![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Competitive Advantage
|
a set of unique features of a company and its products that are perceived by the target market as significant and superior to the competition
|
|
|
Cost Competitive Advantage
|
being the low-cost competitor in an industry while maintaining satisfactory profit margins
|
|
|
Sustainable Competitive Advantage
|
an advantage that cannot be copied by the competition
|
|
|
Marketing Mix
|
a unique blend of product, place (distribution), promotion, and pricing strategies designed to produce mutually satisfying exchanges with a target market
|
|
|
social responsibility
|
a business's concern for society's welfare
|
|
|
sustainability
|
the idea that socially responsible companies will outperform their peers by focusing on the world's social problems and viewing them as opportunities to build profits and help the world at the same time
|
|
|
Environmental Management
|
when a company implements strategies that attempt to shape the external environment within which it operates
|
|
|
What are the four basic American values?
|
self-sufficiency, upward mobility, work ethic, conformity
|
|
|
component lifestyles
|
the practice of choosing goods and services that meet one's diverse needs and interests rather than conforming to a single, traditional lifestyle
|
|
|
purchasing power
|
a comparison of income versus the relative cost of a set of standard of goods and services in different geographic areas
|
|
|
licensing
|
the legal process whereby a lincensor allows another firm to use its manufacturing process, trademarks, patents, trade secrets, or other proprietary knowledge
|
|
|
joint venture
|
when a domestic firm buys part of a foreign company or joints with a foreign company to create a new entity
|
|
|
direct investment
|
developing foreign-based manufacturing or assembling facilities
|
|
|
What are the four profitability drivers?
|
customer acquisition, customer retention, margin, sales per customer
|
|
|
social responsibility
|
Organizations are a
part of a larger society and are accountable to that society for their actions. |
|
|
Sustainability
|
Organizations will focus on
the world’s social problems and view them as opportunities to build profits and help the world. |
|
|
B2B
|
• Individual buyers
> Purchasing agent • Group buyers > The buying center |
|
|
5 things around the family buying center
|
buyers, users, gatekeepers, kidfluencers, deciders
|
|
|
Factors influencing consumer behavior
|
Social, Individual, Social, Psychological
|
|
|
Criteria for Segmentation
|
Measurable, Accessible, Durable, Substantial, Unique Needs |
|
|
Ways to Segment
|
Geographic
• Region, city or metro size, density, climate Demographic • Age, gender, family size and life cycle, race, occupation, income Psychographic • Lifestyle, personality, attitudes, values Behavioral • Usage situations, benefits |
|
|
USP sentence
|
[Product name] competes in [product category] and provides [biggest benefits] to [customer identity] when they are [buying situation]. [Product name] unlike [main competitors] is unique because it provides [element of differentness] |
|
|
Key factors to analyze when determining which foreign market to enter into |
1) Customer needs 2) Customer Purchasing Power 3) Market size 4) Market growth rate 5) Market access |
|
|
Risks of entering new foreign market |
Political, Economic, Competitive, Legal |
|
|
Cross tabulation |
frequency counts conditions, attitudes, behaviors that occur most often |
|
|
Analysis of Variance |
Variability around an average |
|
|
Regression analysis |
divides variables into predictors and outcomes |
|
|
Factor Analysis |
groups together highly correlated variables |
|
|
Cluster analysis |
groups together respondents that answer survey questions in similar ways, have similar demographic profiles, or have similar behaviors. Researchers use cluster analysis to divide markets into segments |
|
|
Discriminant analysis |
group together similar brands or, in some instances, similar people. Researchers use discriminant analysis to generate perceptual maps depicting the relationships between brands and brand attributes |
|
|
Max-diff analysis |
(TURF) ice cream example decide which products to sell and which will not be very profitable Surveyors answer which products are most/least important or most/least appealing |
|
|
Conjoint analysis |
first deconstructs products into component attributes, next estimates the value of each component attribute, and then reconstructs existing and potential products in a way that allows researchers to estimate the value of each product |
|
|
How services differ from products |
Intangible, Inseparable, Variability, Perishable |
|
|
3 P's of Service marketing |
People - good people to do the service Process - good system to get it done Physical Environment - helping customers feel good about the "intangible" |
|
|
Quality Service Providers |
Tiger - high quality and productivity Fox - low quality high productivity Servant's Heart - high quality low productivity Kitten - loser |
|
|
Unit Margin |
= price - unit variable cost (unit contribution) |
|
|
Percent Margin |
Price - Unit variable cost ----------------------------------- Price |
|
|
Break even volume |
Fixed Cost ------------------- Unit contribution |
|
|
price skimming vs penetration |
Skimming: begin with high price and gradually lower it to absorb all possible profits Penetration: begin with a low price to bring in quick revenue |
|
|
4 Pricing approaches |
Golden goose: know own costs and lots about customer value Value: know own costs and a lot about customer value and competitors Competitive: know own costs and a lot about competitors Cost plus: know own costs but not much about customers or competitors |
|
|
Why promote? |
Increase demand Make demand more inelastic |
|
|
Promotion mix |
B2C order: Advertising, Sales promotion, Personal selling, Direct marketing Public relations B2B: Personal selling, sales promotion, Direct marketing, advertising, public relations |
|
|
Push vs Pull strategies |
Push: producer--->intermediaries--->end users Pull: end users--->intermediaries--->producer |
|
|
3 Objectives of Advertising |
Cognitive (build awareness) Affective (gain interest) Behavioral (stimulate action) |
|
|
Media buying |
Reach- number of people who see it Frequency- how often they see it GRP- gross rating points TRP- target rating points CPM- cost per thousand impressions |
|
|
3 red hot rules of thumb |
Product must be obvious Advertiser is obvious Benefit is obvious |
|
|
Intermediaries: benefits |
Intermediary: "middle man" that takes care of all the transactions between buyers and sellers to minimize total amount of transactions 1) break bulk 2) provide assortment 3) hold inventory 4) offer services 5) market efficiency |
|
|
Market exposure |
Intensive distribution: every-day purchases Selective distribution: some effort Exclusive distribution: huge, major purchases (Ferrari) |
|
|
Bottom up marketing |
Build strategy around a differentiating tactic Competitive angles Embracing constraints Startup R&D |
|
|
4 step ideation process |
1) select a problem area that interests you (oysters and eagles)
2) Explore area for opportunities 3) propose and test alternative product ideas (WOW focus groups) (6 hats) 4) Perfect the best idea -sharpen the angle |
|
|
Sharpen product angle |
1) unique product claim 2) need to believe 3) dominate situations 4) reason to believe 5) quantifiable support |
|
|
5 keys to finding big ideas |
1) solve everyday pain 2) ride waves of interest 3) stretch or entertain to the extreme 4) build on a core product 5) cool hunting |
|
|
Leverage leverage
|
Find horses Empower early adopters Land an anchor customer Work with benefactors Build an advisory board |
|
|
Product adoption groups |
Innovators Early adopters Early majority Late majority Laggards |
|
|
Classifying consumer products |
1) convenience 2) shopping 3) specialty 4) unsought |
|
|
Business products |
Materials and parts Capital items Supplies and services |
|
|
Product items, lines, and mixes |
Items: individual products that are sold Lines: variations of the same kind of product Mixes: everything the company sells |
|
|
Product life cycle |
1) limited life 2) distinct stages 3) sales and profits vary 4) require different strategies and different cycle stages |
|
|
5 dimensions of an angle |
1) need to believe
2) reason to believe 3) blows away expectations 4) quantifiable support 5) unique product claim |
|
|
Type I vs Type II errors
|
Type I: reject a good idea Type II: accept a bad idea |
|
|
3 Levels of a product |
Core: benefits of the product Actual: the thing itself Augmented: accessories and add-ons |
|
|
Brands should: |
Resonate with the customer Differentiate from competitors Motivate employees |
|
|
Developing Brand Equity |
Awareness-->Image-->Loyalty-->Equity |
|
|
Brand Matrix (slide 56 on "Products and Brands") |
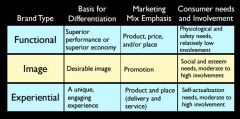
|
|
|
3 Components of Positioning |
1. Competitive frames of reference 2. Points of difference (POD's) 3. Points of parity (POP's) |

