![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Particle Model |
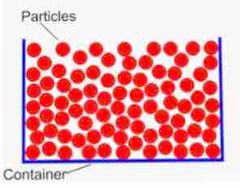
Solid
Liquid Gas |
|
|
Arrangement of solid particles |
Close together and tightly packed into a regular pattern Cannot be compressed as their is nowhere for the particles to go. |
|
|
Movement of solid particles |
Vibrate about a fixed position More heat - more energy - more vibrations - at melting point the solid particles break their formation and turn into a liquid |
|
|
Arrangement of liquid particles |
Close together but more loosely packed than a solid Fixed volume More heat - more energy - more speed the particles move at Cannot be compressed |
|
|
Movement of liquid particles |
They can flow because the particles can slide over each other They can take the shape of their container |
|
|
Arrangement of gas particles |
Far apart and random arrangement Can be compressed |
|
|
Arrangement of gas particles |
Far apart and random arrangement Can be compressed |
|
|
Movement of gas particles |
Random movement but travel at high speed More heat - more energy - more speed |
|
|
What happens at the melting point? |
A solid is heated and heated until it reaches the point where the bonds break completely and turns into a liquid This is the melting point Can be reversed by freezing |
|
|
What happens at the boiling point? |
A liquid is heated and heated until it’s particles travel faster and faster. Particles start coming off the surface of the liquid (evaporation) and eventually all the particles turn into a gas. This is the boiling point Reversed by condensation |

