![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the definition of emotion?
|
Particular mental state with measurable physiological parameters and observable behaviors.
|
|
|
What is a feeling?
|
Subjective (internal) assessment of emotion, e.g. I feel angry.
|
|
|
What is an affect from an emotional viewpoint?
|
Conscious appreciation of emotion plus an outward expression of it.
|
|
|
What is a mood?
|
Sustained emotional state (over weeks or more)
|
|
|
What are the top three emotions listed in class?
|
Fear, anger, happiness.
|
|
|
Describe the somatic marker hypothesis.
|
A somatic marker is basically the storage of a state of the soma (body) at a previous point in time - an emotional and visceral representation. Through experience, these markers become associated with outcomes that tend to be positive or negative. When a similar situation occurs in the future, the brain can use these markers to speed up processing by choosing the appropriate more positive response.
One situation in which this is important relates to behavior in a social setting. By having these markers, an individual can get a "gut feeling" for what is the right way to act. |
|
|
How does neuroendocrine activity contribute to emotion?
|
Various hormones released can affect body physiological behavior such as heart rate, blood pressure, etc.
|
|
|
How does cognitive activity contribute to emotion?
|
The cortex helps to determine a response “consistent w/individual’s expectations
& social context.” |
|
|
How does skeletomotor contribute to emotion?
|
Facial expressions, body posture.
|
|
|
How does autonomic activity contribute to emotion?
|
The ANS can direct physiological changes within the body, e.g. dilation of the eyes during fear, preparation for "fight/flight", etc.
|
|
|
What are three roles of the amygdala?
|
1) Processing of fear and anger
2) Ability to recognize fear and anger in others 3) Acts as a substrate for empathy. |
|
|
What is the major input and output for the amygdala?
|
input: basolateral nucleus
output: central nucleus |
|
|
What is the role of the prefrontal cortex in human emotion?
|
Evaluates the appropriate behavior response consistent with individual's expectations and social content.
|
|
|
Where is the prefrontal cortex?
|
Anterior portion of the frontal lobe.
|
|
|
Describe the types of emotions one might expect with damage to the pre-frontal lobe.
|
Inappropriate behavior for a given social context. May say something hurtful, may go into rage.
|
|
|
In general terms, define the nature of the major mood modulating systems of the brain.
|
There are restricted (tiny nucleus) regions in the brain with widespread projections. These use different neurotransmitter and various “modularly” receptor types are used.
|
|
|
What are three neurotransmitters used in modulating systems?
|
Serotonin (5-HT)
NE ACh |
|
|
What is the origin of one of the primary modulating systems that uses Serotonin?
What function(s) does it modulate? |
Raphe nucleus of the brainstem.
Mood and arousal (alertness) Sleep/wake cycles |
|
|
What is the origin of one of the primary modulating systems that uses NE?
What function(s) does it modulate? |
Locus ceruleus (tegmentum in the pons)
Mood and arousal Results in an increase responsiveness to all sensory inputs. |
|
|
What is the origin of one of the primary modulating systems that uses ACh?
What function(s) does it modulate? What diseases degenerate it? |
nucleus basalis of meynert which is part of the Ventral forebrain (ventral basal ganglis, "septal region")
Motivation? Emotion? Degenerates in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's |
|
|
What are the three major classes of drugs used to treat mood disorders? How do they produce their effects?
|
Tricyclic compounds: non-specific reuptake inhibitor.
Monoamine oxibase: decrease the breakdown of neurotransmitter during reuptake. Specific serotonin reuptake inhibitors. |
|
|
Use a diagram to show the interrelatedness of conscious and subconscious processing of stimuli and the autonomic resposnes of body to emotional states.
|
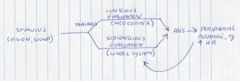
See diagram
|

