![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
89 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which of the following represents a pair of homologous structures?
A) the feathers of a bird and the wing membrane of a bat B) the wing of a bat and the wing of a butterfly C) the wing of a bat and the scales of a fish D) the antennae of an insect and the eyes of a bird E) the wing of a bat and the flipper of a whale |
E) the wing of a bat and the flipper of a whale
|
|
|
Which of the following thinkers argued that organisms tend to produce many more offspring than the environment can support, leading to a struggle for existence, an argument that later influenced Charles Darwin's ideas of natural selection?
A) Thomas Malthus B) Aristotle C) Gregor Mendel D) Jean-Baptiste Lamarck E) Charles Lyell |
A) Thomas Malthus
|
|
|
Darwin found that some of the species on the Galápagos islands resembled species of the South American mainland:
A) more than they resembled animals on ecologically similar but distant islands. B) less than they resembled animals on ecologically similar but distant islands. C) less than they resembled animals in Europe. D) very closely; in most cases, the species from the mainland and the islands were identical. E) less than they resembled animals from Australia. |
A) more than they resembled animals on ecologically similar but distant islands.
|
|
|
After reading the following paragraph, answer the question(s) below.
Desert pupfish live in springs of the American Southwest. Today there are about 30 species of pupfish, but they all evolved from a common Pleistocene ancestor. The southwestern United States was once much wetter than it is now, and the Pleistocene pupfish flourished over a wide geographic area. Over thousands of years, however, the Sierra Nevada Mountain range was pushed upward by geological forces, blocking rainfall from the Pacific Ocean. As the large lakes dried up, small groups of pupfish remained in springs and pools fed by groundwater seepage. Now, although many of these small springs still have pupfish, each population has evolved to become very different from pupfish in other springs. Which of the following statements represents the most probable explanation for the differences between pupfish populations? A) New genes entered the population through migration. B) Each new species contains all the original g |
C) The isolated populations had a restricted gene pool.
|
|
|
Imagine that you are studying a very large population of moths that is isolated from gene flow. A single gene controls wing color. Half of the moths have white-spotted wings (genotype WW or Ww) and half of the moths have plain brown wings (ww). There are no new mutations, individuals mate randomly, and there is no natural selection on wing color.
How will p, the frequency of the dominant allele, change over time? A) p will decrease because of genetic drift. B) p will fluctuate rapidly and randomly because of genetic drift. C) p will increase; the dominant allele will eventually take over and become most common in the population. D) p will increase initially, then decrease until the W allele vanishes from the population. E) p will neither increase nor decrease; it will remain more or less constant under the conditions described. |
E) p will neither increase nor decrease; it will remain more or less constant under the conditions described.
|
|
|
Blue-footed boobies have webbed feet and are comically clumsy when they walk on land. Evolutionary scientists view these feet as
A) one of the unsolvable mysteries of nature. B) a curiosity that has little to teach us regarding evolution. C) an example of a trait that has not evolved. D) an example of a trait that is poorly adapted. E) the outcome of a tradeoff: webbed feet perform poorly on land, but are very helpful in diving for food. |
E) the outcome of a tradeoff: webbed feet perform poorly on land, but are very helpful in diving for food.
|
|
|
8.
Which of the following assumptions or observations contradicts Darwin's idea of natural selection? A) Organisms compete for limited resources. B) Heritable traits that promote successful reproduction should gradually become more common in a population. C) Populations produce more offspring than their environment can support. D) Organisms vary in heritable ways. E) Whether an organism survives and reproduces is almost entirely a matter of random chance. |
E) Whether an organism survives and reproduces is almost entirely a matter of random chance.
|
|
|
9.
In populations of the greater prairie chicken in Illinois, genetic diversity was A) lost through gene flow and restored by mutation. B) lost through mutation and restored by natural selection. C) lost through directional selection and restored by balancing selection. D) lost through genetic drift and restored by natural selection. E) lost through genetic drift and restored by gene flow. |
E) lost through genetic drift and restored by gene flow.
|
|
|
10.
Tay-Sachs is inherited as an autosomal recessive allele. Homozygous individuals die within the first few years of life. However, there is some evidence that heterozygous individuals are more resistant to tuberculosis. Which of the following statements about Tay-Sachs is true? A) This situation is an example of directional selection. B) The allele for Tay-Sachs is selected against. C) This situation is an example of heterozygote advantage if tuberculosis is present in a population. D) This situation is an example of disruptive selection. E) Heterozygotes will be more fit than either homozygote regardless of environmental conditions. |
D) This situation is an example of disruptive selection.
|
|
|
The core theme of biology is
A) ecology. B) genetics. C) evolution. D) taxonomy. E) metabolism |
C) evolution.
|
|
|
Frequency-dependent selection, as seen in the case of the scale-eating fish in Lake Tanganyika, tends to
A) eliminate rare alleles and favor whichever allele is initially most frequent. B) maintain two phenotypes in a dynamic equilibrium in a population. C) lead to heterozygote advantage. D) produce random changes in allele frequencies. E) stimulate new mutations. |
B) maintain two phenotypes in a dynamic equilibrium in a population.
|
|
|
Which of the following would prevent an organism from becoming part of the fossil record when it dies?
A) It is frozen in ice. B) It is buried in fine sediments at the bottom of a lake. C) It is fully decomposed by bacteria and fungi. D) It falls into an acid bog. E) It gets trapped in sap. |
C) It is fully decomposed by bacteria and fungi.
|
|
|
14.
Which of the following statements would Darwin have disagreed with? A) Descent with modification occurs by natural selection. B) Descent with modification occurs through inheritance of acquired characteristics. C) Living species have arisen from earlier life forms. D) Species change over time. E) Modern species arose through a process known as "descent with modification." |
B) Descent with modification occurs through inheritance of acquired characteristics.
|
|
|
Which of the following best expresses the concept of natural selection?
A) inheritance of acquired characteristics B) survival of the fittest C) change in response to need D) differential reproductive success based on inherited characteristics E) a process of constant improvement, leading eventually to perfection |
D) differential reproductive success based on inherited characteristics
|
|
|
Which sentence best describes the true nature of natural selection?
A) Only the strongest survive. B) The strong eliminate the weak in the race for survival. C) Survival of the fittest. D) Heritable traits that promote reproduction become more frequent in a population from one generation to the next. E) Organisms change by random chance. |
D) Heritable traits that promote reproduction become more frequent in a population from one generation to the next
|
|
|
The three-domain system
A) separates plants, animals, and fungi into domains. B) subdivides the prokaryotes into two different domains. C) is based upon the presence or absence of cell walls. D) no longer recognizes eukaryotes as a monophyletic group. E) subdivides the eukaryotes into two different domains |
B) subdivides the prokaryotes into two different domains.
|
|
|
During the ________, over 96% of marine species and many terrestrial species became extinct, possibly because intense volcanic activity warmed Earth's climate.
A) Cenozoic B) Permian C) Cretaceous D) Precambrian E) Mesozoic |
B) Permian
|
|
|
Over the past 500 million years, ________ mass extinctions have occurred in which at least ________ of the species on Earth became extinct.
A) two . . . 50% B) two . . . 25% C) twelve . . . 96% D) five . . . 25% E) five . . . 50% |
E) five . . . 50%
|
|
|
Which of the following options lists major events in the history of life on Earth in the proper order, from earliest to most recent?
A) photosynthesis; first prokaryotes; first eukaryotes; colonization of land by plants and fungi B) first prokaryotes; photosynthesis; colonization of land by plants and fungi; first eukaryotes C) first prokaryotes; first eukaryotes; photosynthesis; colonization of land by plants and fungi D) first eukaryotes; photosynthesis; colonization of land by plants and fungi; first prokaryotes E) first prokaryotes; photosynthesis; first eukaryotes; colonization of land by plants and fungi |
E) first prokaryotes; photosynthesis; first eukaryotes; colonization of land by plants and fungi
|
|
|
Which of the following options lists taxonomic categories in the correct order from most specific to most general?
A) genus, phylum, family, order, class B) genus, family, class, order, phylum C) family, genus, order, phylum, class D) genus, family, order, class, phylum E) family, genus, class, order, phylum |
D) genus, family, order, class, phylum
|
|
|
Which of the following would be considered an effective way to decrease the production of acid precipitation?
A) Drive more full-size SUVs. B) Consume only organically grown foods. C) Build more coal-generated electricity power plants. D) Whenever possible, walk or ride a bicycle instead of driving a car. E) Discourage the use of alternative energy resources such as solar, wind, and geothermal energy. |
D) Whenever possible, walk or ride a bicycle instead of driving a car.
|
|
|
What happens to an atom if the electrons in the outer shell are altered?
A) The atom becomes radioactive. B) The atom will remain the same. C) The atom's characteristics change and it becomes a different element. D) The properties of the atom will change. E) The atom will disintegrate. |
D) The properties of the atom will change.
|
|
|
Which of the following statements best describes a compound?
A) A compound is less common than a pure element. B) A compound contains two or more different elements in a fixed ratio. C) A compound is a pure element. D) A compound is a solution. E) A compound is exemplified by sodium. |
B) A compound contains two or more different elements in a fixed ratio.
|
|
|
What is the atomic mass of an atom that has 6 protons, 6 neutrons, and 6 electrons?
A) 18 B) +1 C) 8 D) 12 E) 6 |
D) 12
|
|
|
An uncharged atom of boron has an atomic number of 5 and an atomic mass of 11. How many electrons does boron have?
A) 15 B) 0 C) 5 D) 2 E) 11 |
C) 5
|
|
|
Which of the following is another term used for atomic mass?
A) dalton B) calvin C) roberts D) darwin E) mendel |
A) dalton
|
|
|
Compared to a solution of pH 3, a solution of pH 1 is
A) 100 times more basic. B) neutral. C) 100 times more acidic. D) 10 times more acidic. E) 10 times more basic |
C) 100 times more acidic.
|
|
|
Photosynthesis requires many steps to make glucose. As a result of the synthesis process,
A) more atoms are present at the beginning than at the end. B) water is synthesized by the plant from H2 and O2. C) more carbon dioxide is released from the plant than is absorbed. D) all the carbons from the six carbon dioxide atoms are found in glucose. E) more water is released from the leaves than is absorbed through the roots. |
D) all the carbons from the six carbon dioxide atoms are found in glucose.
|
|
|
Which of the following particles is found in the nucleus of an atom?
A) protons and neutrons B) only neutrons C) only protons D) only electrons E) protons and electrons |
A) protons and neutrons
|
|
|
What is likely to happen to wild salmon prices if the burning of fossil fuels continues at the current rate?
A) Prices will drop to pre-fossil fuel burning levels. B) Prices will stay the same because fossil fuel has nothing to do with salmon. C) Prices will increase due to decreased salmon harvests. D) Prices will fluctuate wildly due to illogical fear in the marketplace. E) Prices will initially decline and then stabilize |
C) Prices will increase due to decreased salmon harvests.
|
|
|
Which of the following hypotheses would be supported if liquid water were found on Mars and contained evidence of bacteria-like organisms?
A) The chemical evolution of life is possible. B) Life spontaneously arises from the decaying flesh of organisms. C) Life is guided by intelligent design. D) Life must evolve in the presence of oxygen. E) Life on Earth must have originated on Mars |
A) The chemical evolution of life is possible.
|
|
|
Why did the lactose tolerance mutation in the East African herders spread so rapidly within the population?
A) Milk provided calcium for strong bones. B) Milk from cows could be used to feed infants instead of breast milk. C) Lactose was a better source of energy than glucose. D) Milk was a good source of protein during the winter. E) It was a selective advantage for survival during droughts. |
E) It was a selective advantage for survival during droughts.
|
|
|
DNA differs from RNA because DNA
A) consists of a single rather than a double polynucleotide strand. B) is always double-stranded, while RNA is never double-stranded. C) contains the sugar ribose rather than the sugar deoxyribose. D) contains thymine in place of uracil. E) contains phosphate groups not found in RNA. |
D) contains thymine in place of uracil.
|
|
|
Mad cow disease serves as an example of how interdependent ________ and ________ are to protein.
A) solubility . . . texture B) validity . . . reliability C) structure . . . function D) form . . . construction E) adaptability . . . development |
C) structure . . . function
|
|
|
The results of dehydration synthesis can be reversed by
A) the addition of an amino group. B) the addition of a phosphate group. C) polymerization. D) condensation. E) hydrolysis. |
E) hydrolysis.
|
|
|
A scientist suspects that the food in an ecosystem may have been contaminated with radioactive nitrogen over a period of months. Which of the following substances could be examined for radioactivity to test the hypothesis?
A) the hair produced by humans living in the ecosystem B) the cholesterol in the cell membranes of organisms living in the ecosystem C) the sugars produced during photosynthesis by plants growing in the ecosystem D) the adipose tissue from animals living in the ecosystem E) the cell walls of plants growing in the ecosystem |
A) the hair produced by humans living in the ecosystem
|
|
|
After reading the following paragraph, answer the question(s) below.
You're the manager of a factory that produces enzyme-washed blue jeans (the enzymes lighten the color of the denim, giving a "faded" appearance). When the most recent batch of fabric came out of the enzyme wash, however, the color wasn't light enough to meet your standards. Your quality control laboratory wants to do some tests to determine why the wash enzymes didn't perform as expected. Based on your understanding of enzyme structure, which of the following would you recommend that they also investigate? A) the pH of the liquid in the washing vat B) how long the fabric has been in storage C) the temperature of the liquid in the washing vat D) the manufacturer of the fabric E) the primary structure of the enzyme |
C) the temperature of the liquid in the washing vat
|
|
|
The storage form of carbohydrates is ________ in animals and ________ in plants.
A) chitin . . . glycogen B) glycogen . . . cellulose C) starch . . . glycogen D) cellulose . . . glycogen E) glycogen . . . starch |
E) glycogen . . . starch
|
|
|
A diet high in animal products and hydrogenated vegetable margarine may increase the risk for atherosclerosis. This is because
A) most hydrogenated vegetable margarines are hydrogenated oils and most animal products contain high levels of phospholipids. B) most animal fats are used for energy storage and most hydrogenated vegetable margarines contain high levels of unsaturated fats. C) most animal products contain high levels of unsaturated oils and most hydrogenated vegetable margarines contain anabolic steroids. D) most animal fats are unsaturated and most hydrogenated vegetable margarines contain high levels of steroids. E) most animal fats are saturated and many hydrogenated vegetable margarines contain high levels of trans fats. |
E) most animal fats are saturated and many hydrogenated vegetable margarines contain high levels of trans fats.
|
|
|
Which of the following is an example of secondary structure in a protein?
A) an alpha helix B) a globular shape C) the joining of two polypeptide chains D) a particular amino acid sequence E) a fibrous shape |
A) an alpha helix
|
|
|
Foods that are high in fiber are most likely derived from
A) poultry. B) dairy products. C) plants. D) fish. E) red meats |
C) plants.
|
|
|
Which of the following functional groups is capable of regulating gene expression?
A) -CH3 B) COOH C) OH D) NH2 E) CO |
A) -CH3
|
|
|
A drug that interferes with microtubule formation is likely to completely disrupt
A) contraction of muscle cells. B) the movements of sperm cells. C) the amoeboid motion of a cell. D) the production of ribosomes. E) the function of lysosomes. |
B) the movements of sperm cells.
|
|
|
Dynein arms
A) are found on microtubules in cilia and flagella and cause movement by grabbing and pulling at adjacent microtubule doublets. B) are knobs of carbohydrate that are essential to the movement of cilia and flagella. C) are the anchoring proteins in basal bodies. D) join microfilaments to the cell membrane. E) are present in cilia but not in flagella |
A) are found on microtubules in cilia and flagella and cause movement by grabbing and pulling at adjacent microtubule doublets.
|
|
|
A scientist wants to magnify a pollen grain 8,000 times and examine the ridges and pores on its surface. Which one of the following instruments would be best?
A) an inverted light microscope B) a transmission electron microscope C) a differential interference-contrast microscope D) a fluorescence confocal microscope E) a scanning electron microscope |
E) a scanning electron microscope
|
|
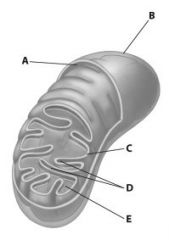
Which part of the mitochondrion shown is its matrix?
|
E
|
|
|
Which of the following cells has the greatest surface-to-volume ratio?
A) human muscle cell B) ostrich egg C) bacterium D) frog egg E) human red blood cell |
C) bacterium
|
|
|
Most animal cells are
A) attached to each other via plasmodesmata. B) embedded in a lipid matrix. C) surrounded by a cell wall. D) embedded in an endomembrane system. E) embedded in an extracellular matrix. |
E) embedded in an extracellular matrix.
|
|
|
A cell is exposed to a substance that prevents it from dividing. The cell becomes larger and larger. This situation
A) should present no problem to the cell, because the surface area of the cell will increase as the volume of the cell increases. B) should be beneficial, since the cell will be able to divert the ATP normally used for cell division to other processes. C) should present no problem to the cell, since it can continue to perform all other necessary functions. D) will eventually lead to the cell's deterioration, since functional organelles will not proportionally increase with the size of the cell. E) will eventually be problematic, since the cell's ability to absorb nutrients through its outer membrane will not keep increasing as quickly as its cytoplasmic needs. |
E) will eventually be problematic, since the cell's ability to absorb nutrients through its outer membrane will not keep increasing as quickly as its cytoplasmic needs.
|
|
|
Which of the following statements about plant cell walls is false?
A) Plant cell walls consist of cellulose fibers embedded in a matrix of polysaccharides and proteins. B) Plant cell walls protect plant cells by forming an impermeable layer around the cell. C) The cell wall of one plant cell is separated from the cell wall of another by a layer of sticky polysaccharides. D) Wood is primarily composed of plant cell walls. E) Plant cell walls are multilayered structures. |
B) Plant cell walls protect plant cells by forming an impermeable layer around the cell.
|
|
|
Skin cells are attached to the extracellular matrix by
A) basal bodies. B) communicating junctions. C) tight junctions. D) plasmodesmata. E) anchoring junctions. |
E) anchoring junctions.
|
|
|
It is essential for heart muscle cells to beat in a coordinated fashion. The cell junctions that would best facilitate this are
A) plasmodesmata. B) occluding junctions. C) communicating junctions. D) tight junctions. E) anchoring junctions |
C) communicating junctions.
|
|
|
The endosymbiosis hypothesis proposes that
A) a small cell lived inside a larger cell to the benefit of both cells. B) two cells merged into one cell, improving the enzyme function of the new cell. C) one cell was dependent on the other for survival. D) a large cell engulfed and digested a smaller cell, exposing its enzymes for use by the larger cell. E) two cells were juxtaposed and one benefited from the other. |
A) a small cell lived inside a larger cell to the benefit of both cells.
|
|
|
Which organelle is involved in the catabolism of fatty acids and the detoxification of alcohol?
A) Golgi apparatus B) peroxosome C) smooth ER D) nucleus E) ribosomes |
B) peroxosome
|
|
|
Which of the following statements about lysosomes is false?
A) Lysosomes fuse with food vacuoles to expose nutrients to lysosomal enzymes. B) Lysosomes recycle materials within the cell. C) Lysosomes synthesize proteins from the recycled amino acids. D) Lysosomes help to digest worn-out or damaged organelles. E) Lysosomes destroy harmful bacteria engulfed by white blood cells |
C) Lysosomes synthesize proteins from the recycled amino acids.
|
|
|
The nucleoid region of a prokaryotic cell
A) is surrounded by a nucleoid membrane. B) is the site of organelle production. C) separates the RNA from the cytoplasm. D) contains the cell's DNA. E) contains the cell's nucleoli. |
D) contains the cell's DNA.
|
|
|
Plasma membranes are permeable to
A) small ions such as Na+. B) nonpolar molecules such as CO2. C) large molecules such as proteins. D) large molecules such as starch. E) hydrophilic molecules such as glucose. |
B) nonpolar molecules such as CO2.
|
|
|
Which of the following statements about the cytoskeleton is false?
A) The cytoskeleton helps to support cells. B) The cytoskeleton plays an important role in amoeboid motion. C) The cytoskeleton is composed of three types of fibers: microfilaments, microtubules, and intermediate filaments. D) Once laid down, the elements of the cytoskeleton are fixed and remain permanently in place. E) The cytoskeleton includes fibrous and globular proteins |
D) Once laid down, the elements of the cytoskeleton are fixed and remain permanently in place.
|
|
|
A manufacturing company dumps its wastes into a nearby pond. One of the wastes is found to paralyze the contractile vacuoles of certain protists. A biologist looking at individual samples of these organisms taken from the pond would find that they
A) have gained water and burst. B) are surviving but are unable to reproduce. C) have died because wastes have built up in the cytoplasm. D) have lost water and shrunk. E) have died of malnutrition. |
A) have gained water and burst.
|
|
|
The function of chloroplasts is
A) intracellular transport of proteins. B) lipid synthesis. C) photosynthesis. D) cellular respiration. E) intracellular digestion. |
C) photosynthesis.
|
|
|
A child dies following a series of chronic bacterial infections. At the autopsy, the physicians are startled to see that the child's white blood cells are loaded with vacuoles containing intact bacteria. Which of the following explanations could account for this finding?
A) A defect in the lysosomes of the white blood cells prevented the cells from destroying engulfed bacteria. B) A defect in the cell walls of the white blood cells permitted bacteria to enter the cells. C) A defect in the surface receptors of the white blood cells permitted bacteria to enter the cells. D) A defect in the rough endoplasmic reticulum prevented the synthesis of the antibodies (defensive proteins) that would have inactivated the bacteria. E) A defect in the Golgi apparatus prevented the cells from processing and excreting the bacteria. |
A) A defect in the lysosomes of the white blood cells prevented the cells from destroying engulfed bacteria.
|
|
|
Your throat is dry, and you want the last cough drop in the box to last a long time in your mouth. What should you do?
A) Keep the cough drop whole. This maintains the largest surface-to-volume ratio, and slows the dissolution of the cough drop. B) It doesn't matter if the cough drop is in one piece or many pieces; the total amount of cough drop is all that matters. C) Break the cough drop into little pieces and put them all in your mouth. Since each little piece must be dissolved separately, the drop will last longer. D) Break the cough drop into little pieces, put them all in your mouth, and drink plenty of water. E) Break the cough drop into little pieces and put them all in your mouth. This decreases the surface-to-volume ratio, and slows the dissolution of the cough drop. |
A) Keep the cough drop whole. This maintains the largest surface-to-volume ratio, and slows the dissolution of the cough drop.
|
|
|
Which of the following statements about internal membranes in eukaryotic cells is false?
A) In eukaryotic cells, internal membranes contain proteins essential for metabolic processes. B) In eukaryotic cells, internal membranes provide an additional area for many metabolic processes occur. C) In eukaryotic cells, internal membranes greatly increase a cell's total membrane area. D) In eukaryotic cells, internal membranes standardize the internal environment of all cellular organelles. E) In eukaryotic cells, internal membranes form membranous compartments called organelles. |
D) In eukaryotic cells, internal membranes standardize the internal environment of all cellular organelles.
|
|
|
Unlike animal cells, plant cells have ________ and ________. Unlike plant cells, animal cells have ________.
A) chloroplasts . . . cell walls . . . a nucleus B) chloroplasts . . . cell walls . . . cell membranes C) centrioles . . . cell walls . . . large central vacuoles D) centrioles . . . chloroplasts . . . cell walls E) chloroplasts . . . cell walls . . . centrioles |
E) chloroplasts . . . cell walls . . . centrioles
|
|
|
After reading the following paragraph, answer the question(s) below.
The skin is the body's largest organ. It's made up of many different types of cells. Oils, produced by the sebaceous glands, prevent the skin from drying and splitting. The protein melanin, produced by melanocytes in the epidermis, protects the skin from the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation. Sweat, released through ducts to the skin surface, helps to cool the body. The types of cells that produce these compounds have different numbers of specific organelles, depending on their function. The oil from the sebaceous glands is produced by which of the following cell organelles? A) smooth endoplasmic reticulum B) cell membrane C) central vacuole D) ribosomes E) rough endoplasmic reticulum |
A) smooth endoplasmic reticulum
|
|
|
Which of the following processes can move a solute against its concentration gradient?
A) osmosis B) active transport C) facilitated diffusion D) passive transport E) diffusion |
B) active transport
|
|
|
Which of the following will have no effect on the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction?
A) temperature B) competitive inhibitors C) noncompetitive inhibitors D) pH E) net change in energy |
E) net change in energy
|
|
|
The transfer of a phosphate group to a molecule or compound is called
A) hydrogen bonding. B) phosphorylation. C) hydrogenation. D) ionization. E) carboxylation. |
B) phosphorylation.
|
|
|
Bacterial production of the enzymes needed for the synthesis of the amino acid tryptophan declines with increasing levels of tryptophan and increases as tryptophan levels decline. This is an example of
A) irreversible inhibition. B) competitive inhibition. C) noncompetitive inhibition. D) feedback inhibition. E) positive feedback. |
D) feedback inhibition.
|
|
|
A plant cell in a hypotonic solution
A) lyses. B) shrivels. C) is turgid. D) is flaccid. E) wilts. |
C) is turgid.
|
|
|
Which of the following substances could be a cofactor?
A) a ribosome B) a protein C) a zinc atom D) collagen E) a polypeptide |
C) a zinc atom
|
|
|
In the lab, you use a special balloon that is permeable to water but not sucrose to make an "artificial cell." The balloon is filled with a solution of 20% sucrose and 80% water and is immersed in a beaker containing a solution of 40% sucrose and 60% water. The solution in the balloon is ________ relative to the solution in the beaker.
A) hydrophilic B) isotonic C) hydrophobic D) hypotonic E) hypertonic |
D) hypotonic
|
|
|
Facilitated diffusion across a biological membrane requires ________ and moves a substance ________ its concentration gradient.
A) transport proteins . . . down B) energy and transport proteins . . . against C) energy . . . down D) transport proteins . . . against E) energy and transport proteins . . . down |
A) transport proteins . . . down
|
|
|
Certain cells that line the stomach synthesize a digestive enzyme and secrete it into the stomach. This enzyme is a protein. Which of the following processes could be responsible for its secretion?
A) diffusion B) pinocytosis C) passive transport D) endocytosis E) exocytosis |
E) exocytosis
|
|
|
Living systems
A) violate the second law of thermodynamics. B) violate the first law of thermodynamics. C) decrease their entropy while increasing the entropy of the universe. D) are only compelled to follow the first law of thermodynamics. E) are examples of a closed system |
C) decrease their entropy while increasing the entropy of the universe.
|
|
|
Which of the following is a coenzyme?
A) zinc B) vitamin B6 C) hydrogen ions D) iodine E) iron |
B) vitamin B6
|
|
|
In most green plants, chloroplasts are
A) concentrated in a portion of the leaf called the stroma. B) found throughout the plant. C) concentrated in a zone of leaf tissue called the mesophyll. D) found throughout the leaf tissue. E) concentrated in the stomata. |
C) concentrated in a zone of leaf tissue called the mesophyll.
|
|
|
Carbon fixation
A) occurs when carbon and oxygen from CO2 are incorporated into an organic molecule. B) powers the process of glucose synthesis by supplying the cell with ATP. C) provides the cell with a supply of NADPH molecules. D) occurs during the light reactions. E) uses noncyclic electron flow to capture energy in glucose. |
A) occurs when carbon and oxygen from CO2 are incorporated into an organic molecule.
|
|
|
In photophosphorylation, energy from electron flow is used to transport ________ from the ________ to the thylakoid compartment, generating a concentration gradient of ________.
A) electrons . . . grana . . . H+ B) H+ . . . grana . . . electrons C) H+ . . . stroma . . . H+ D) H+ . . . stroma . . . ATP E) electrons . . . stroma . . . H+ |
C) H+ . . . stroma . . . H+
|
|
|
The greenhouse effect is
A) of little concern, since it is part of the normal cycle for the planet. B) made worse by photosynthesis, which adds carbon dioxide to the atmosphere. C) reduced by the burning of fossil fuels, which removes oxygen from the atmosphere. D) reduced by the addition of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere, since carbon dioxide removes excess heat from the Earth's surface and reflects it back into space. E) reduced by photosynthesis, which removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. |
E) reduced by photosynthesis, which removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
|
|
|
Photophosphorylation differs from oxidative phosphorylation in that
A) energy is stored in the form of a proton concentration difference. B) its enzymes are membrane-bound. C) it involves an electron transport chain. D) the final electron acceptor is NADP+ and not oxygen. E) regeneration of ATP is driven by a flow of protons through an ATP synthase. |
D) the final electron acceptor is NADP+ and not oxygen.
|
|
|
The full range of electromagnetic energy is called the ________ spectrum.
A) ultraviolet B) energy C) electromagnetic D) wavelength E) visible |
C) electromagnetic
|
|
|
A concentration gradient is a form of
A) kinetic energy. B) an exergonic reaction. C) life. D) potential energy. E) entropy. |
D) potential energy.
|
|
|
Which of the following statements regarding glycolysis is false?
A) Glycolysis is considered to be an ancient metabolic system because it does not require oxygen. B) Glycolysis is considered to be an ancient metabolic system because glucose is the universal substrate for glycolysis. C) Glycolysis is considered to be an ancient metabolic system because it is the most efficient metabolic pathway for ATP synthesis. D) Glycolysis is considered to be an ancient metabolic system because it occurs universally. E) Glycolysis is considered to be an ancient metabolic system because it is not located in a membrane-bound organelle. |
C) Glycolysis is considered to be an ancient metabolic system because it is the most efficient metabolic pathway for ATP synthesis.
|
|
|
The conversion of CO2 and H2O into organic compounds using energy from light is called
A) glycolysis. B) photosynthesis. C) photorespiration. D) fermentation. E) cellular respiration |
B) photosynthesis.
|
|
|
If you were able to stop the process of cellular respiration after completing electron transport but prior to chemiosmosis, you would find the pH of a mitochondrion to be at its lowest
A) in the cytoplasm. B) in the intermembrane space. C) in the mitochondrial matrix. D) on the outer membrane. E) on the inner membrane. |
B) in the intermembrane space.
|
|
|
A mutant protist is found in which some mitochondria lack an inner mitochondrial membrane. Which of the following pathways would be completely disrupted in these mitochondria?
A) biosynthesis B) oxidative phosphorylation C) alcoholic fermentation D) glycolysis E) the citric acid cycle |
B) oxidative phosphorylation
|
|
|
Cyanide differs from dinitrophenol in that
A) cyanide increases the rate of H+ crossing to the intermembrane beyond the capacity to synthesize ATP, while dinitrophenol blocks the transfer electrons from NADH. B) cyanide is highly toxic to human cells, while dinitrophenol is nontoxic. C) cyanide is an electron transport blocker, while dinitrophenol is a reaction uncoupler. D) cyanide makes the membrane of mitochondria leaky to H+ ions and prevents a concentration gradient from building up, while dinitrophenol blocks the passage of electrons through electron carriers. E) cyanide inhibits the production of ATP by inhibiting ATP synthase, while dinitrophenol causes mitochondrial membranes to become less permeable to H+ ions. |
C) cyanide is an electron transport blocker, while dinitrophenol is a reaction uncoupler
|
|
|
During which of the following phases of cellular respiration does substrate-level phosphorylation take place?
A) "grooming" of pyruvate B) glycolysis C) the citric acid cycle D) glycolysis and the citric acid cycle E) oxidative phosphorylation |
D) glycolysis and the citric acid cycle
|

