![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the general function of the pyramids?
|
Motor tracts
|
|
|
General function of the olive.
|
Input to the cerebellum.
|
|
|
General function of the fasciculus cuneatus.
|
Position sense from spinal cord.
|
|
|
General function of fasciculus gracile
|
Position sense from spinal cord.
|
|
|
General function of the inferior cerebellar peduncle.
|
Input to cerebellum from medulla/spinal cord.
|
|
|
General function of transverse fibers of the pons.
|
Input to cerebellum from pons.
|
|
|
General function of the superior colliculi.
|
Visual reflexes.
|
|
|
General function of the inferior colliculi.
|
Auditory relays.
|
|
|
General function of the Crus cerebri (cerebral peduncles).
|
Motor tracts from cerebelum to brainstem.
|
|
|
General function of the Brachium of the inferior colliculus.
|
Auditory pathway.
|
|
|
General function of the superior cerebellar peduncle.
|
Output of cerebellum.
|
|
|
General function of the thalamus.
|
Relay nuclei.
|
|
|
General function of the pulvinar nuclear complex.
|
Somatosensory relay - most caudal portion of the thalamus.
|
|
|
General function of the medial genticulate body.
|
Auditory relay.
|
|
|
General function of the lateral geniculate body.
|
Visual relay.
|
|
|
General function of the hypothalamus.
|
Autonomic and endocrine functions.
|
|
|
To what does the infundibular stalk attach?
|
Pituitary gland.
|
|
|
General function of the mammillary bodies.
|
Role in memory.
|
|
|
General function of the dorsal column nucleus.
|
Body position sense.
|
|
|
General function of the principle olivary nucleus.
|
Projections to the cerebellum.
|
|
|
General function of the vestibular nuclei located in the tegmentum.
|
Balance and postural reflexes.
|
|
|
General function of the middle cerebellar peduncle.
|
Input to the cerebellum.
|
|
|
General function of the superior colliculi.
|
Visual reflexes.
|
|
|
General function of the inferior colliculi.
|
Auditory relays.
|
|
|
General function of the periaqueductal gray.
|
Pain modulation.
|
|
|
General function of the red nucleus.
|
Motor neurons. Limited role in humans. For other primates, it's important for fine movement of peripheral limbs, e.g. fingers.
|
|
|
General function of the oculomotor nucleus and nerve.
|
Eye movement.
|
|
|
General function of the substantia nigra compacta.
|
Most fibers are concerned with a modulation function within the basal ganglia. It's projections produce dopamine.
|
|
|
General function of the crura cerebri.
|
Motor systems.
|
|
|
Names of cranial nerves numbered I through VI.
|
I Olfactory
II Optic III Oculomotor IV Trochlear V Trigeminal VI Abducens |
|
|
Names of cranial nervers numbered VII through XII.
|
VII Facial
VIII Vestibulocochlear IX Glossopharyngeal X Vagus XI Accessory XII Hypoglossal |
|
|
What is the mneumonic to help remember the cranial nerves?
|
Old Opie occasionally tries trig and feels very gloomy, vague and hypoactive.
|
|
|
What foramina is associated with the olfactory cranial nerve?
|
Cribriform Plate.
|
|
|
What two cranial nerves exit through the optic foramen?
|
optic and oculomotor.
|
|
|
What two cranial nerves exit through the superior orbital fissure?
|
Trochlear (IV) and trigeminal(V).
|
|
|
What foramina are associated with the exit of the facial nerve?
|
Internal acousitc meatus => stylomastoid foramen
|
|
|
What cranial nerves exit through the jugular foramen?
|
Glossopharyngeal, vagus, accessory.
|
|
|
Through what foramen does the hypoglossal nerve exit?
|
Hypoglossal foramen.
|
|
|
What are the functions of the occulomotor CN?
|
1) Efferent for abducens muscle of eye.
2) Pupillary constriction and accomodation. (parasympthetic) |
|
|
What is the general function of the trochlear crainial nerve?
|
Extraocular muscle.
|
|
|
What is the general function of Trigeminal (V1)?
|
GSA and GVA skin of forehead.
|
|
|
What are the general functions of Trigeminal (V2)?
|
GSA and GVA skin of cheek, upper teeth.
|
|
|
What are the general functions of Trigeminal (V3)?
|
GSA and GVA skin of lower jaw, anterior 2/3rds of tongue, lower teeth. GSE and SVE: mm(muscles) of mastication.
|
|
|
What is the general function of the abducens cranial nerve?
|
Extraocular muscles.
|
|
|
What are the general functions of the facial cranial nerve?
|
GSE & SVE: mimetic muscles.
GSA & GVA: ear canal, part of auricle. SSA & SVA: Gustation (anterior 2/3rds of tongue) GVE: Lacrimal & some salivary glands. |
|
|
What are the general functions fo the vestibulocochlear cranial nerve?
|
SSA & SVA: Audition & vestibular sense.
|
|
|
What are the general functions of the glossopharyngeal cranial nerve?
|
GSE & SVE: Pharyngeal and laryngeal mm
GSA & GVA: Pharynx, posterior 1/3 tongue SSA & SVA: Gustation (posterior 1/3 tongue) GVE: Some salivary glands |
|
|
What are the general functions of the vagus nerve?
|
GSE & SVE: Phyaryngeal & laryngeal mm
GSA & GVA: Ear canal, larynx SSA & SVA: Gustation (pharyngeal region) GVE: Thoracic & most of abdominal viscera. |
|
|
What is the reticular formation (composition)?
|
A complex netlike fabric of nerve cell bodies and interwoven processes.
|
|
|
Where is the reticular formation located?
|
In the central region of the brainstem, occupying most of the tegmentum of the midbrain, pons, and medulla.
|
|
|
What are the primary functions of the reticular formation?
|
Involved in activities ranging from visceral functions to consciousness making it the core integrating structure of the brain.
|
|
|
What are the four primary structures found in the brainstem? Some books only include three of these.
|
Medulla oblongata, Pons, Midbrain, Diencephalon.
|
|
|
#1 - Foramina of Cribriform plate
#2 - Optic canal #3 - Superior orbital fissure #4 - Foramen rotundum #5 - Foramen ovale #6 - Cartoid canal #7 - Internal acoustic meatus #8 - Jugular foramen #9 - Hypoglossal canal 10 - Foramen magum |
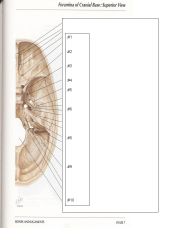
Name the foramen, fissures, and canals by each of the numbers.
|
|
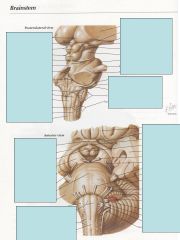
Fill in the names of all tagged structures
|
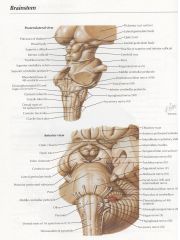
Check each tagged item versus the key.
|
|
|
Name the GSA cranial nerves.
|
V, VII, IX, X
|
|
|
Name the GVA cranial nerves.
|
V, VII, IX, X
|
|
|
Name the SVE cranial nerves
|
V, VII, IX, X, XI
|
|
|
Name the GVE cranial nerves.
In what tract are these found? |
VII, IX, X
Solitary tract |
|
|
Name the SVA cranial nerves.
|
I, VII, IX, X
|
|
|
Name the GSE cranial nerves.
|
III, IV, VI, XII
|
|
|
Name the SSA cranial nerves.
|
II, VIII
|

