![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
kinesin
|
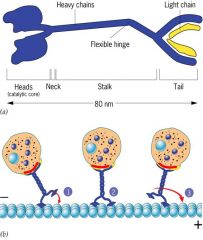
-move from - to +.....out of cell
globular heads have atp binding sites heads bind to microtubules and initiate atpase activety |
|
|
1)cargo
|
vesicles, protein complexes and organelles, which are bound to specific members
|
|
|
what binds kinesin to cargo?
what binds dyneins to cargo? |
1) kinectin
2)dynactin |
|
|
most cells, not just axons, are supportd by what?
|
arrays of microtubules
|
|
|
where is the + and - end of microtubules?
|
+ end points away from the middle of the cell
|
|
|
which direction to dynein and kinesin travel?
|
dynein moves things toward the middle of the cell +to-
kinesin moves things away from the middle of the cell: - to + |
|
|
dynein
|
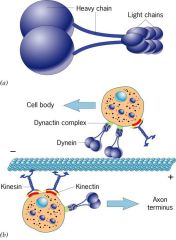
microtubules based motor protein
two atp bingding heads...just like kinesin move from + to - |
|
|
name one big function dyneins can be involved in
|
positioning the spindles for chromosome movement during cell division
|
|
|
draw a picture of kinesins and dyneins involved in transport with golgi complex, ER and the otside of cell
|
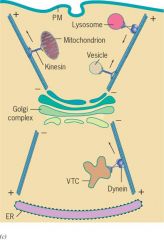
aa
|
|
|
how can microtubule assembly be achieved in vitro
|
from a homogenate cell mixture or from purified alpha, beta tubulins
-add mg2+, gtp and egta |
|
|
what does egta do in vitro for microtubule assembly
|
binds Ca2+ which inhibits assembly
|
|
|
how can assembly/dissassembly of microtubules be cycled through
|
raisings and lowering the temperature
|
|
|
in vitro, how can microtubule assembly be sped up>
|
by adding existing microtubule fragments
|
|
|
what does assembly of microtubules in vitro and vivo begin with?
requires? |
creation of dimers between alpha and beta tubulin
GTP molecule bound to beta-tubulin |
|
|
what happens after gtp binds to beta-tubulin
|
dimers associate into microtubule fragments, and then the microtubule elongates
|
|
|
where would you expect to find gdp and gtp on a microtubule?
|
gdp - end
gtp + end (cap will stabalize the + end) |
|
|
what does gtp bind to in microtubules?
|
beta tubulin
|
|
|
what happens to gdp on the tubulins when they disasseble?
|
replaced by a new gtp after dissassembly of the microtubule back into tubulins
|
|
|
gtp dimers
|
gtp binded to beta tubulin when it forms the chain
|
|
|
how can the growth or shrinkage of microtubules be regulated
|
mainly by altering the balance of addition and removal of tubulin dimers
|
|
|
katanin
|
can cut microtubules into pieces, exposing the (-) end for depolymerization
|
|
|
MTOC
ex. |
microtubule organizing centers
play a role in nucleation ex. centrosomes basal bodies others scattered in plant cells which lack centrosomes |
|
|
2 microtubule phases
|
nucleation and elongation
|
|
|
nucleation
|
small portion of tubule formed at the begining
|
|
|
are centrosomes found in all animal and plant cells?
|
no they are only found in every animal cell
|
|
|
when do centrosomes divide
|
before cell division begins
|
|
|
PCM
|
peri-centriolar material
surounds the centrosome |
|
|
draw and describe centrosome structure
|

Centrosome
One found in each animal cell. Divides before cell division begins. A complex structure with two barrel-shaped centrioles – 0.2 micrometers in diameter and twice as long - surrounded by electron-dense peri-centriolar material (PCM) Centrioles contain nine fibrils in a pinwheel pattern, each composed of three microtubules A,B,C B,C are fragments that “piggyback” onto A The pair of centrioles in a centrosome are at right angles to each other. Large numbers of microtubules converge onto the centrioles. |
|
|
how can microtubule assembly be studied in living cells
|
depolorizing them into tubulins with cold or drugs
re-polimerization occurs when the drugs are washed out or heating occurs bix cells at various times and stain them with fluorescent anti tubulin antibodies |
|
|
what will be seen when studying microtubule assembly in cells
|
within 15-30 minutes of removing the drug or heating, microtubule re-assembly occurs
the + end will radiate outwards and the - end will be found in the PCM |
|
|
do all microtubules originate at the cetrosome?
|
no
microtubules in the axons of neurons originate in cytoplasm throughout the length of the axon |
|
|
microtubules in axons do what with respect to the centrosome?
|
possibly polymerize there
|
|
|
oocytes
|
egg precursors
|
|
|
mouse oocytes importance
|
do not have centrosomes yet still form mitotic spindles
|
|
|
basal bodies
|
non-centrosome MTOCS
found at the base of cilium or flagellum identical in structure to the centrosome |
|
|
describe pcm
|
pericentriolar material
has gamma tubulin will only bind to alpha tubulin |

