![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Explain how the pH scale works.
|
From 0-6 the solution is acidic with 0 being the strongest and 6 being the least acidic. 7 is neutral. 8-14 indicates the solution is alkaline with 8 being the weakest and 14 being the strongest.
|
|
|
How does the universal indicator identify the pH?
|
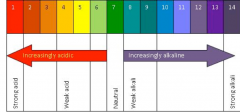
Universal indicator is a mixture of dyes that changes color depending on the range of pH. The general colours from acidic to alkaline are: Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Purple.
|
|
|
How does the litmus paper indicator identify the pH?
|
Litmus indicator is a paper that is red when acidic, purple when neutral, and blue when alkaline.
|
|
|
How does the methyl orange indicator identify the pH?
|
Methyl orange indicator is yellow in alkaline solutoins and red in acidic ones.
|
|
|
How does the phenolphthalein indicator identify the pH?
|
Phenolphthalein is bright pink when alkaline and colourless in acidic solutions.
 |
|
|
What ion do all acids share?
|
Acids have positive hydrogen ions (H+).
|
|
|
What ion do all alkalis share?
|
Alkalis have negative hydroxide ions (OH-).
|
|
|
What is a titration?
|
When creating a neutralisation reaction, at times the resultant is a colourless solution. In this case, titration is required in order to find out how much acid and alkali is needed neautralise each other.
|
|
|
How are titrations carried out?
|
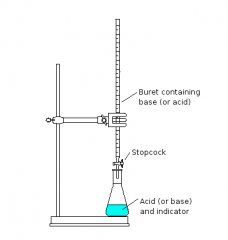
1)The solution is transferred to a conical flask and the volume of the solution is noted.
2)A few drops of methyl orange are added as an indicator. 3)The acid is then run in from a burette until the indicator turns from yellow to orange. 4)The volume of acid added is noted. |
|
|
What happens when you react an acid with a metal?
|
Metal + Acid -> Salt + Hydrogen (remember that metals below hydrogen in the reactivity series will not react with dilute acids).
|
|
|
What happens when you react an acid with a metal hydroxide?
|
Metal Hydroxide + Acid -> Salt + Water (all metal hydroxides will react with acids).
|
|
|
What happens when you react an acid with a metal oxide?
|
Metal Oxide + Acid -> Salt + Water (almost all metal oxides will react with acids).
|
|
|
What happens when you react an acid with a carbonate?
|
Carbonate + Acid -> Salt + Carbon dioxide + water (all carbonates(CO3) react with acids).
|
|
|
Based on the rules of solubility, what are the SOLUBLE rules?
|
i) all common sodium, potassium and ammonium salts are soluble
ii) all nitrates are soluble iii) common chlorides are soluble, except silver chloride and lead(II) chloride iv) common sulfates are soluble, except those of barium, lead(II) and calcium |
|
|
Based on the rules of solubility, what are the INSOLUBLE rules?
|
v) common carbonates are insoluble, except those of sodium, potassium and ammonium
vi) most metal hydroxides are insoluble except sodium, potassium and ammonium hydroxides |
|
|
How can you prepare soluble salts without precipitation?
|
After the reaction to create the salt, you let the solution cool and it crystalizes. You must filter off the unreacted solid.
In the cases of making sodium, potassium and ammonium salts, we use titration, as the unreacted solution cannot be identified in the solution. |
|
|
How can you prepare insoluble salts with precipitation?
|
A precipitate is a fine solid that is formed by a chemical reaction involving liquids or gases. When two solutions are insoluble, by mixing one containing the correct positive ion and the other with the correct negative ion, the attractions are strong enough to make the salt.
|
|
|
How is salt extracted through mining?
|
The electrolysis of brine is a form of solution mining where concentrated salt is extracted from underground deposits and then cleaned. Through electrolysis, sodium chloride solution can be used to produce sodium hydroxide contaminated with sodium chloride, chlorine and hydrogen inside a diaphragm cell.
|
|
|
Why is a diaphragm cell used in the electrolysis of brine?
|
Designed to keep the products apart. Mixing the products may react to make bleach or could explode violently.
|
|
|
What happens at the titanium anode in the electrolysis of brine?
|
Chloride with a negative charge are discharge to produce chlorine gas.
2Cl-(aq) -> Cl2(g) + 2e- |
|
|
What happens at the steel cathode in the electrolysis of brine?
|
As sodium ions are hard to discharge, hydrogen ions are discharged instead to produce hydrogen gas. As hydrogen ions are discharged, water splits up as hydrogen must be diatomic, which creates an excess of hydroxide ions left in the water.
Steel cathode- 2H+(aq) + 2e- -> H2 (g) |
|
|
What happens to the excess of hydroxide ions in the electrolysis of brine?
|
The hydroxide ions mixes with the sodium to create sodium hydroxide. The sodium hydroxide is then concentrated by evaporation. These leaves crystalized sodium chloride, which is now a solid salt.
|
|
|
What is sodium hydroxide used for?
|
-manufacture of aluminum
-paper making (sodium hydroxide helps break wood down into pulp) -soap making (reacts with animal and vegetable fats and oils to make compounds) -bleach is formed when reacting sodium hydroxide and chlorine in the cold |
|
|
What is chlorine used for?
|
-sterilizing water for safe drinking
-making hydrochloric acid -bleach |

