![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Although they are involuntary, cardiac muscles appear ______________.
|
striated. smooth muscles are not striated but cardiac are
|
|
|
How many nuclei does a muscle fiber (cell) have?
|
multinucleated
|
|
|
How do you remember the organization of the bands found in a sarcomere?
|
Medical Mnemonics Help Amnesiacs Improve Z-score
(Mline in M band, which is within the H band, within the A band, flanked by the I band, each of which are divided by the Z line) |
|
|
You find myosin ONLY, AT ALL TIMES (no actin) in what band?
|
H band
|
|
|
During contraction, ___________ move closer to one another and the __________ reduces in size. The ___________ remains the same.
|
-z disks
-I band AND H band reduce in size -A band remains the same (always constant in length as it describes where the myosin spans the sarcomere) |
|
|
How many myosin molecules can be found in a thick filament?
|
250
|
|
|
F-actin is a polymerization of
|
g-actin
|
|
|
The thin filament is a twisted combination of what?
|
two f-actins
|
|
|
What protein serves as a template for polymerization of F-actin?
|
nebulin
|
|
|
Explain the contraction (power stroke) cycle of skeletal muscle.
|
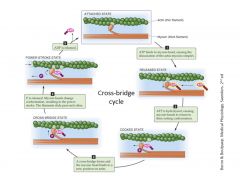
|
|
|
What is the point of ATP binding to the myosin head during skeletal muscle contraction?
|
it dissociates the myosin head from actin
|
|
|
What causes the actual powerstroke, where the myosin head changes confirmation?
|
P is released. NOTE: ATP hydrolysis causes the myosin head to change confirmation into the cocked position. The releasing of P is a different step that comes later and causes the powerstroke
|
|
|
The thick filament is symmetrical about the ____________.
|
m-line
|
|
|
Relaxed muscle is found in what state of the contraction cycle?
|
the cocked stage (myosin is not associated with actin in this stage and the myosin head is in a functional position to cause sliding)
|
|
|
What is the regulated step in the skeletal muscle contraction cycle?
|
cross bridge formation between the cocked myosin head and actin
|
|
|
What is the protein polymer that wraps around actin?
|
tropomyosin
|
|
|
TnT?
|
binds the troponin complex to Tropomyosin
|
|
|
TnC?
|
binds to calcium
|
|
|
TnI?
|
binds the troponin complex to actin (at the grooves for myosin heads), preventing cross bridge formation
|
|
|
What does calcium do to the troponin-tropomyosin complex?
|
Normally, the troponin tropomyosin complex is blocking cross bridge formation. When calcium binds to TnC, it causes the troponin complex to move, revealing the actin-myosin binding site and allowing cross bridge formation to occur
|
|
|
What protein stabilizes myosin and provides the elasticity needed for the sarcomere to return to the relaxed state after contraction?
|
Titin (largest protein ever)
|
|
|
The nicotinic Ach receptor is an _____________ receptor.
|
ionotropic (Na and K)
|
|
|
What are the 2 antagonists of the nicotinic Ach receptor?
|
curare, alpha-bungarotoxin.
agonist is nicotine, of course |
|
|
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease with antibodies against the _____________ receptor.
|
nicotinic Ach
|
|
|
What is the end plate potential (EPP)?
|
the depolarization of muscle induced by the motor neuron
|
|
|
The arrangement of _______________ is known as the triad.
|
2 terminal cisternae of the SR flanking one T tubule
|
|
|
How is Calcium released out of the SR terminal cisternae, starting with the action potential?
|
Ach causes influx of sodium into the muscle cell, which causes the propagation of a new action potential through the sarcolemma. This action potential reaches the DHP receptor on the sarcolemma, which is connected to the RyR receptor on the cisternae. When activated, the RyR receptor opens and calcium leaves the SR and goes into the muscle fiber, binding to troponin, causing cross bridge formation and then contraction
|
|
|
What pumps calcium back into the SR following contraction?
|
SERCA pumps (require ATP)
|

