![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The three parts of the cell theory are
|
1. All organisms are composed of one or more
cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of organization. 3. All cells come from preexisting cells. |
|
|
Regulates what enters and leaves the cell
|
plasma membrane
|
|
|
Protects and supports the cell
|
cell wall
|
|
|
Contains all the cell’s DNA
|
nucleus
|
|
|
Assembles ribosomes
|
nucleolus
|
|
|
DNA wrapped around proteins
|
Chromatin
|
|
|
Site where proteins are assembled
|
RIbosome
|
|
|
Fluid inside the cell
|
cytoplasm
|
|
|
Network of protein filaments that helps the cell
maintain its shape |
cytoskeleton
|
|
|
Organize the spindles in cell division
|
centrioles
|
|
|
Assembles lipids, proteins, and other materials
in the cell |
Endoplasmic reticulum
|
|
|
Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and
other materials for storage in the cell or transport out of the cell |
Golgi body
|
|
|
Stores water, food, waste, and other materials
|
vacuole
|
|
|
Contain enzymes to break down molecules and
recycle cell parts |
lysosomes
|
|
|
Converts chemical energy stored in food into
energy the cell can use; site of cellular respiration |
mitochondria
|
|
|
Converts energy of the sun into chemical
energy; site of photosynthesis |
chloroplast
|
|
|
Long projections that move with a whiplike
motion |
flagella
|
|
|
Short hairlike projections that beat in a coordinated
wave |
cilia
|
|
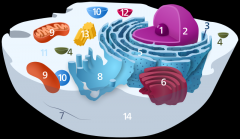
Structure 1 is the
|
nucleolus
|
|
Structure 2 is the
|
nucleus
|
|
Structure 3 is the
|
ribosome
|
|
Structure 5 is the
|
Endoplasmic reticulum
|
|
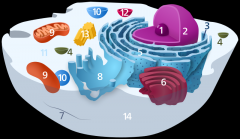
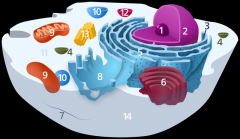
Structure 6 is the
|
Golgi body
|
|
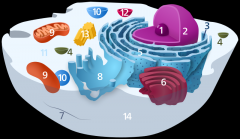
Structure 7 is the
|
cytoskeleton
|
|
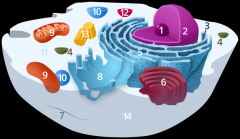
Structure 9 is the
|
mitochondria
|
|
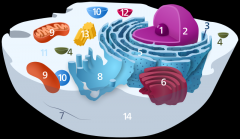
Structure 10 is the
|
vacuole
|
|
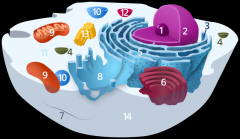
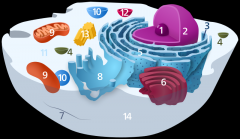
Structure 11 is the
|
cytoplasm
|
|
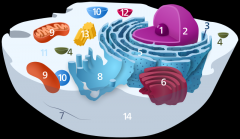
Structure 12 is the
|
lysosome
|
|
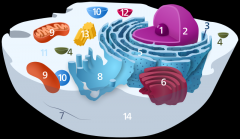
Structure 13 is the
|
centriole
|
|
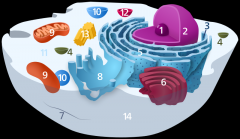
Structure 14 is the
|
plasma membrane
|
|
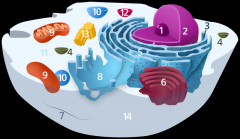
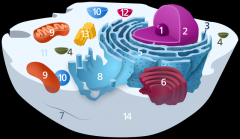
Is the cell pictured an animal, plant or bacteria cell?
|
animal
|
|
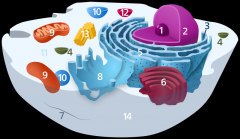
Is the cell pictured eukaryotic or prokaryotic?
|
eukaryotic
|
|
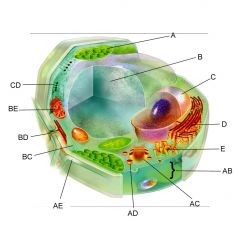
Structure A is the
|
chloroplast
|
|
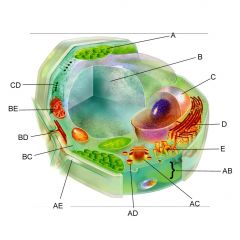
Structure B is the
|
vacuole
|
|
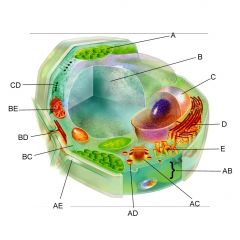
Structure C is the
|
nucleus
|
|
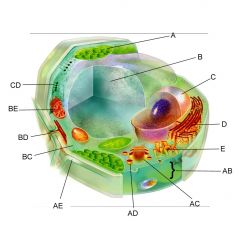
Structure D is the
|
Endoplasmic reticulum
|
|
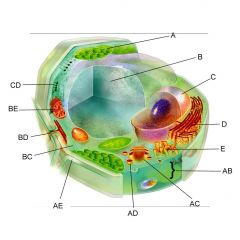
Structure AB is the
|
Plasma membrane
|
|
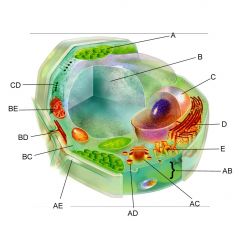
Structure AC is the
|
Golgi body
|
|
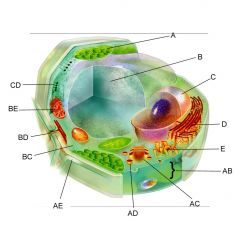
Structure AE is the
|
cell wall
|
|
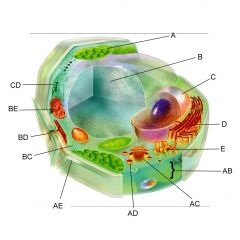
Structure BC is the
|
cytoplasm
|
|
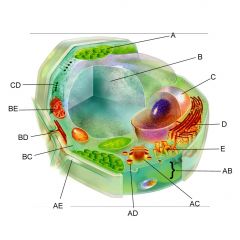
Structure BE is the
|
mitochondria
|
|
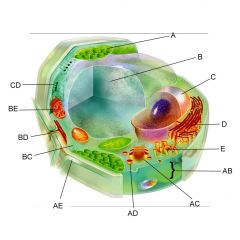
Is the cell pictures an animal, plant, or bacteria cell?
|
plant
|
|
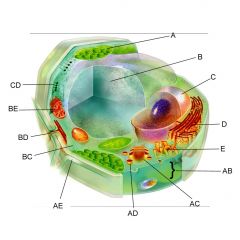
Is the cell pictured eukaryotic or prokaryotic?
|
eukaryotic
|
|
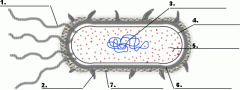
Structure 1 is the
|
flagella
|
|
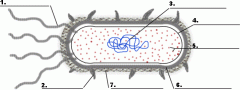
Structure 3 is the
|
DNA
|
|
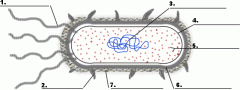
Structure 5 is the
|
ribosome
|
|
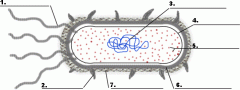
Structure 4 is the
|
plasma membrane
|
|
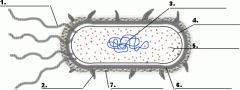
Structure 6 is the
|
cell wall
|
|
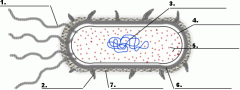
Is the cell pictured a plant, animal or bacteria cell?
|
bacteria
|
|
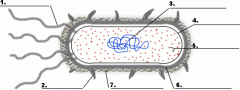
Is the cell pictured eukaryotic or prokaryotic?
|
prokaryotic
|
|
|
This type of cell has membrane-bound organelles, including a nucleus
|
eukaryotic
|
|
|
This type of cell does not have membrane-bound organelles
|
prokaryotic
|

