurin series? |
f(0) + f'(0)x + (f"(0)x^2) / 2! + (f"'(0)x^3) / 3! + .... |
|
|
|
What is a taylor series? |
(F^n(a) / n!) (x - a)^n |
|
|
|
What is a binomial series? |
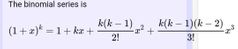
|
|
|
|
Example 1 of maclaurin problem |

|
|
|
|
Example 2 of maclaurin problem |

|
|
|
|
Example 3 of maclaurin problem |

|
|
|
|
How to solve a maclaurin problem? |
1) memorize the known maclaurin like those for sin and cos, otherwise find the derivatives of the for the amount of terms asked for. 2) once you have the derivative, plug in 0 into all the terms. 3) take the results and plug them into the series : f(0) + f'(0)x + (f"(0)x^2) / 2! + (f"'(0)x^3) / 3! + ... |
|
|
|
Example 1 of a taylor problem |
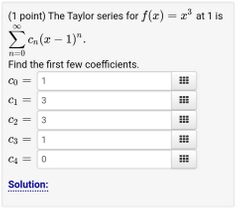
|
|
|
|
Example 2 of a taylor problem |

|
|
|
|
Example 3 of taylor problem |

|
|
|
|
How do you solve a taylor problem? |
1) find the amount of derivatives requested 2) place in the given value for a for each of the derivatives. 3) treat each result as the coefficient for the corresponding term in the format : (f^n(a))/ n!) |
|
|
|
Example of a binomial problem |

|
|
|
|
How do you solve a binomial problem? |
1) rearrange the function so it has the format (1 + x)^k 2) equate it to the series: 1 + kx + (k(k-1)/2!) x^2 + (k(k-1)(k-2)/3!)x^3 + ... |
|
|
|
What are all the topics in ch. 8? |
- Series - Other Convergence Tests - Power Series - Representing Functions as Power Series - Taylor and Maclaurin Series |
|

