![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
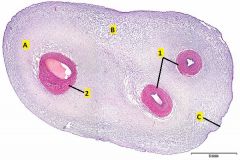
Where is this slide taken from?
Identify 1 and 2. Where is the best place to find mucous c.t., A, B, or C? |
Umbilical cord.
1 - umbilical arteries 2 - umbilical vein Mucous ct is best found is at the edge of the cord between the large vessel and one of the two small vessels. Mucous c.t. is a developmental c.t. that has far fewer collagen fibers than mature connective tissues. Hyaluronic acid comprises a large proportion of the ground substance in situ but is lost during tissue preparation. This results in the very loose appearance. |
|
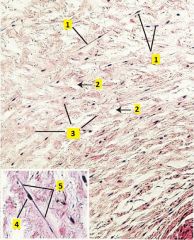
Image taken from umbilical cord. What type of tissue is shown?
What type of cell is 1? Identify what kind of substance is labeled 2 and 3. What is 4 and 5? |
Mucous c.t.
1 - fibroblasts 2- ground substance (largely composed of hyaluronic acid) 3 - collagen fibers 4 - nucleus of fibroblast 5 - cytoplasm of fibroblast |
|
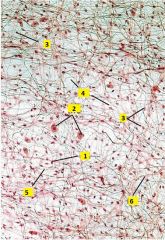
What type of connective tissue is this?
Identify the cells types of 1-3. Identify what type of substance is labeled 4-6. |
Areolar (loose) c.t. (whole mount of messentery)
1 - macrophage (small dense nucleus) 2 - mast cell (round nucleus with grainy cytoplasm) 3 - fibroblast (nucleus more pale than macrophage) 4 - ground substance 5 - elastic fibers (black, thin, straight, branching) 6 - collagen fibers (pink, thick, wavy, ribbon-like) |
|
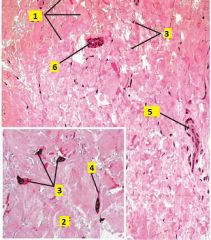
What type of connective tissue is this?
Identify 1-6. |
Dense irregular collagenous c.t. (from reticular layer of the dermis).
1 - collagen fiber bundles 2 - collagen fibril 3 - fibroblast nuclei. Inactive fibroblast, a fibrocyte, has a dense flat nucleus. Active fibroblastts have lighter, larger elongated nuclei. 4 - fibroblast cytoplasm 5 - blood vessel 6 - duct |
|
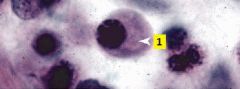
What type of cell is this?
|
Plasma cell
It has a round, eccentrically-located nucleus with the heterchromatin in a "clockface" pattern. Cytoplasm has light basophilia due to staining of the extensive RER. |
|
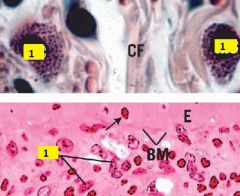
What type of cell is labeled 1?
|
Mast cell.
They have a round to oval nucleus and numerous small granules in the cytoplasm. |
|
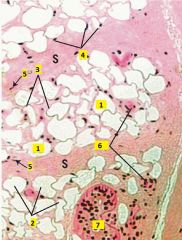
What type of connective tissue is this?
Identify 1-7. |
Adipose (unilocular) tissue (from the hypodermis).
1 - fat droplet 2 - adipocyte 3 - cytoplasm of adipocyte 4 - nuclei of adipocyte 5 - nuclei of fibroblast 6 - blood vessels 7 - sweat gland |
|
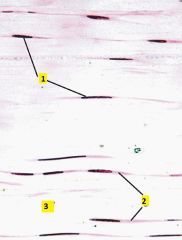
What type of connective tissue is this?
Identify 1-3. |
Dense regular collagenous c.t. (from muscle tendon)
1 - fibroblast (nucleus parallel with collagen) 2 - cytoplasm of fibroblast 3 - collagen fibers (thick pink, parallel bundles of collagen fibers) |
|
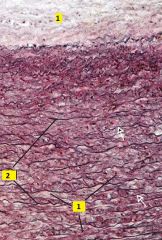
What type of connective tissue is this?
What type of fibers are 1 and 2? |
Dense regular elastic c.t. (from aorta, stained with orecin and H&E)
1 - collagen fibers 2 - elastic fibers Note: within tunica media collagen is secreted by smooth muscle cells instead of fibroblasts. Outermost layer (tunica adventitia) is loose areolar or dense irregular collagenous c.t. |
|
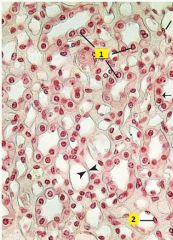
What type of cell is 1 and 2?
|
1 - Simple cuboidal epithelium.
2 - Simple squamous epithelium (appear flattened with nuclei bulging into lumen). Image of medulla of the kidney. |
|
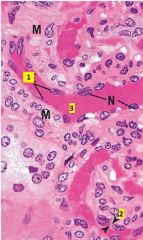
What type of cell is 1?
Identify 2 and 3. |
1 - simple squamous epithelium
2 - cytoplasm of simple squamous epithelium 3 - lumen of small arteriole (notice smooth muscle (M) lining of vessel) |
|
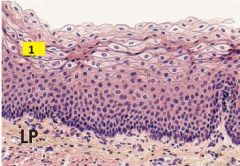
What of cells are labeled 1?
|
1 - stratified squamous epithelium.
Section from epithelium lining lumen of esophagus. |
|
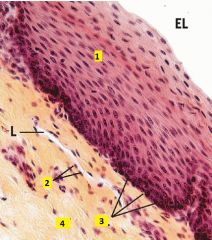
What are the cell types of 1 and 2?
Identify 3 and 4. |
1 - stratified squamous epithelium
2 - simple squamous epithelium 3 - basal layer 4 - connective tissue |
|
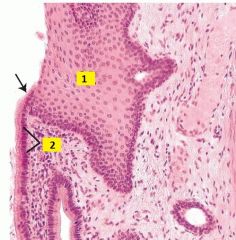
What type of cells are 1 and 2?
|
1 - stratified squamous epithelium
2 - simple columnar epithelium Image of esophagogastric junction (arrow). |
|
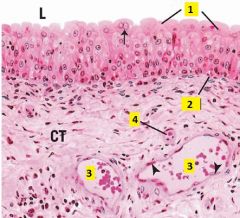
What of type of cells are labeled 1?
Identify 2-4. |
1 - transititonal epithelium (dome-shaped when bladder is relaxed, appear squamous when distended; occasionally binucleate)
2 - basement membrane 3 - veins 4 - arteriole (notice muscular layer) |
|
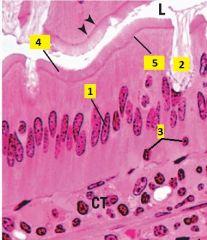
Identify the cell type of 1-3.
What are 4 and 5? |
1 - simple columnar epithelium (nuclei are oval and at about the same level)
2 - goblet cell 3 - lymphocyte (small, deeply-basophilic round nucleus) 4 - brush border (microvili + glycocalyx) 5 - terminal web Image of villi of duodenum. |
|
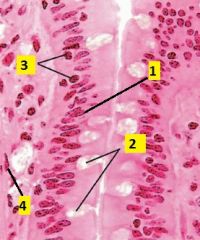
What type of cells are 1-4?
|
1 - simple columnar epithelium
2 - goblet cells (unicellular mucus-secreting glands) 3 - lymphocytes 4 - smooth muscle cell |
|
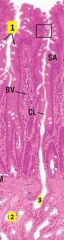
Identify 1-3.
|
1 - goblet cells
2 - multicellular gland (gland of Brunner) 3 - duct |
|
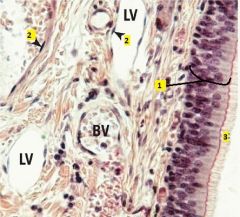
What type of cells are 1 and 2?
What is 3? |
1 - pseudostratified columnar epithelium (notice the several layers of nuclei on the basal side)
2 - simple squamous epithelium 3 - cilia |
|
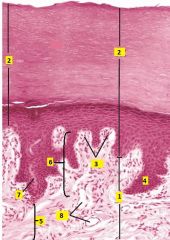
What type of tissue is this?
Identify 1-8. |
Thick skin
1 - dermis 2 - epidermis 3 - dermal ridges 4 - epidermal ridges 5 - reticular layer 6 - papillary layer 7 - duct 8 - blood vessels |
|
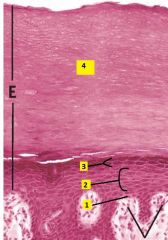
Identify the layers 1-4.
|
1 - stratum basale
2 - stratum spinosum 3 - stratum granulosum 4 - stratum corneum Stratum lucidum is not seen in this image |
|
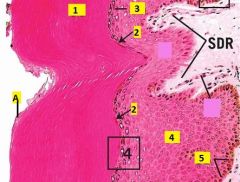
Identify the layers 1-5.
Identify A. |
1 - stratum corneum
2 - stratum lucidum 3 - stratum granulosum 4 - stratum spinosum 5 - stratum basale A - squames (very flattened, individual tile-like cells at apical surface which will be sloughed off). |
|
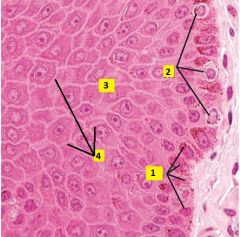
Image taken from dermal-epidermal junction. What type of cells are 1-3?
What is 4? |
1 - Basal keratinocytes (stem cells). Stratum basale is a single row of mitotic stems cells responsible for renewal of keratinocytes.
2 - Melanocytes. Pigment-synthesizing cells of skin, tend to be round and stain lighter; derived from neural crest, not keratinocytes. These are found in the stratum basale. 3 - Keratinocytes. Stratum spinosum is the thickest layer of keratinocytes; cells are cube-shaped and become flatter towards the stratum granulosum. 4 - Sites of desmosome attachments (structures have "spiny" appearance). |
|
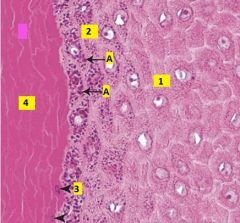
Image taken of epidermis of thick skin. What are the layers labeled 1-4?
Identify A. |
1 - Stratum spinosum
2 - Stratum granulosum. Usually 1-3 layers of flattened cells with numerous distinct keratohyalin granules. 3 - Stratum lucidum. Only present in thick skin, transitional cells in which nuclei and organelles are degenerated, and cytoplasm is becoming filled with keratin intermediate filaments. Stains lighter than corneum. 4 - Stratum corneum. Layer of dead, fully keratinized cells. A - keratohyalin granules (in keratinocytes of stratum granulosum). |
|
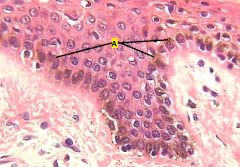
What type of skin is this?
|
Pigmented skin, A is highlighting a couple areas of melanin pigment. It appears brown and is mostly confined to thee basal keratinocytes.
|
|
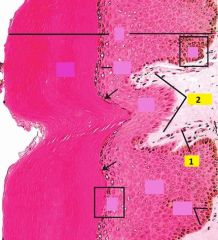
Identify 1 and 2.
|
1 - capillary loop (persent in virtually every dermal papilla)
2 - dermal papillae (finger-like dermal projections) |
|
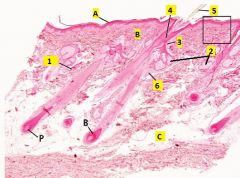
What type of tissue is this?
Identify the layers A,B, and C. Identify 1-6. |
Thin skin.
A - epidermis B - dermis C - hypodermis (loose c.t. with much adipose) 1 - sweat glands 2 - sebaceous glands 3 - duct 4 - hair follicle 5 - hair 6 - arrector pili muscle B - bulb of hair P - papilla of hair |
|
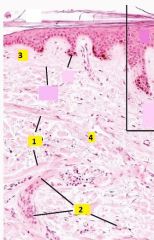
Identify 1 and 2.
What type of connective tissue is present at 3 and 4? |
1 - arrector pili muscles
2 - blood vessels 3 - papillary layer is composed of relatively loose irregular collagenous connective tissue (loose areolar c.t.). 4 - reticular layer is composed of dense irregular collagenous c.t. |
|
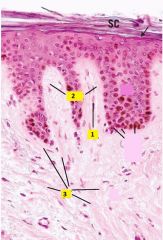
Identify 1-3.
|
1 - capillary loop
2 - dermal papillae 3 - collagen fibers |
|
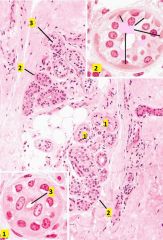
This structure is found in the skin, what is it?
What portion of it is 1 and 2? Identify 3. |
Sweat gland. The base of a sweat gland (the secretory portion) is a highly coiled tube, hence a single section slices through the tube many times. This appears as multiple round profiles, each with a central lumen lined by cuboidal epithelium.
1 - secretory portion (simple cuboidal epithelium) 2 - duct portion (stratified cuboidal epithelium, stain darker) 3 - lumen |
|
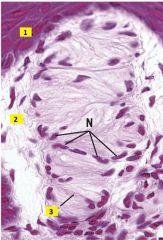
What type of structure is this that is found in the dermis?
Identify 1-3. |
Meissner's corpuscle - light touch sensory receptor present in those few dermal papillae that do not possess capillary loops. They lie just deep to the stratum basale.
1 - stratum basale 2 - capsule 3 - nerve fiber |
|
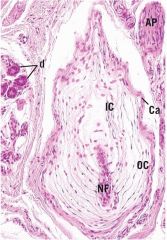
What type of structure is this which is found in the dermis?
|
Pacinian corpuscle - relatively large, light-staining structure that appears as a series of concentric rings. It is a mechanoreceptor.
NF - nerve fiber d - duct Ca - capsule AP - arrector pili |

