![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
probability definition
|
a numerical value ranging from 0 to 1;
indicates the chance of a specific event occurring: -if there is no chance of the event occurring, the probability is 0; -if the event is absolutely going to occur, the probability is 1 |
|
|
experiment definition
|
the process of measuring or observing an activity for the purpose of collecting data;
an example is rolling a single 6 sided die |
|
|
sample space definition
|
all the possible outcomes of an experiment;
the sample space for our single-die experiment is {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} -numbers in braces signal they represent sample space |
|
|
event definition
|
1 or more outcomes of an experiment;
the outcome(s) is a subset of the sample space; an example of an event is rolling a pair with two dice |
|
|
simple event definition
|
an event with a single outcome in its most basic form that cannot be simplified;
an example of a simple event is rolling a 5 with a single die |
|
|
methods of assigning probability
|
classical, empirical, and subjective
|
|
|
classical probability forumula
|
# of possible outcomes that constitute event A
P(A) = ---------------------------------------------------------------- total number of possible outcomes in the sample space where: P(A) = the probability that event A will occur |
|
|
empirical probability definition
|
involves conducting an experiment to OBSERVE the frequency of which an event occurs
|
|
|
formula for empirical probability
|
frequency in which event A occurs
P(A) = --------------------------------------------------------- total number of observations |
|
|
law of large numbers
|
states that when an experiment is conducted a large number of times, the empirical probabilities of the process will converge to the classical probabilities;
example: flip a coin a large number of times, the observed number of heads would be very close to 50% |
|
|
subjective probability definition
|
used when classical and empirical probabilities aren't available;
instead use experience or intuition to estimate the probabilities; |
|
|
basic properties of a probability
|
rule 1: if P(A) = 1, then with certainty, event A must occur
rule 2: if P(A) = 0, then with certainty, event A will not occur rule 3: the probability of any event must range from 0 to 1 rule 4: the sum of all the probabilities for the simple events in the sample space must be equal to 1 rule 5: the complement to event A is defined as all of the outcomes in the sample space that are not part of event A; the complement is denoted as A' |
|
|
formula for the complement rule
|
P(A) + P(A') = 1
or P(A) = 1 - P(A') |
|
|
probability rules for more than one event
|
many situations involve 2 or more events that intersect with one another;
a contingency table can be used to show the number of occurrences of events that are classified according to 2 categorical variables |
|
|
marginal probability is another term used for...
|
simple probability
|
|
|
intersection
|
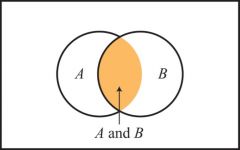
represents the number of instances in which events A and B occur at the same time
|
|
|
joint probability definition
|
probability of the intersection of 2 events
|
|
|
P(Ace∩Red)
Intersection of events |
also denoted as P(Ace and Red)
|
|
|
The union of events A and B represents...
|
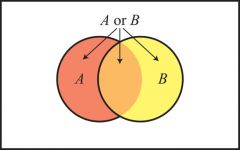
the number of instances where EITHER event A or B occur OR both events occur together
|
|
|
P(Ace∪Red)
Union of events |
is also denoted as P(ace or red)
|
|
|
The addition rule for probabilities...
|
is used to calculate the probability of the union of events;
the probability that event A, or event B, or both events will occur; the 2 events are considered to be MUTUALLY EXCLUSIVE if they can't occur at the same time during the experiment |
|
|
Mutually exclusive forumula
|
P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B)
|
|
|
If events A and B are NOT mutually exclusive formula
|
P(A or B) = P(A) +P(B) - P(A and B)
|
|
|
Conditional probability definition
|
the probability of event A occurring, given the condition that event B has occurred;
AKA posterior probability |
|
|
formula for calculating conditional probability
|

|
|
|
Independent events definition
|
2 events are considered independent of one another if the occurrence of one event has no impact on the occurrence of the other event
|
|
|
Dependent event definition
|
if the occurrence of one event affects the occurrence of another event, the events are considered dependent
|
|
|
formula for determining if events A and B are independent
|
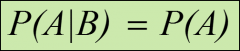
|
|
|
If P(A|B) ≠ P(A) then...
|
events A and B are NOT independent
|
|
|
The multiplication rule...
|
is used to determine the probability of the intersection (joint probability) of 2 events occurring, or P(A and B)
|
|
|
Multiplication rule formula for dependent events
|

|
|
|
Multiplication rule formula for dependent events (other way)
|

|
|
|
formula for the multiplication rule for 2 independent events
|

|
|
|
convert table frequencies into probabilities by...
|
dividing each number in the table by the total number of observations
|
|
|
Decision trees definition
|
used to display marginal and joint probabilities from a contingency table
|

