![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In order to
a government has |
1. A set of objectives
2. A set of policy instruments
3. Some economic theory |
|
|
The main objectives government are:
(4 main objectives) |
full employment
the avoidance of inflation
economic growth
external balance |
|
|
Policy instruments broad categories: |
1. Monetary policy
2. Fiscal policy
3. Supply side policy |
|
|
Economic theory is necessary in |
the formulation of
in order to
inform policy makers of how economies work. |
|
|
Keynesian economists
The main beliefs of this school of thought are: 4 |
The economy is not necessarily a
Money is a vital link between markets, and because money can be stored, the level of demand may be insufficient to ensure full employment.
Inflation may be caused by a combination of demand pull and cost push pressures.
The govt must take the responsibility for managing the economy and adopt an interventionist approach to economic policy. |
|
|
Monetarist/ new classical economists
believe: 5 |
the market should be broadly left to market forces.
Real and monetary forces are separate, prices in the economy.
Inflation is always the result of money supply causing excessive AD.
Full employment is best achieved by
Govts should, on the whole, adopt a approach to |
|
|
Monetary policy is concerned with |
managing the in order to (consumers, investors and businesses)
by affecting either |
|
|
The main feature of
is ...
since ... |
the policy of
since they are |
|
|
The central rate of interest |
the rate at which lends to the money market
based on treasury bill rates. |
|
|
The real interest rate
When the |
there is a
implying that in real terms but savers are gaining. |
|
|
When the rate of inflation exceeds |
there is a
implying that |
|
|
Five consequences
the main effects of
an increase in
include: |
fall in spending
fall in investment
fall in asset values
rise in the exchange rate
attraction of foreign funds into the country |
|
|
The primary objective monetary policy |
limit inflation
and thereby
maintain the |
|
|
A monetary policy of low interest rates
AD curve...
Output, employment, inflation ... |
increase spending
The AD curve will
Output and employment |
|
|
A |
decrease spending
The AD curve will
Output and employment |
|
|
A central bank
faces
in applying monetary policy: |
1. Lack of sufficient, up-to-date information on the economy, particularly money supply
2. Banks' aversion to close supervision
3. Over-vigorous control stifle the initiative of the banks profit-maximising ethos
4. Conflicting objectives |
|
|
A government's fiscal policy is concerned with |
the balance between
and its expenditure
and the effects that |
|
|
The primary function of taxation is |
to enable the government to finance public expenditure, on
goods and services:
transfer payments: |
|
|
Taxation
(4 uses) |
To change markets (e.g., taxing harmful goods to reduce consumption)
To influence the level of aggregate monetary demand
To finance the provision of (defence and education)
To change the distribution of (changing the balance between direct and indirect taxes) |
|
|
The
6 |
Certainty
Convenience
Equity
Economy
Efficiency
Flexibility |
|
|
Efficiency
(canons)
of a tax are |
principles since Adam Smith's day. |
|
|
The normal distinction two types of tax:
1. |
Direct taxes
are levied on income and capital,
and the incidence of the tax and the burden of the tax fall on the same person. |
|
|
The normal distinction two types of tax:
2. |
Indirect taxes
are levied on expenditure,
and the incidence and burden may fall on different persons. |
|
|
The distinction in taxation
3 types |
Progressive taxes Regressive taxes Proportional taxes |
|
|
Progressive taxes |
are ones where
the proportion of income paid in tax Most income taxes are progressive. |
|
|
Regressive taxes |
are ones where
the proportion of income paid in tax falls
Most indirect taxes are regressive. |
|
|
Proportional taxes |
are ones where
the proportion of income paid in tax |
|
|
The difference between
central government income and expenditure
is termed |
the budget deficit or budget surplus |
|
|
The balance between
|
public sector borrowing. The current term for |
|
|
The |
the flow of |
|
|
The |
the flow of |
|
|
In recession, tax yields fall as |
income and output
and public expenditure on rises unemployment increases. |
|
|
The government |
1. To deal with unemployment 2. To finance public expenditure |
|
|
A distinction 1. |
Cyclical element where the deficit and will decrease |
|
|
A distinction 2. |
Structural element where the deficit is the result of
and will not be affected by |
|
|
The ways in which 2 |
Borrowing from Issuing various types of |
|
|
The golden rule for 1. |
over the whole trade cycle, government current expenditure on services and should not exceed its |
|
|
The golden rule for 2. |
only |
|
|
The golden rule for
3. |
the overall burden of go above sustainable levels. |
|
|
If a government > it can finance the deficit > It will have to |
> borrowing. > it will have to |
|
|
The objective of a supply side policy is |
to shift the aggregate supply curve to the right,
which would have the effect of
raising national income and lowering unemployment at the same time as reducing inflationary pressures in the economy. |
|
|
Graph of Aggregate Demand and Supply model (Shift in supply curve) |
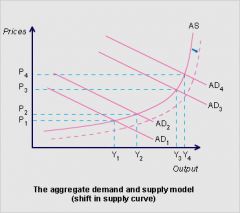
|
|
|
Supply side policy consists of a wide range of measures,
the most important of which are: 5 |
shifting taxation away from direct to indirect taxation
reducing social security payments
emphasising vocational education and training
reducing the power of trade unions and employee organisations
deregulating and privatising |
|
|
Significant consequences of supply side policies are: 4 |
making the taxation system much more regressive
a more unequal distribution of income
a greater degree of uncertainty for workers with less employment protection
a fall in the relative (and sometimes absolute) standard of living of many who are dependent on social security payments |
|
|
The typical prices and incomes policy involved: |
a limit on the annual increase in wages and salaries.
some controls on prices, especially those directly controlled by the government. |

