![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
144 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Calcium |
Red flame |
|
|
Potassium |
Lilac flame |
|
|
Copper |
Green/blue flame |
|
|
Sodium |
Yellow flame |
|
|
What colour is the precipitate of Aluminium? |
White |
|
|
What colour is the precipitate of Calcium? |
White |
|
|
What colour is the precipitate of Copper (ll)? |
Pale blue |
|
|
What colour is the precipitate of Iron (ll)? |
Green |
|
|
What colour is the precipitate of Iron (lll)? |
Brown (rust) |
|
|
How do you test for metal cations? |
Add sodium hydroxide to the solution and a precipitate is formed. |
|
|
How do you differentiate between an Aluminium and Calcium precipitate? |
Add more sodium hydroxide and the Aluminium precipitate will redissolve. |
|
|
How do we treat our water in the UK? |
1) Filtering 2) Chemicals are added to remove other impurities 3) Chlorine is added to kill bacteria |
|
|
What are cations attracted to? |
Cathodes |
|
|
What are anions attracted to? |
Anodes |
|
|
How do you test water for Halide Ions? |
Halide Ions are anions (-) which means they are attracted to the anode in electrolysis. |
|
|
What is the positively charged electrode called? |
Anode |
|
|
What is the negatively charged electrode called? |
Cathode |
|
|
What is the precipitate of Flourine when it is added to silver nitrate and acidified with nitric acid? |
None |
|
|
What colour is the precipitate of Chlorine when it is added to silver nitrate and acidified with nitric acid? |
White |
|
|
What colour is the precipitate of Bromine when it is added to silver nitrate and acidified with nitric acid? |
Cream |
|
|
What colour is the precipitate of Iodine when it is added to silver nitrate and acidified with nitric acid? |
Yellow |
|
|
How do you test for Ammonium Ions in water? |
Add Sodium Hydroxide. If the Ions are present: a distinct ammonia Snell is emitted when heated. |
|
|
What colour does Ammonium gas turn litmus paper? |
Damp red litmus paper turns blue then bleaches |
|
|
Why does the government set standards for water purity? |
To make sure that our water looks good, tastes good and is safe to drink. |
|
|
Where do dissolved substances in our drinking water come from? |
They come from: 1) rocks over which it flows 2) the chemicals used in water treatment |
|
|
Who checks the purity of our water against government standards? |
Analytical chemists |
|
|
What indicators would alert hospital doctors to order blood tests for Sodium Ions? |
• High blood pressure • Kidney disease |
|
|
What are analytical chemists employed in hospitals to do? |
Test patients' blood for Aluminium, Iron, Sodium and other dissolved substances |
|
|
What would researchers have to do to see if there is a link between fluride levels and Alzheimer's? |
•Measure blood Aluminium levels in a considerable number of patients and monitor their blood compositions • Look at areas that have high levels of fluride |
|
|
What doesn't soft water contain? |
Calcium and Magnesium ions |
|
|
What does hard water contain? |
Calcium and Magnesium ions |
|
|
What does hard water contain? |
Calcium and Magnesium ions |
|
|
What happens when soap is added to hard water? |
A scum is formed (a precipitate) by the Calcium and Magnesium. |
|
|
When are soap suds created in hard water? |
When all the Calcium and Magnesium is precipitated. |
|
|
What is temporary hardness (water)? |
Hardness that can be removed by heating |
|
|
What is permanent hardness (water)? |
Hardness that cannot removed by heating |
|
|
How is hardness measured in water? |
By the amount of Calcium and Magnesium ions that are in the solution |
|
|
What happens when temporary hard water is heated? |
The dissolved Calcium and Magnesium compounds decompose to form limescale |
|
|
What is the equation for the heating up of temporary hard water? |
Ca(HCO3)2 > CaCO3 + CO2 + H2O |
|
|
What can Ion exchange columns do? |
Remove all of the Calcium and Magnesium Ions. |
|
|
How do ion exchange columns work? |
In the column the Calcium and Magnesium Ions are exchanged for Sodium in solid resin beads |
|
|
What is the units for concentration? |
g/dm3 |
|
|
What is 1dm3 equivalent to? |
1 litre |
|
|
What is the equation for concentration? |
Concentration = mass(g) ÷ volume (dm3) |
|
|
What is a mole of an atom equivalent to? |
It's relative atomic mass |
|
|
What does mr moles wear? |
A mass hat |
|
|
What is a base? |
A substance that will react with an acid to produce only salt + water |
|
|
What is an alkali? |
A soluble base |
|
|
How do you create a soluble salt? |
1) Add a base to an acid until no more reacts 2) Warm the mixture to speed up the reaction 3) Filter off the unreacted solid 4) Leave the mixture to cool and crystallise 5) Filter the crystals and leave to dry on filter paper |
|
|
What does a metal + acid make? |
Salt + hydrogen |
|
|
What does a metal oxide + acid make? |
Salt + water |
|
|
What does a metal hydroxide + acid make? |
Salt + water |
|
|
What does a metal carbonate + acid make? |
Salt + water + CO2 |
|
|
How is a titration used? |
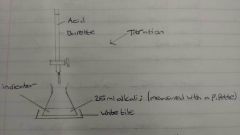
A titration is used to determine the exact amount of soluble reactant that reacts with an acid to make a soluble salt |
|
|
What type of reaction is an acid + base titration? |
A neutralisation reaction |
|
|
What is an electrolyte? |
An iconic substance in molten form or dissolved in water |
|
|
What charge are anions? |
Negative |
|
|
What charge are cations? |
Positive |
|
|
What is the anion in NaCL? |
CL- |
|
|
What is the cation in NaCL? |
Na+ |
|
|
What is the anion in CuSO4? |
SO4 (2-) |
|
|
What is the cation in CuSO4? |
Cu (2+) |
|
|
What is the anion in CuCL2? |
CL- |
|
|
What is the cation in CuCL2? |
Cu (2+) |
|
|
What is the anion in Na2SO4? |
SO4 (2-) |
|
|
What is the cation in Na2SO4? |
Na (2+) |
|
|
What is the anion in PbBr2? |
Br- |
|
|
What is the cation in PbBr2? |
Pb (2+) |
|
|
What are the uses of sodium? |
• Street lamps - Sodium vapour emits a yellow light when electricity is passed through • A coolant in a nuclear reactor - liquid Sodium has a high thermal conductivity and transfers heat efficiently from the reactor to water |
|
|
What is oxidation? |
A loss of electrons |
|
|
What is reduction? |
A gain in electrons |
|
|
What is OIL RIG? |
Oxidation Is Loss Reduction Is Gain |
|
|
Is the following an oxidation or reduction: C > C(4+) + 4e- |
Oxidation |
|
|
Is the following an oxidation or reduction: Cu(2+) + 2e- > Cu |
Reduction |
|
|
What is the half equation if the electrolyte contains SO4 (2-)? |
4OH- > O2 + 2H2O + 4e- |
|
|
What is the half equation if the electrolyte contains Na+? |
2H+ + 2e- > H2 |
|
|
What is the half equation if the electrolyte contains CL- (aq/L)? |
2CL- > CL2 + 2e- |
|
|
What is the half equation if the electrolyte contains Cu (aq/L)? |
Cu (2+) + 2e- > Cu |
|
|
What is the half equation if the electrolyte contains molten metals eg Na ? |
Na+ + e- > Na |
|
|
What is the half equation if the electrolyte contains other halides eg Br- (aq/L) ? |
2Br- > 2e- + Br2 |
|
|
Why should you trail a titration? |
To gain an approximate of what the ideal should be |
|
|
Why should you carry out further titrations? |
To achieve a repeatable set of results |
|
|
What is electroplating? |
Depositing a thin layer of one metal onto the surface of another |
|
|
Why is electroplating used? |
To improve resistance to corrosion. It protects the plated metal by preventing contact with air |
|
|
What is the volume of ALL gases at room temperature (25°) and at same pressure? |
24dm3 |
|
|
What is the equation for the volume? |
Volume = moles ÷ concentration |
|
|
Why does a current only flow in an electric circuit when lead bromine is melted? |
Because the ions can move more freely allowing a current to flow |
|
|
Which is the negative electrode? |
Cathode |
|
|
Which is the positive electrode? |
Anode |
|
|
What do fertilisers contain? |
Soluble nitrogen compounds which plants need to make proteins |
|
|
When ammonia (NH3) is used to make fertiliser what do we call it? |
Nitrogenous fertiliser |
|
|
What is the Haber process designed to do? |
Maximise the yield of ammonia, at an acceptable rate from the reversible reaction |
|
|
What is the equation for nitrogenous fertiliser? |
N2 + 3H2 >< 2NH3 |
|
|
What are the optimum conditions for the Haber Process? |
• 450°c • Iron Catalyst • 200 atmospheres |
|
|
What is the Haber Process? |
An industrial process in which ammonia is made from the reaction between hydrogen and nitrogen |
|
|
What is dynamic equilibrium? |
When the forwards and backwards reactions are occuring at the same rate |
|
|
What is an exothermic reaction? |
A type of reaction that releases heat energy |
|
|
What is an endothermic reaction? |
A type of reaction that takes in heat energy from its surroundings |
|
|
What does increasing the pressure do in the Haber Process? |
Shifts the equilibrium to the forward direction |
|
|
What does increasing the pressure do in the Haber Process? |
Shifts the equilibrium to the forward direction |
|
|
What does the catalyst do in the Haber Process? |
Reach the equilibrium position as fast as possible |
|
|
What would happen if you reduced the temperature in the Haber Process? |
Reducing the temperature would encourage more NH3 but the rate of production would be too slow |
|
|
What is a catalyst? |
A substance that speeds up the rate of a reaction without being used up in the reaction |
|
|
How is ethanol produced? |
Microorganisms break down large molecules of glucose, using enzymes, to produce ethanol |
|
|
What is the fermentation equation? |
(yeast) Sugar > ethanol + C02 |
|
|
What is yeast? |
A single-celled fungus that can use sugars, from carbohydrates and fruits, for a type of respiration that produces ethanol |
|
|
In fermentation what does yeast act as? |
A catalyst |
|
|
What can ethanol do to people in small amounts? |
Make them less self-conscious and more talkative |
|
|
What can ethanol do to people in large amounts? |
• Lower inhibition • Slow reaction times • Bring on violent/ aggressive behaviour • Vomiting and fainting |
|
|
What problems does excessive drinking cause over a long period of time? |
It increases the risk of heart disease, strokes and cancer, and causes liver cirrhosis. |
|
|
What are the social issues involved in excessive drinking? |
- Antisocial behaviour - Public order problems - Crime |
|
|
How do you make a more concentrated solution of ethanol? |
Heat the fermentation mixture - ethanol boils at a lower temperature than water, so the fraction of the liquid that boils first will contain a higher percentage of ethanol |
|
|
What are the conditions required for fermentation? |
- Anaerobic (no oxygen) - Warmth |
|
|
What happens when fermentation occurs at higher temperatures? |
The yeast is killed |
|
|
What happens if oxygen is present in fermentation? |
Aerobic respiration will take place, producing CO2 and H2O, instead of ethanol |
|
|
What temperature does pure ethanol boil at? |
78°c |
|
|
How is ethanol made from crude oil? |
(catalyst) Ethene + steam > ethanol |
|
|
What factors will affect the method chosen to produce ethanol? |
• Sustainability (are the resources renewable) • The concentration produced • The quality of the final product • Whether it needs further processing • The relative availability of sugar cane/ sugar beet and crude oil |
|
|
What is the advantage of making ethanol by fermentation? |
Biofuel is used, which is renewable |
|
|
What are the disadvantages of making ethanol by fermentation? |
• It produces ethanol at only 15% concentration • The correct climate is needed |
|
|
What are the advantages of making ethanol by crude oil? |
• It gives a product that is nearly 100% concentration • Little or no waste is made |
|
|
What are the disadvantages of making ethanol by crude oil? |
• Crude oil is non-renewable • Drilling for crude oil is time consuming |
|
|
What is the dehydration reaction of ethanol? |
(catalyst) Ethanol > ethene + steam |
|
|
How are large amounts of ethene made? |
By cracking larger molecules in the higher-boiling fractions of crude oil |
|
|
What are the conditions required for the dehydration of ethanol? |
High temperature and catalyst |
|
|
What is methanol's formula? |
CH3OH |
|
|
What is ethanol's formula? |
C2H5OH |
|
|
What is propanol's formula? |
C3H7OH |
|
|
What is butanol's formula? |
C4H9OH |
|
|
What is a homologous series? |
A series of compounds which: a) have the same general formula b) show a gradual variation in physical properties as exemplified by their boiling points c) have similar chemical properties |
|
|
Name 4 families of compounds that have homologous series. |
1) alkanes 2) alkanes 3) alcohols 4) carboxylic acids |
|
|
What is methane's formula? |
CH4 |
|
|
What is ethane's formula? |
C2H6 |
|
|
What is propane's formula? |
C3H8 |
|
|
What is butane's formula? |
C4H10 |
|
|
What is methene's formula? |
It doesn't have one |
|
|
What is ethene's formula? |
C2H4 |
|
|
What is propene's formula? |
C3H6 |
|
|
What is butene's formula? |
C4H8 |
|
|
What is methanoic's formula? |
HCOOH |
|
|
What is ethanoic's formula? |
CH3COOH |
|
|
What is propanoic's formula? |
C2H5COOH |
|
|
What is butanoic's formula? |
C3H7COOH |
|
|
What does ethanol + oxygen produce? |
Ethanoic acid |

