![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|

|
|
|
Where are the adrenal glands located?
What are the shapes of the adrenal glands? |
-above kidneys
-right adrenal - pyramid shaped -left adrenal - crescent shaped |
|
|
The outer adrenal (cortex/medulla) is derived from ______ and is the _____ secreting portion of the gland
The inner adrenal (cortex/medulla) is derived from ____ and is the _____ secreting portion of the gland |
-cortex - embryonic mesoderm - steroid secreting
-medulla - neural crest - catecholamine |
|
|
What are the 3 layers of the adrenal cortex?
|
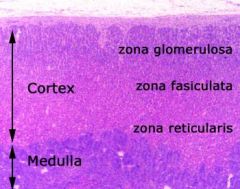
-Zona glomerulosa
-Zona fasciculata -Zona reticularis |
|
|
Zoma glomerulosa secretes:
|
Mineralocorticoid hormones - involved in fluid/electrolyte balance
-Aldosterone - major mineralcorticoid - stimulates Na resorption at the distal convoluted tubule and other locations (retain water) |
|
|
Zona fasciculata cells are called:
|
-Spongiocytes - names of cells due to "spongy" cytoplasmic appearance caused by lipid droplets
|
|
|
Zona fasciculata secrets:
|
-Glucocorticoid hormones - cortisol and corticosterone (regulate carbohydrate metabolism - acts on liver, adipose tissue, fibroblasts and immune system)
|
|
|
How is glucocorticoids of the zona fasciculata regulated?
|
-feedback system of hypothalamus and hypophysis
Corticotropin releasing factor (CSF) released when low glucocorticoids --> CSF stimulat ACTH synthesis --> ACTH secreted by adenohypophysis --> ACTH essential for growth and maintenance of cells in zona fasciulata and stimulates glucocorticoid synthesis and increased flow of adrenal gland |
|
|
Zona reticularis secrets:
|
-weak androgens which can be converted to testosterone and estrogen
-stiulates secondary sex characteristics for women (major androgen secretion for women and minor for men) *** May be the a zone of cellular degeneration |
|
|
What are the differences in the histological appearances of the zona glomerulosa, fasiculata, and reticularis?
|
-glomerulosa - small columnar in oval clusters; small dark nucleus and acidophilic cytoplasm
-fasciculata - stain lightly acidophilic and larger than glomerulosa (spongy) -reticularis - smiliar to fasciculata but smaller and more irregular |
|
|
What are the cells located in the adrenal medulla?
These are modified _____ |
-chromaffin cells
-modified sympathetic postganglionic neurons (from neural crest) that have lost axons and dendrites |
|
|
Chromaffin cells of adrenal medulla secretes:
|
Catecholamines:
-norepinephrine - large, dense granules -epinephrine - small, less dense granules |
|
|
What are chromogranins?
|
-major component of granules of norepinephrine and epinephrine
-may be binding proteins for catcholamines |
|
|
What innervates chromaffin cells and how are they controlled?
|
-innervated by preganglionic sympathetic neurons
-Ach release by neuron depolarizes the cell, leading to catecholamine release -different innervations = norepinephrine:epinephrine release may vary |
|
|
Describe fight or flight response:
|
increase secretion of catecholamines (mainly epinephrine) resulting in increased cardiac output, heart rate, blood flow through organs, alertness and liver glycogenolysis
|
|
|
The arteries that supply the adrenal gland branches before entering the capsule. What are these three branches and what do they do?
|
-Fenestrated sinusoidal capillaries - supply cortex
-Medullary sinusoidal capillaries - receive blood from cortical sinusoids -Medullary arterioles - carry arterial blood directly to medullary sinusoidal capillaries |
|
|
What are the endocrine portion of the pancreas?
|
Islets of Langerhans
|
|
|
What are the three main cell types of the islets of Lnagerhans and what do they secrete?
What are the other 2 cells in the islet that comprises less than 1%? |
-alpha cells - glucagon (activates gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis in liver)
-beta cells - insulin (uptake of glucose) -gamma cells - somatostatin paracrine and endocrine functions (paracrine - inhibits hormone release of alpha and beta) (endocrine - reduces smooth muscle contraction in alimentary tract and gall bladder) -G cells - produce gastrin (stimulates stomach parietal HCl production) -PP cells (F cells) - produce pancreatic polypeptide (inhibitor of exocrine pancreas secretion) |
|
|
Control mechanism of insulin and glucagon secretions is also due to ______ and ____ innervations
|
sympathetic and parasympathetic innervations of endocrine pancreas
|
|
|
____ between cells of islets permits cell-to-cell communication
|
Gap junctions
|
|
|
The pineal gland develops from _____ and is a cone-shaped projection from the floor of the ______
|
-neuroectoderm
-diencephalon |
|
|
What are synaptic ribbons?
|
-dense tubular structures unique to pinealocytes (function unknown)
|
|
|
What does pinealocytes secrete?
|
Melatonin:
-circadian and seasonal rhythms (increase at night) -scavenges free radicals during oxidative stress (protective mechanism for the CNS) *production and release is under sympathetic nerves that innervate pinealocytes |
|
|
What are the two cell types of the pineal gland?
|
-pinealocytes
-interstitial cells (astrocytes) - structurally comparable to supportive neuroglial cells |
|
|
What is brain sand?
|
-calcium phosphate and bicarbonate concentrations in pineal gland (function unknown)
-they are x-ray opaque and are used for radiographic markers |

